How To Recover a Deleted Virtual Machine Using Its OS Disk.
 lolade ogundijo
lolade ogundijo
Recovering a deleted virtual machine using its OS disk can be a lifesaver in situations where important data or configurations were lost due to accidental deletion. The OS disk (operating system disk) contains the essential files and data necessary to run the virtual machine and can often be used to restore it to its previous state.
In this blog, I will guide you through the process of creating a virtual machine, intentionally deleting it, and then recovering it using its OS disk.
However, before we discuss how to recover a deleted virtual machine using its OS disk, let’s clarify the difference between the OS disk and the data disk.
The OS disk is a virtual hard disk that contains the operating system and other essential system files required for the virtual machine to function properly. On the other hand, a Data disk is a separate virtual hard disk that stores user data, applications, and additional files.
It is important to note that both the OS disk and the data disk cannot be reduced. Reducing disk size is not supported in Azure to prevent data loss.
To proceed with recovering a deleted virtual machine using its OS disk, you can follow these steps:
To create your virtual machine, see my blog guide-on-how-to-create-a-windows-11-pro-virtual-machine-on-microsoft-azure
After creating your VM, Click on it
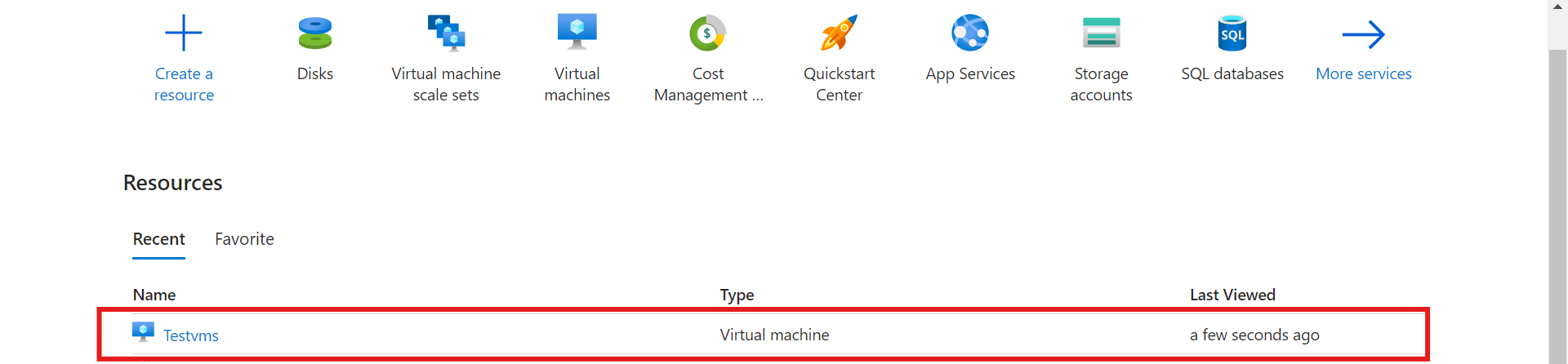
Click “delete” to delete your virtual machine
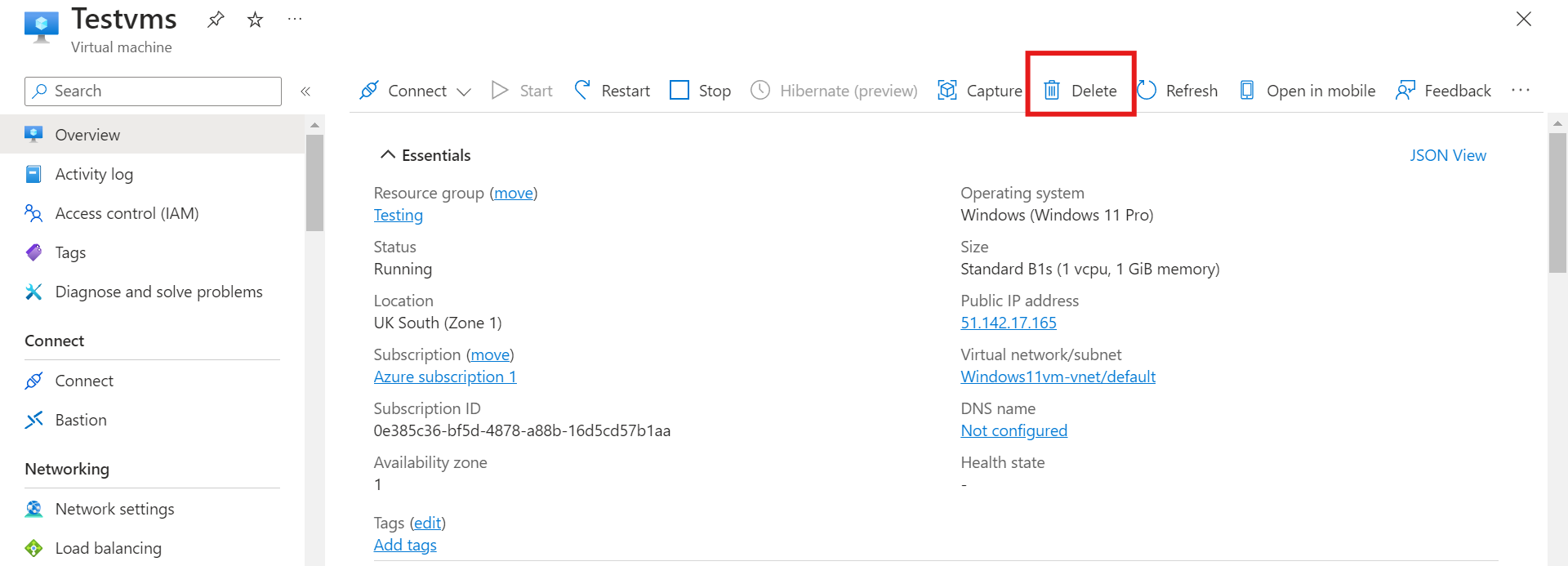
Before you delete the VM, uncheck the associated resources, then proceed to delete it.
