Installing Langflow and Flowise.
 Brian King
Brian King
TL;DR.
Installing Langflow and Flowise involves setting up an environment using Miniconda, installing Node.js via NVM, and creating the necessary directories and scripts. Langflow, a user-friendly interface for LangChain, allows easy AI application creation with minimal coding. Flowise, an open-source platform for building AI workflows, supports extensive integrations and operates in secure environments. Both tools are designed to streamline AI application development but cater to different needs: Langflow is used for rapid prototyping and Flowise is used for customizable workflows. The choice between these tools depends on specific requirements like ease of use, customization, and deployment scope.
Attributions:
An Introduction.
Langflow and Flowise are are two AI tools that that serve different purposes. This means that using both tools expands my ability to create amazing AI experiences.
The purpose of this post is to describe the installation of Langflow and Flowise.
The Big Picture.
- Below is an image of the newly-installed Langflow UI:
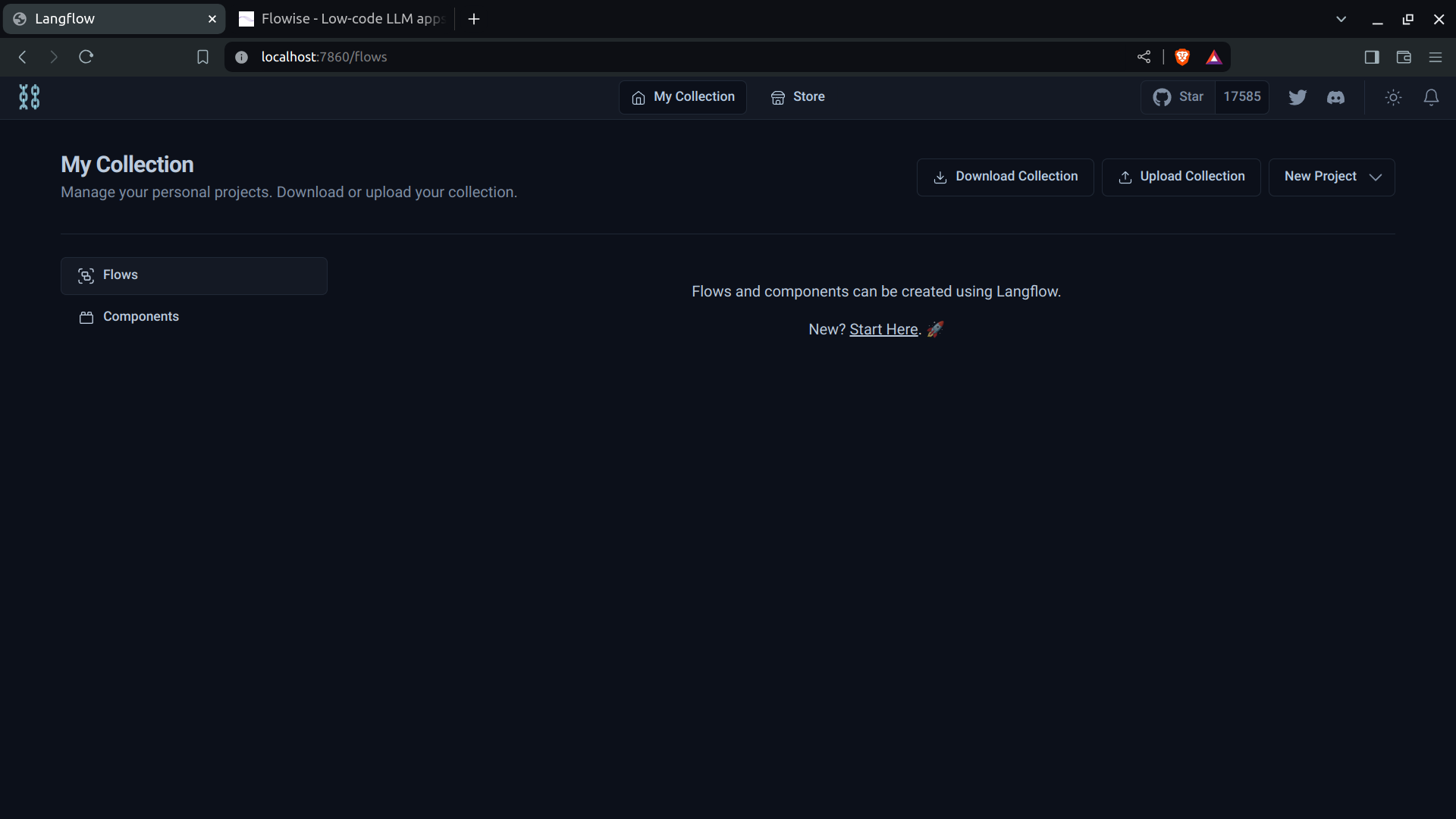
- Below is an image of the newly-installed Flowise UI:
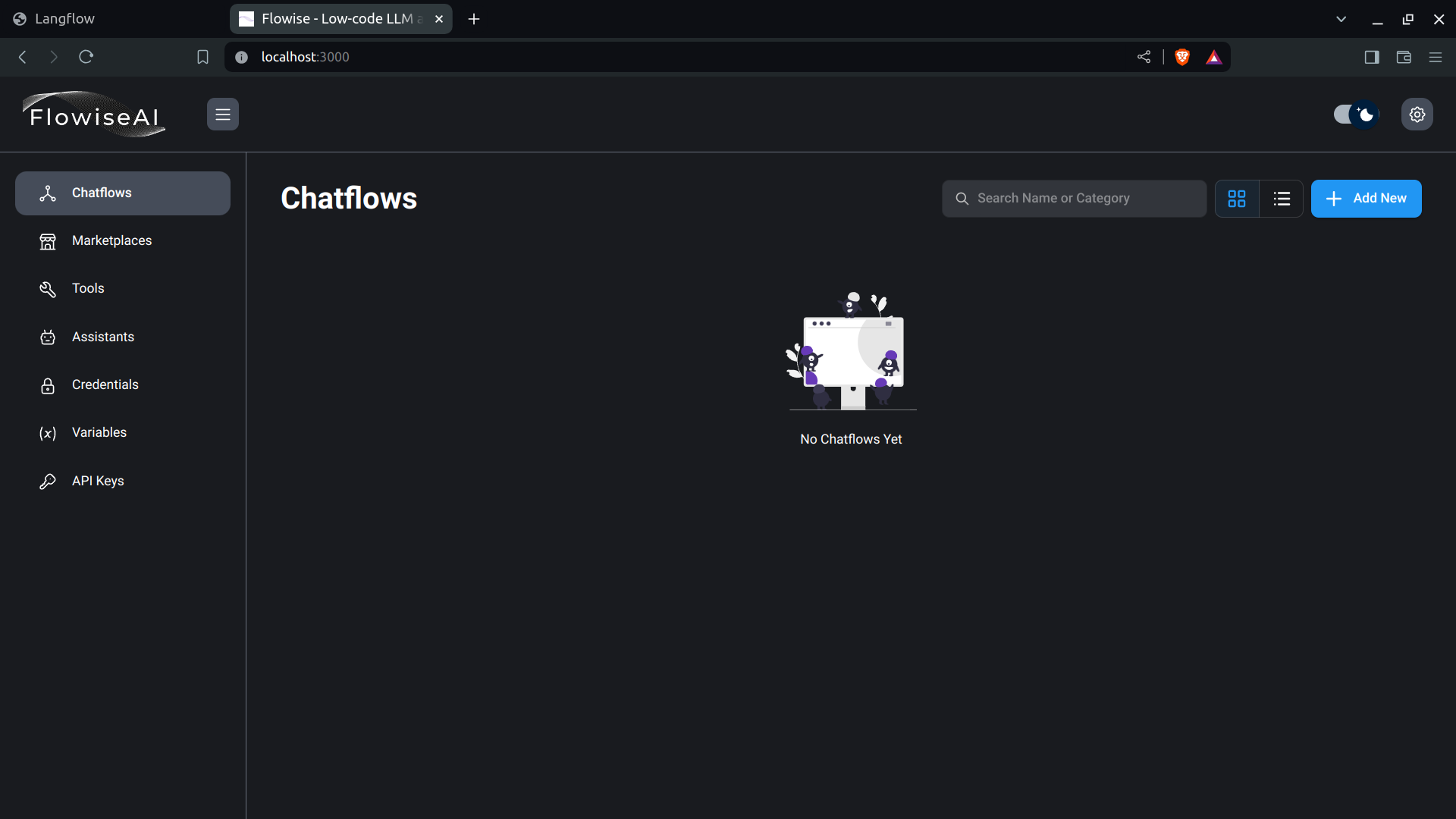
Combined, these tools provide a wide range of options when developing AI solutions.
