Lua Script in Redis: Strength and Implement
 Nguyen Van Tuan
Nguyen Van Tuan
I. Redis Introduce
Redis is a database management system with key-value data in memory. It is open-source. Redis means "Remote Dictionary Server" and now it has developed to become a system with a lot of functions. It supports pretty much any type of data, and we can use it for a lot of targets.
This is a few advantages of Redis
High performance: Redis is designed to reach high performance because all of Redis's data is stored in memory, which can access and modify data with high speed. Redis can be stored on disk.
Support lots of datatype: Redis supports lots of data types. Example: string, list, set, hash, bitmap, etc., so we can store and work with complex datatypes so easily.
Memory sharing: Redis uses the memory sharing mode for all connections, so we will save the resource and increase the performance. Redis can handle thousands of requests per second.
Scalability and distributed: Redis supports shadring and replicate and scale and distribute system so easily. We can use master-slave replicate.
Other funtions: Redis can use pub/sub (publish/subscribe), transactions, Lua scripting and it supports lots of language programing.
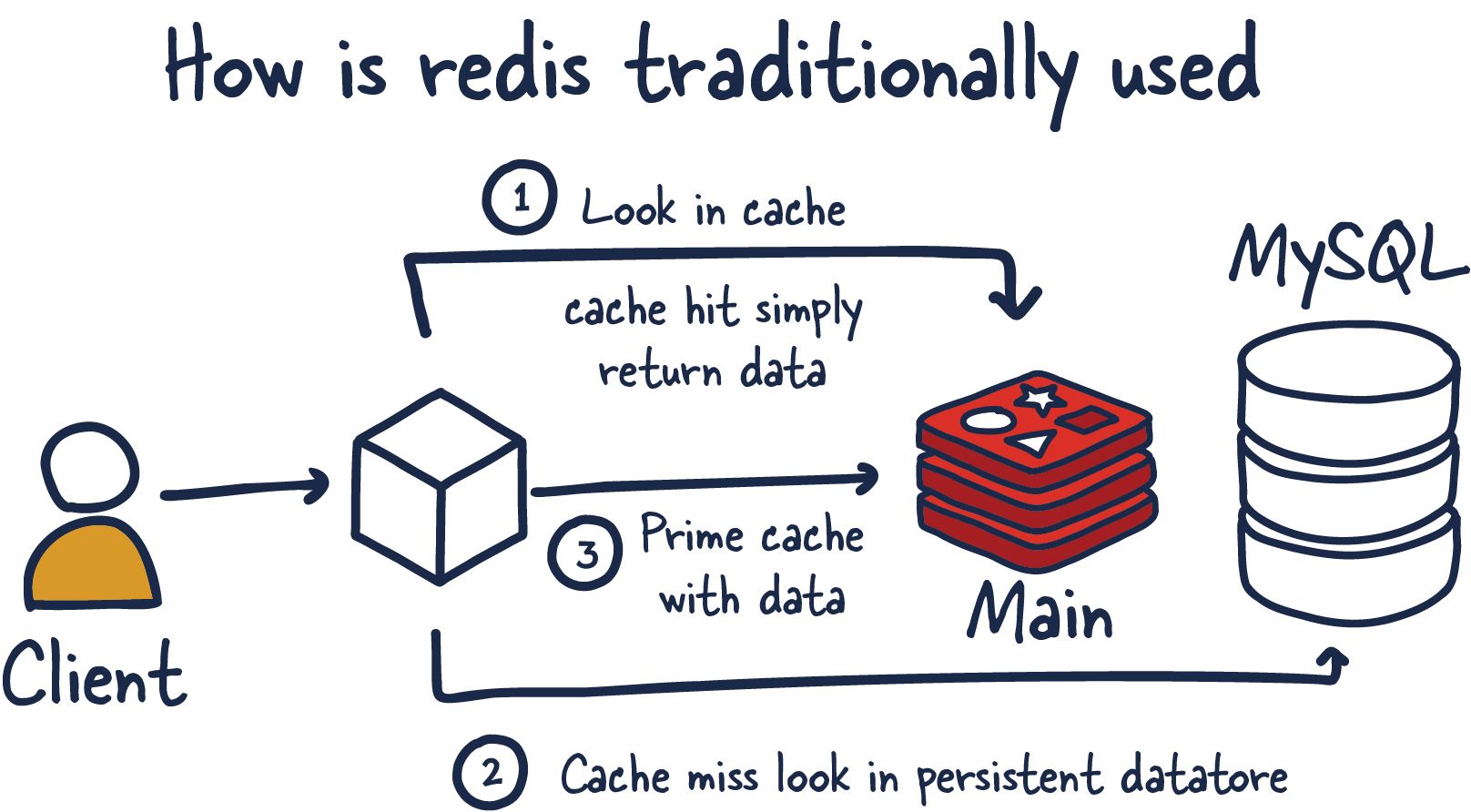
Reference: Introduction to Redis
II. Lua Script in Redis
Running lua script into Redis server is an important function of Redis. In the article, we will use the strength of lua script in Redis and implement lua script with Go.
1. Lua Script
Lua is a language programming embedded. It is a light-weight language and scalability. Redis uses Lua Scripting Engine to execute Lua's codes in Redis server.
2. Advantages of Lua Script in Redis
Performance: Lua Script is executed in the Redis server, so it decreases the network connection and increases the speed at which the command is executed. Redis supervises sharing memory for all Lua Script, so increase performance.