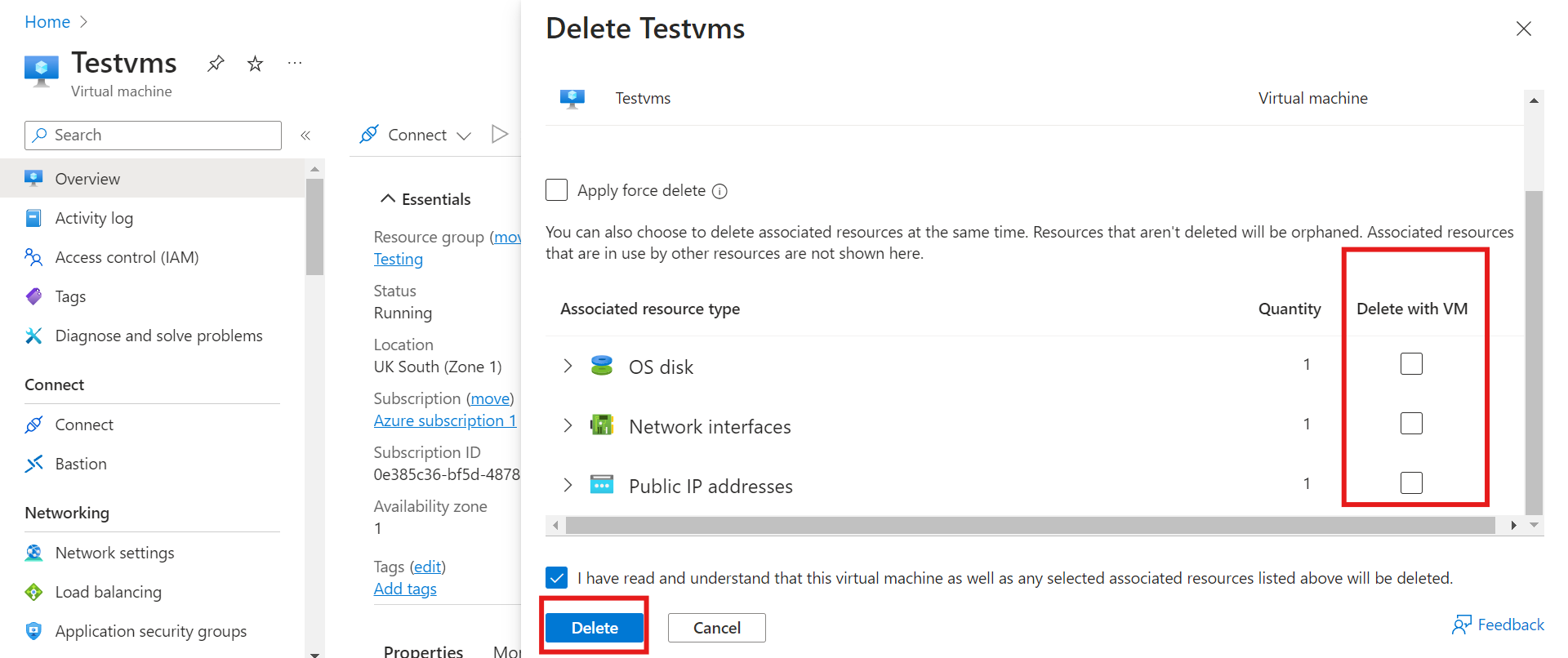
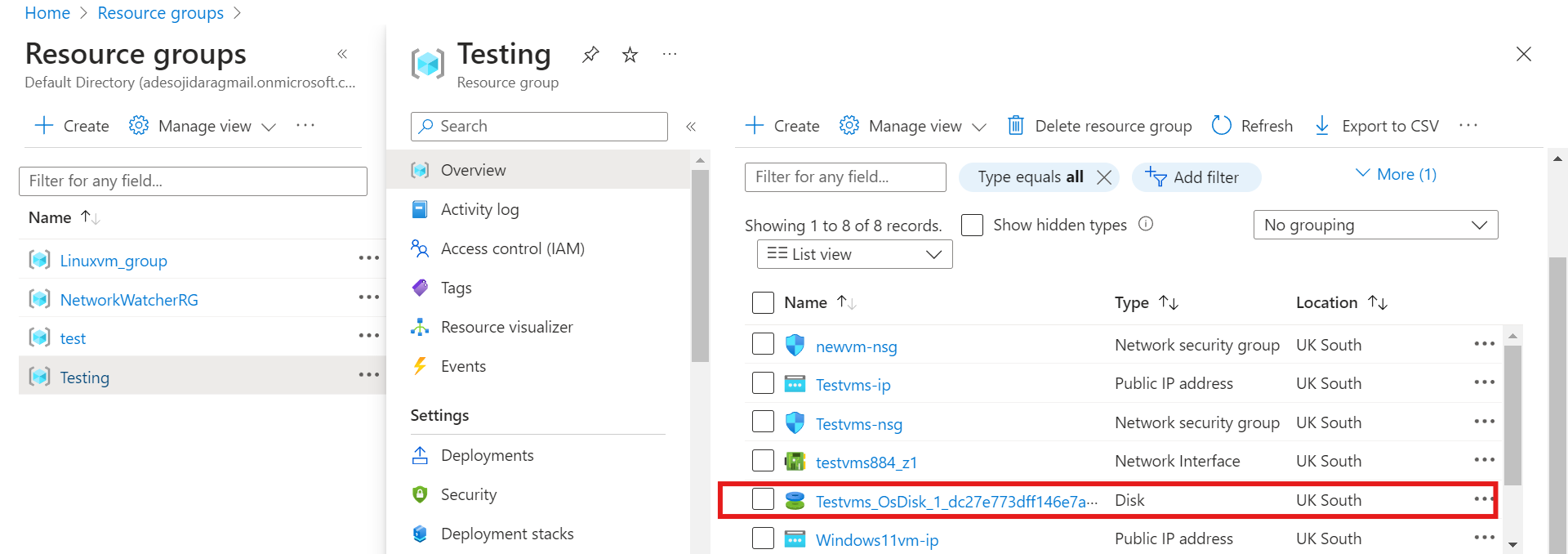
Once your VM has been deleted, search for the resource groups in the console.
