Overview of CLI commands.
 Khajappa Biradar
Khajappa BiradarThis blog is going to explain some of the commands used in UNIX-based operating systems.These commands are going to help execute software programs when we run in CLI.
List of commands:
man
cd
mkdir
mv
cp
ls
pwd
rm
chmod
touch
grep
find
1 . man
Basically man command is an interface to the system reference manuals.In order to run the man command we have to write following command in the terminal.
$mancommand_name
One of the example I executed in my terminal is given below

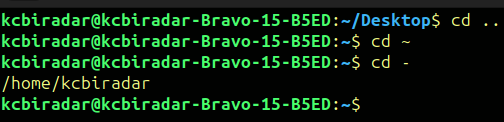
2 . cd
The cd command is going to help in changing the directory or for displaying the current directory.
To execute the cd command we have run following line in terminal.
$cddirectory_name
There are different options/flags used in cd command some of them are below
. .(dot dot) -> This will move up one directory from existing location
~ (tilde) -> This is represents the user's home directory.
- (hyphen) -> This is shortcut for the previous working directory.
3 . mkdir
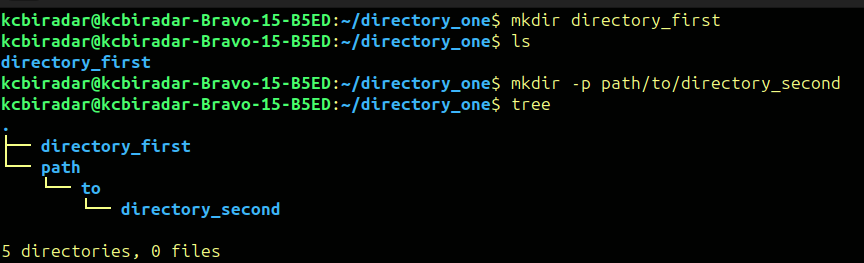
The command mkdir is going to help creating new directories within a file system.
To execute the mkdir command we have to run following line in terminal.
$mkdirnew_directory_name
We can create multiple directories at a time by doing
$mkdirdirectory_one directory_two directory_three
By giving the -p option we can create nested directories
$mkdir -p path/to/directory_one
4 . mv
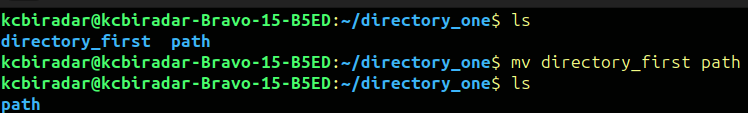
The command mv is used to move files or directories from one location to another within a file system. It can also be used to rename files or directories by effectively moving them to the same location but with a different name.
To execute the mv command we have to run following line in terminal.
$mvsource_file_name destination_file_name
5 . cp
The cp command is used to copy files or directories from one location to another within a file system. It creates a new copy of the file or directory at the specified destination while leaving the original file or directory intact.
To execute the cp command we have to run following line in terminal
$cp [source] [destination]

6 . ls
The ls command is used to list the contents of a directory. When we run ls without any options, it displays the names of files and directories in the current directory.
To execute the ls command we have to run following line in terminal
$ls [options] [directory]
options :
'-l' - Long format, displaying detailed information about each file or directory including permissions, owner, size and modification time.
'-a' - Includes hidden files and directories.
'-r' - Reverse order , listing files and directories.
7 . pwd
The pwd command stands for printing working directory, when we run pwd in a terminal it displays the full path to the current working directory
$pwd

8 . rm
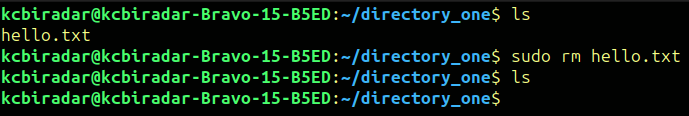
The rm command is used to remove files or directories from the file system. It is permanently deletes files and directories, and they cannot be easily recovered.
The basic syntax for rm is :
$rm [options] [file/directory]
9 . chmod
The chmod command is used to change the permissions of files and directories.It allows you to modify the read, write and execute permissions for the owner of the file, members of the group associated with file and others.
The basic syntax for chmod is:
$chmod [permissions][file/directory]
The permission part specifies the new permissions for the file or directory.
Each permission is represented by a numeric value:
Read : 4
Write : 2
Execute : 1
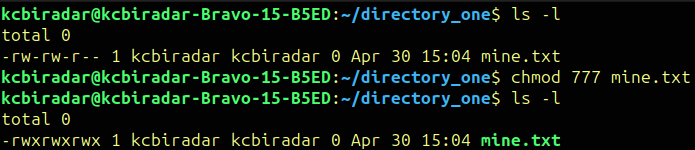
$chmod 777 mine.txt
It sets the all permissions for owner , group members and others.
10 . touch
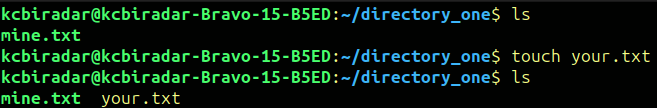
The touch command is used to create new empty files or update the timestamp of existing files.
The basic syntax for touch is :
$touch [options][file]
Here are some common options for touch
'-a' - Update only the access time of the file
'-m' - Update only the modification time of the file.
11 . grep
The grep command is used for searching text pattern in files or standard input. Its name stands for "global regular expression print".
The basic syntax for grep is:
$grep [options] pattern [file]
[options]: Optional flags that modify the behavior ofgrep'pattern': The text pattern you want to search for. This can be a simple string or a more complex regular expression.['file']: Optional file search in. If not specified,grepreads from standard input.
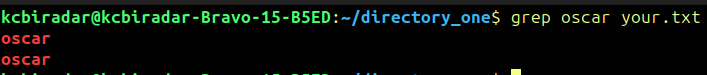
$grep oscar hello.txt
12 . find
The find command is used to search for files and directories within a specified directory hierarchy. It's a versatile tool that allows you to search based on various criteria such as file name, file type, size, and permissions.
The basic syntax for the find command is:
$find [directory] [options] [expression]
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Khajappa Biradar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Khajappa Biradar
Khajappa Biradar
Quick Learning, Developer from INDIA