ACID: Redis supports ACID. Lua Script can execute many Redis commands and ensure data consistency.
3. Applications of Lua Script in Redis
Atomically Increment và Decrement: Lua Script allows you to atomically increase or decrease the value of a Redis key. This is useful in cases like counting views, counting likes, or handling any operation that requires increasing or decreasing numbers.
Filtering và Sorting: Using Lua Script, you can perform filtering and sorting operations on Redis data structures such as sorted sets or lists. This allows you to retrieve and query data according to your specific needs.
Atomicity và isolation: Lua Script provides atomicity and isolation in a distributed environment. You can use Lua Script to perform complex operations on multiple Redis keys in a single transaction, ensuring data consistency.
Xử lý dữ liệu phức tạp: Lua Scripting allows you to write custom code to process Redis data in complex logic. You can perform calculations, conditional expressions, loops, and call Redis functions in a single Lua code.
III. Implement Lua Script in Redis
1. Problem
We need to count one parameter, "counter" that was saved in the Redis server. Whenever the server receives the request, the counter will add one unit.
Before we implement by using Lua Script, we will init the Redis server.
Init Redis with Golang
func initRedis() (*redis.Client, error) {
var redisClient *redis.Client
opts, err := redis.ParseURL("redis://:@localhost:6384")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("failed to init redis:", err)
return nil, err
}
opts.PoolSize = 30
opts.DialTimeout = 10 * time.Second
opts.ReadTimeout = 5 * time.Second
opts.WriteTimeout = 5 * time.Second
opts.IdleTimeout = 5 * time.Second
redisClient = redis.NewClient(opts)
cmd := redisClient.Ping(context.Background())
if cmd.Err() != nil {
return nil, cmd.Err()
}
return redisClient, nil
}
2. Handle without Lua Script
Step 1: Get the value of "counter". If counter is not existed then counter = "0".
Step 2: Convert "counter" to number.
Step 3: counter++
Step 4: Save counter into the Redis server.
About the basics, we need four steps to add the "counter" one unit and request to Redis server two times ( set and get )
Implement with Golang
func DoNotUseLuaScript(redisClient *redis.Client) int {
// Step 1
currentCountStr, err := redisClient.Get(context.Background(), "counter").Result()
if err != nil && err != redis.Nil {
logrus.Warnf("Get value redis by key %v is failed with err: %v", "counter", err)
return 0
}
if err == redis.Nil {
currentCountStr = "0"
}
// Step 2
currentCount, err := strconv.Atoi(currentCountStr)
if err != nil {
logrus.Warnf("Convert string to int is failed with err: %v", err)
return 0
}
// Step 3: increase
newCount := currentCount + 1
// Step 4: Set value redis
isSet := redisClient.Set(context.Background(), "counter", newCount, 0).Val()
if isSet != "OK" {
logrus.Warnf("Set value redis by key %v is failed with err: %v", "counter", err)
return 0
}
return newCount
}
3. Handle with Lua Script
We will use Lua Script to resolve the problem. We will combine the 4 processing steps above into 1 script and request the Redis server. We will one time to request the Redis server.
Implement with Golang
func UseLuaScript(redisClient *redis.Client) int {
script := `
local currentCount = tonumber(redis.call('GET', KEYS[1]) or '0')
local newCount = currentCount + tonumber(ARGV[1])
redis.call('SET', KEYS[1], newCount)
return newCount
`
// Running Lua Script
resultStr, err := redisClient.Eval(context.Background(), script, []string{"counter-lua"}, 1).Result()
if err != nil {
logrus.Warnf("Running Lua Script is failed with err: %v", err)
return 0
}
result, err := strconv.Atoi(fmt.Sprintf("%v", resultStr))
if err != nil {
logrus.Warnf("Convert string to int is failed with err: %v", err)
return 0
}
return result
}
4. Main function
func main() {
// init redis
redisClient, err := initRedis()
if err != nil {
logrus.Warnf("init redis client is failed with err: %v", err)
return
}
// use lua script
resultLua := 0
startLua := time.Now()
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
resultLua = UseLuaScript(redisClient)
}
endLua := time.Now()
logrus.Infof("Result lua script type: %v and time %v ms", resultLua, endLua.Sub(startLua).Milliseconds())
// do not use lua script
result := 0
start := time.Now()
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
result = DoNotUseLuaScript(redisClient)
}
end := time.Now()
logrus.Infof("Result do not use lua script type: %v and time %v ms", result, end.Sub(start).Milliseconds())
}
5. Result
To clearly see the effectiveness and advantages of using lua script in Redis, we will run the main function to measure the processing time of two methods.
10 request
INFO[0000] Result lua script type: 10 and time 17 ms
INFO[0000] Result do not use lua script type: 10 and time 26 ms
100 request
INFO[0000] Result lua script type: 100 and time 99 ms
INFO[0000] Result do not use lua script type: 100 and time 121 ms
Looking at the results, we can also see that applying the lua script to Redis will help process things very quickly. Here, I just took a very simple example. If the processing logic is complex, applying the lua script to Redis will have many advantages: fast, less resources to call Redis, clean code,...
IV. Source code
Source code: Example with Golang
Reference: Scripting with Lua
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nguyen Van Tuan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Nguyen Van Tuan
Nguyen Van Tuan
I'm Tuan. I graduated Hanoi University of Science and Technology in 2019 Major: Information Technology Leetcode : nguyenvantuan2391996 My blog: https://tuannguyenhust.hashnode.dev/ Linkedin : Tuan Nguyen Van