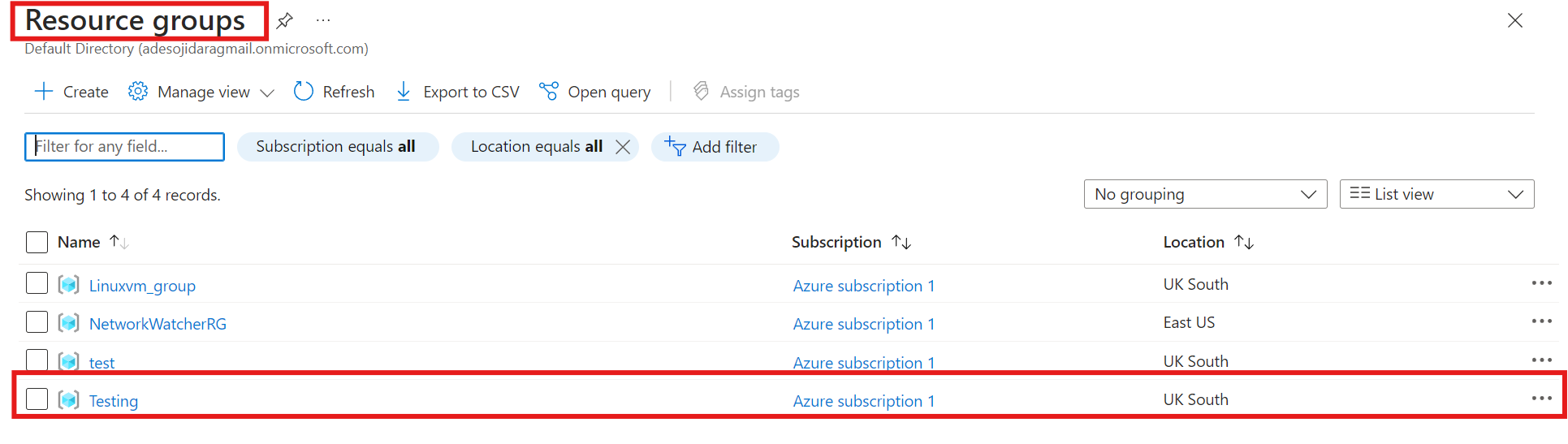
Click on the resource group you assigned to your deleted virtual machine and its resource. "Testing" was the resource group I assigned when creating my VM
Search for the OS disk of the deleted virtual machine and click on it.
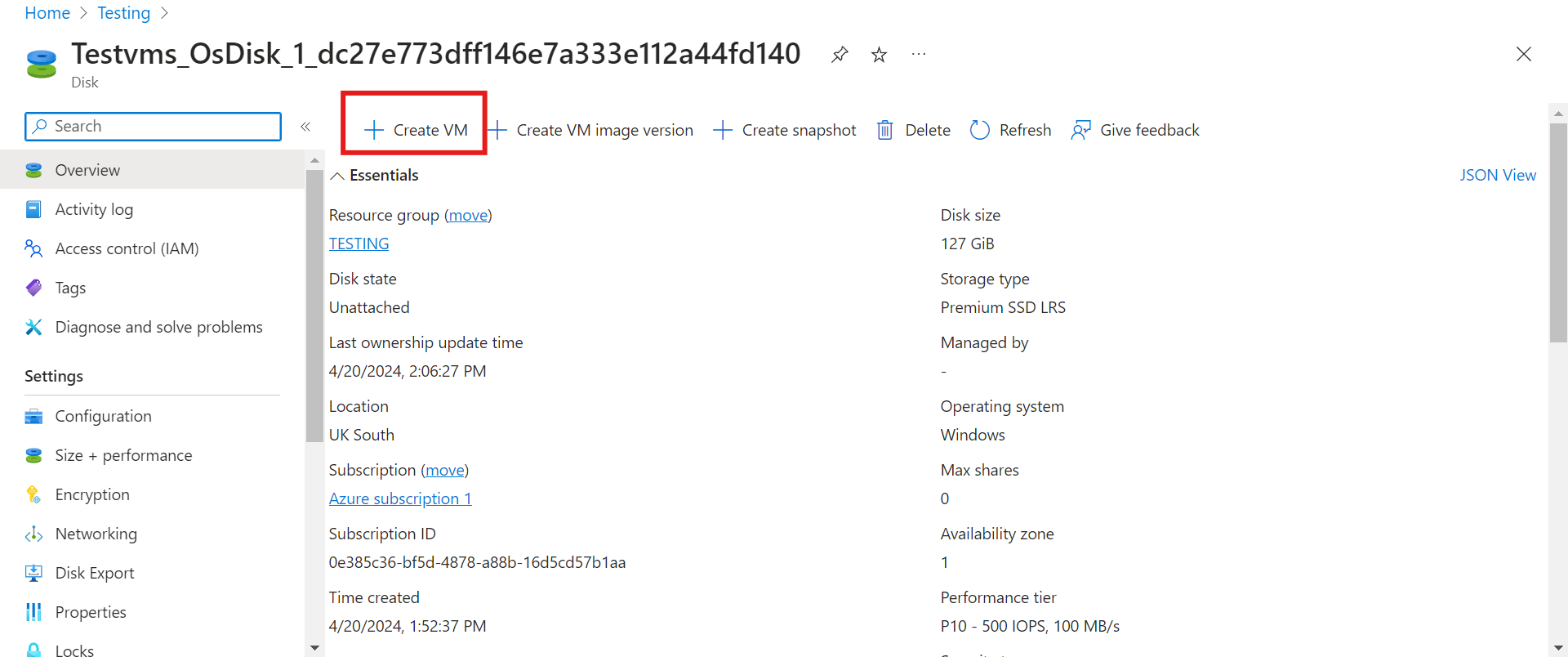
We can proceed to create our VM
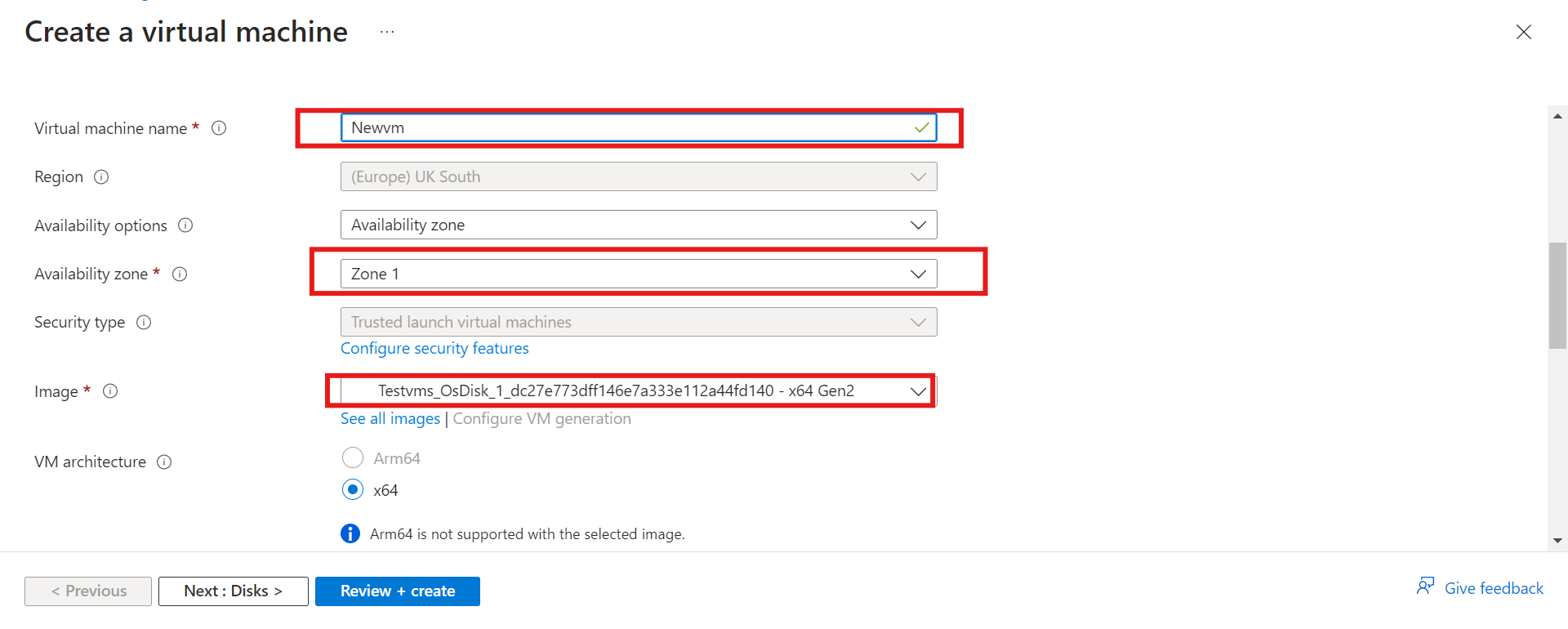
i) Select your subscription and resource group
ii) Give your VM a name and select your availability option in the drop-down menu; your image is the OS disk.
Note: You will notice some areas have been grayed out, such as regions, which means you can’t make any changes.
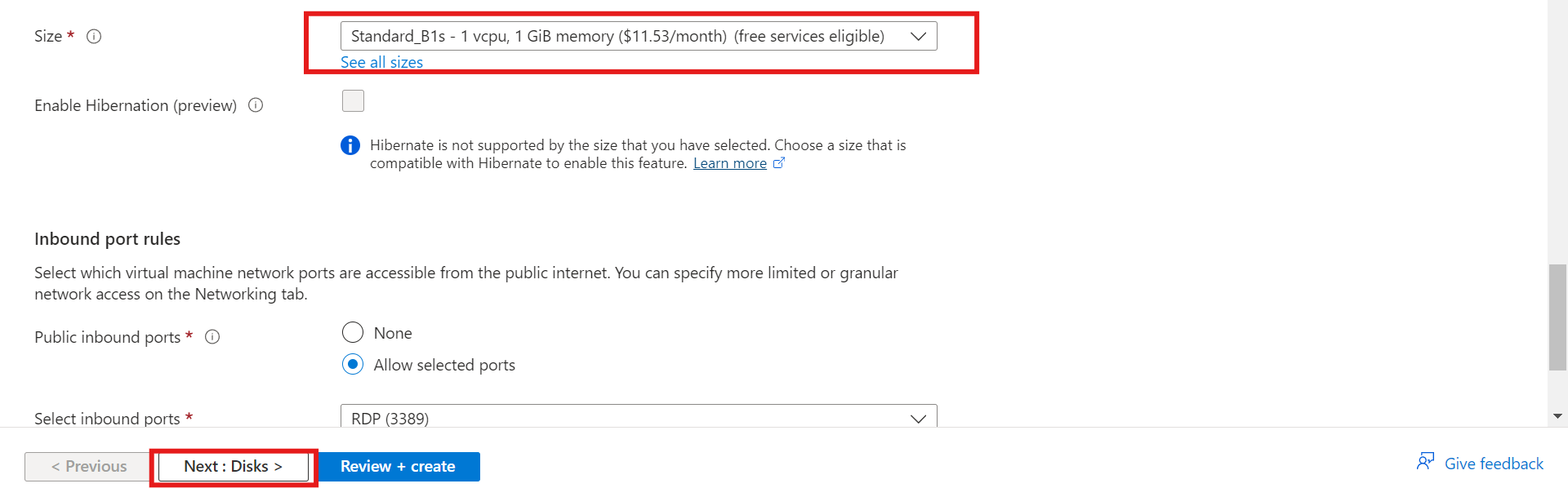
iii) Select the size of your virtual machine from the drop-down menu or see all sizes.
iv) Select any inbound port depending on the connection route you want to take. Click on “Next: Disk>” to direct you to the disk page.
i) On the disk page, scroll down to OS disk, and note that you can’t change the disk type. This is because it is an existing OS disk.
ii) Scroll down to the data disk. Create and attach a new data disk or attach an existing data disk. In this case, we will be creating a new data disk.
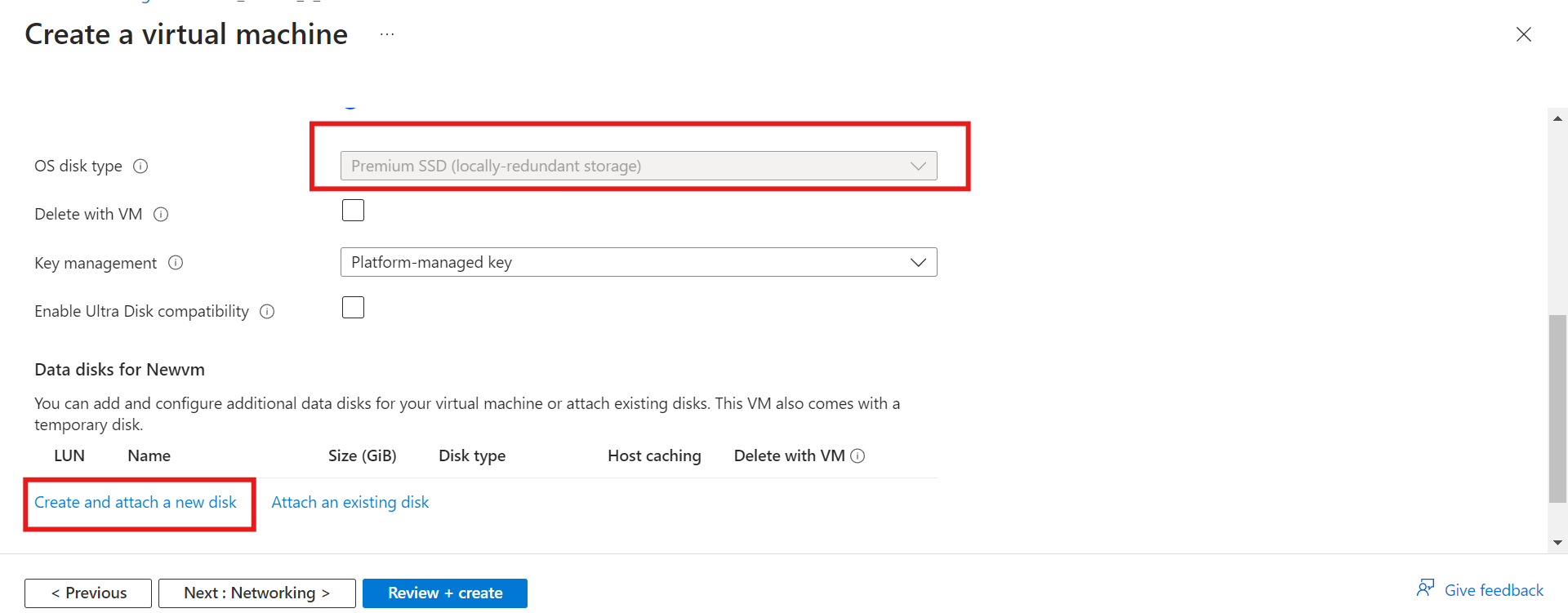
iii) Give your data disk a name and select the source type and the size of your disk. Then proceed to click "OK."
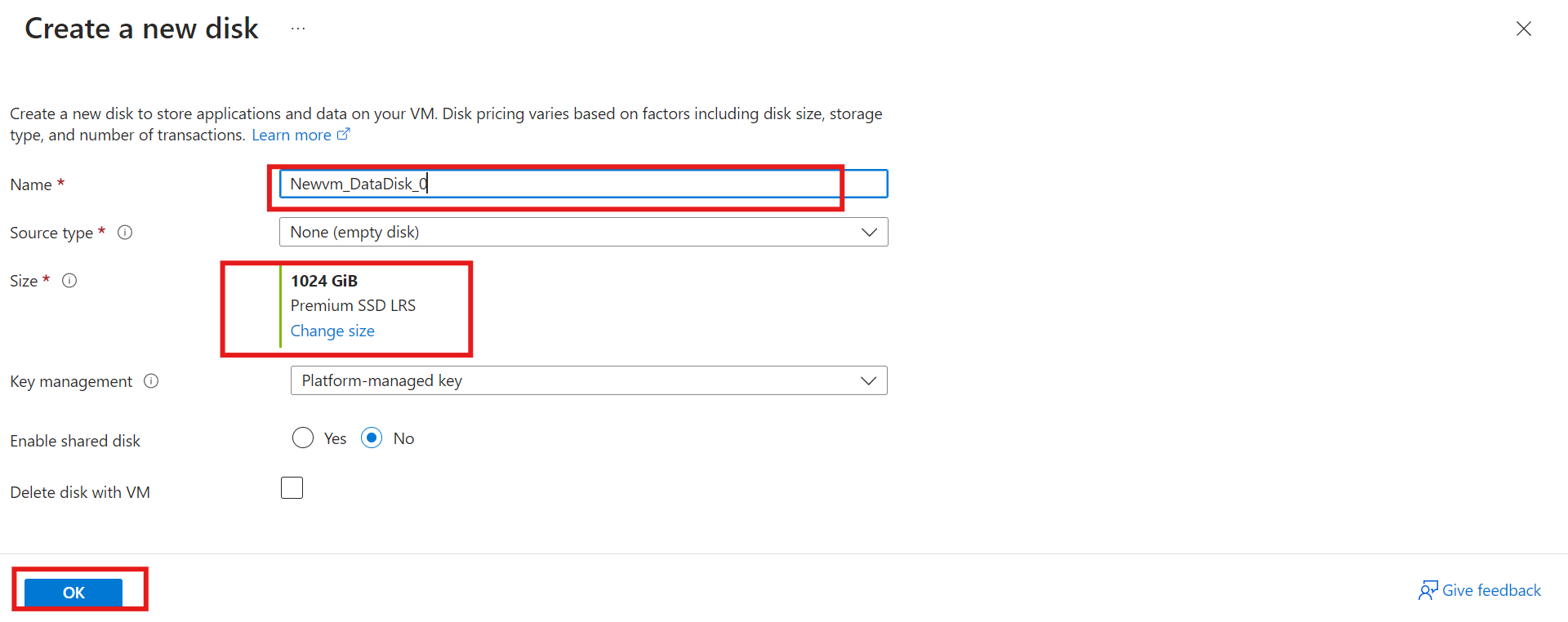
iv) We have our newly created data disk.
Leave the networking, management, monitoring, advanced, and tags pages as default.
Click on the “Review+create” button
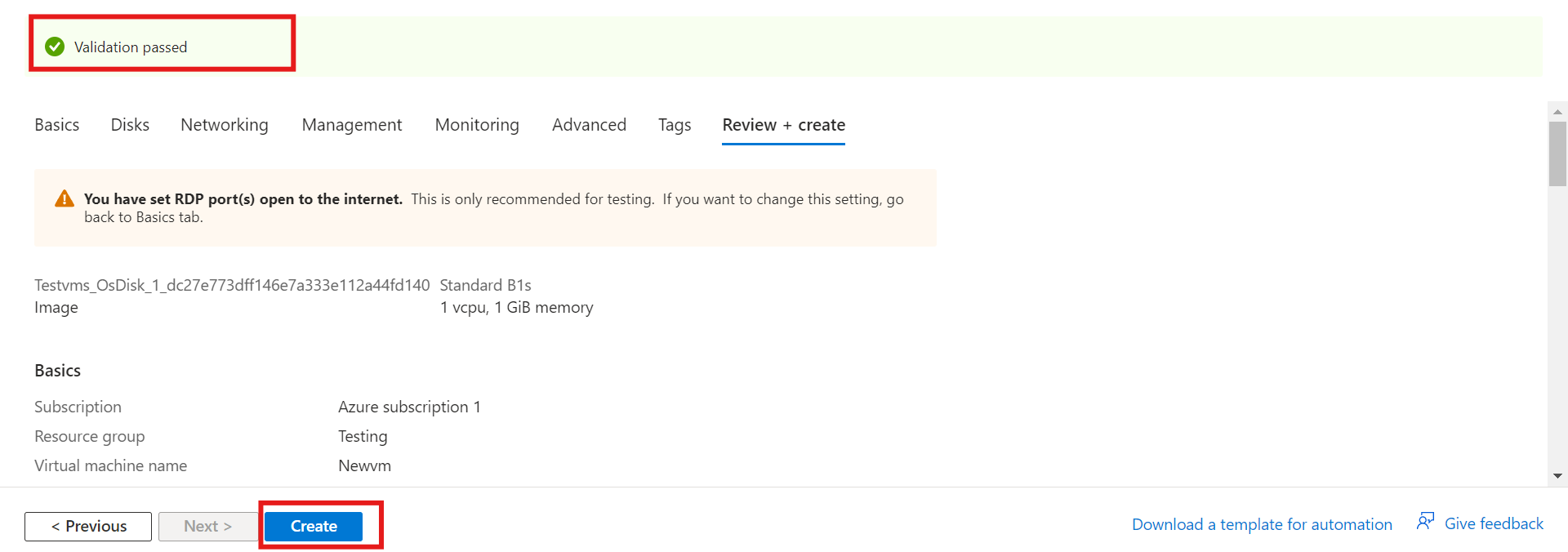
Once validation is passed, click on the “Create” button.
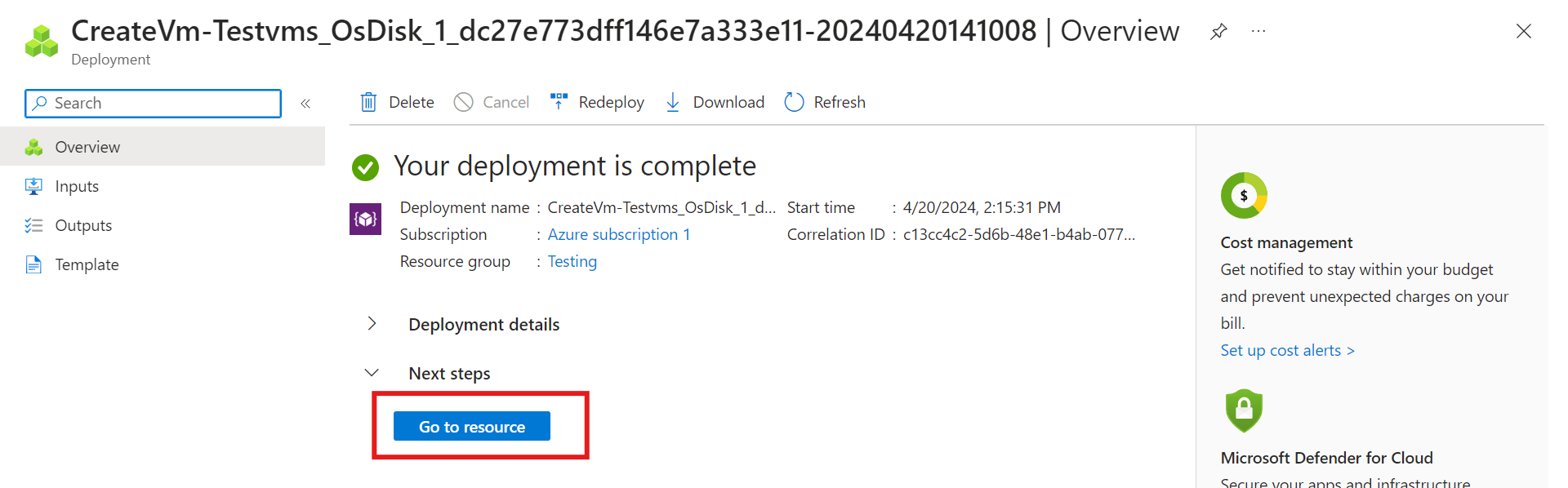
Once your deployment is ready, click on “Go to Resources.”
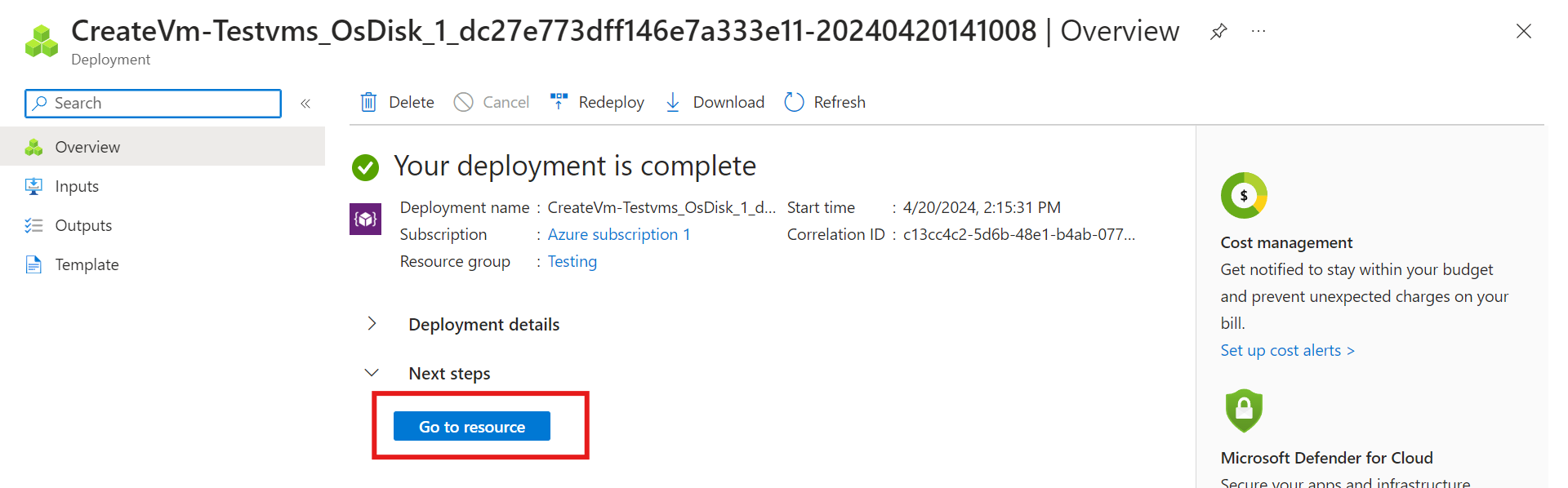
BOOOM! Your virtual machine is restored!
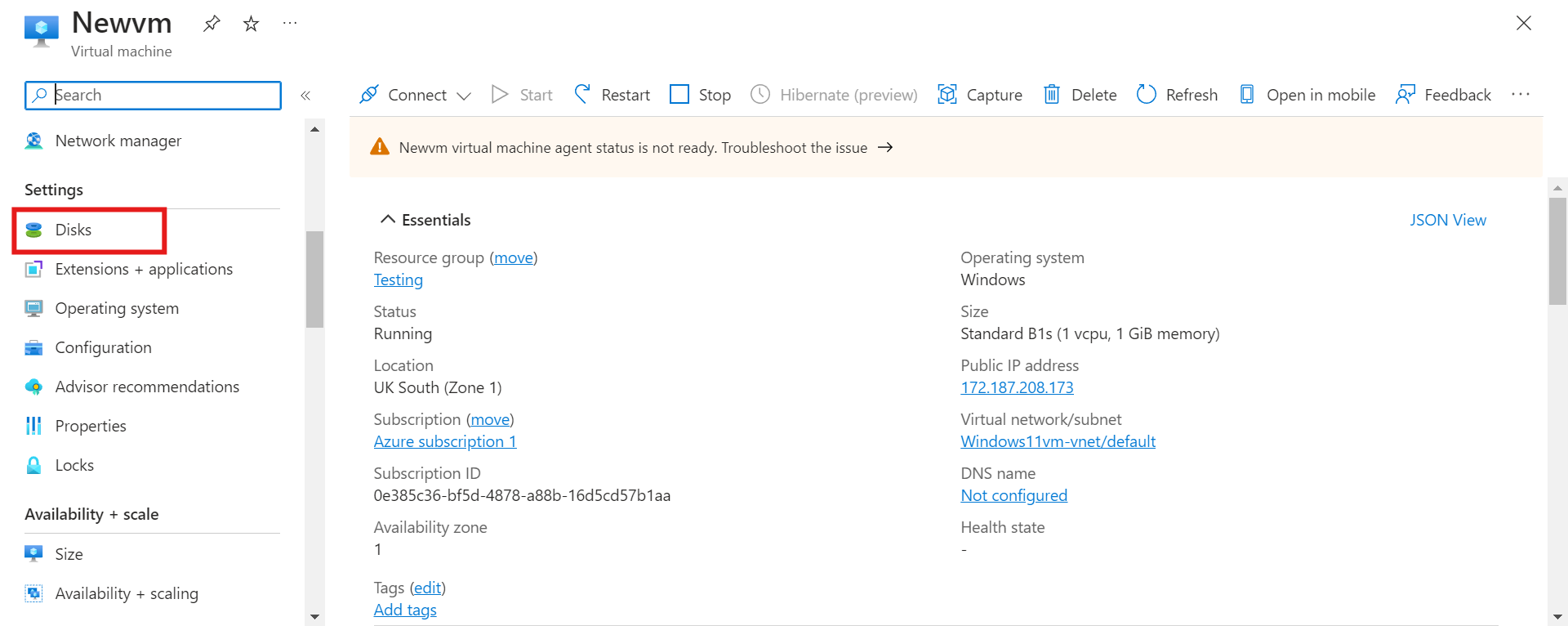
Now that we've restored our virtual machine, let's get in to view our disk types.
OS Disk and Data Disk
- To view your disk, click on “Disk” in the middle left corner to view disks
We can see our OS disk and data disk
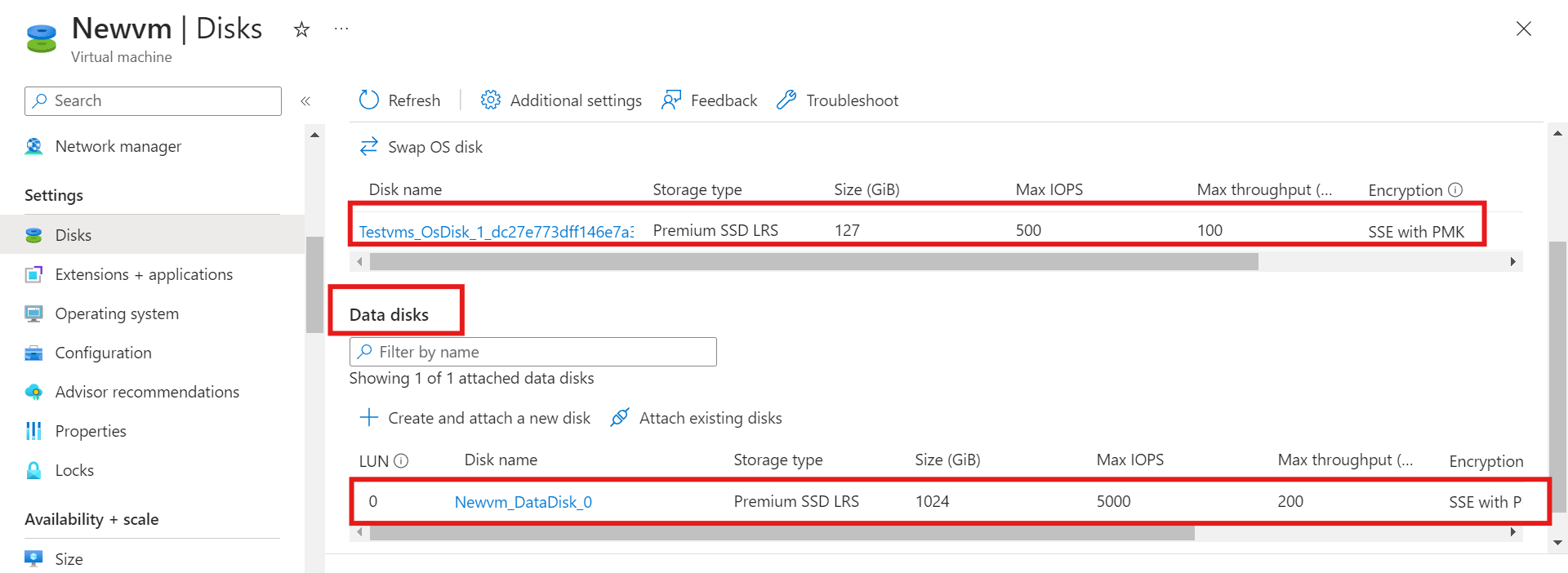
In this blog, we have discussed the importance of using an operating system disk to recover a deleted virtual machine. By utilizing the OS disk, valuable data and evidence that may have been lost due to accidental deletion or system failure can be recovered.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from lolade ogundijo directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