Prerequisites.
Updating my Base System.
- From the (base) terminal, I update my (base) system:
sudo apt clean && \
sudo apt update && \
sudo apt dist-upgrade -y && \
sudo apt --fix-broken install && \
sudo apt autoclean && \
sudo apt autoremove -y
NOTE: The Ollama LLM manager is already installed on my (base) system.
What is Node.js, NPM, and NVM?
Node.js is a free, JavaScript (JS) server runtime. It runs JS code as single-threaded, non-blocking, asynchronous programs, which makes it very memory efficient. Node.js performs many system-level tasks, but is commonly used to run JS servers.
NPM (Node Package Manager) is the world's largest software registry. Open source developers use it to share packages with each other. Many organizations use NPM to manage private development as well. Most developers interact with NPM using the CLI (Command Line Interface), and usually ships with Node.js.
NVM (Node Version Manager) is used to switch between versions of Node.js. NVM works on any POSIX-compliant shell (sh, dash, ksh, zsh, bash) and runs on Linux distros, macOS, and Windows WSL.
https://nodejs.org/en/learn/getting-started/introduction-to-nodejs↗,
https://docs.npmjs.com/about-npm↗,
https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#intro↗, and
https://solodev.app/installing-node-and-npm-with-nvm.
Node.js must be installed (node -v) before continuing with this post.
Installing Node and NPM with NVM.
I open a terminal.
I install CURL:
sudo apt install -y curl
- I install the NVM (Node Version Manager):
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.7/install.sh | bash
NOTE: The version numbers are listed on the NVM GitHub page.
- I activate the NVM:
source ~/.bashrc
- I use the NVM to install the LTS version of Node.js:
nvm install --lts
NOTE: The Node and NPM versions are listed on the screen.
- I make Node LTS the default NVM version, as listed in the previous command:
nvm alias default 20.12.2
- I confirm the Node installation:
node -v
- I confirm the NPM installation:
npm -v
What is Anaconda and Miniconda?
Python projects can run in virtual environments. These isolated spaces are used to manage project dependencies. Different versions of the same package can run in different environments while avoiding version conflicts.
venv is a built-in Python 3.3+ module that runs virtual environments. Anaconda is a Python and R distribution for scientific computing that includes the conda package manager. Miniconda is a small, free, bootstrap version of Anaconda that also includes the conda package manager, Python, and other packages that are required or useful (like pip and zlib).
https://docs.anaconda.com/free/miniconda/index.html↗, and
https://solodev.app/installing-miniconda.
I ensure Miniconda is installed (conda -V) before continuing with this post.
Creating a Miniconda Environment.
- I use the
condacommand to display alistof Minicondaenvironments:
conda env list
- I use
condatocreate, andactivate, a new environment named (-n) (Flow):
conda create -n Flow python=3.11 -y && conda activate Flow
NOTE: This command creates the (Flow) environment, then activates the (Flow) environment.
Creating the Flow Home Directory.
NOTE: I will now define the home directory in the environment directory.
- I create the Flow home directory:
mkdir ~/Flow
- I make new directories within the (Flow) environment:
mkdir -p ~/miniconda3/envs/Flow/etc/conda/activate.d
- I use the Nano text editor to create the
set_working_directory.shshell script:
sudo nano ~/miniconda3/envs/Flow/etc/conda/activate.d/set_working_directory.sh
- I copy the following, paste (CTRL + SHIFT + V) it to the
set_working_directory.shscript, save (CTRL + S) the changes, and exit (CTRL + X) Nano:
cd ~/Flow
- I activate the (base) environment:
conda activate
- I activate the (Flow) environment:
conda activate Flow
NOTE: I should now, by default, be in the
~/Flowhome directory.
What is Langflow?
Langflow is a user-friendly interface for LangChain, built using react-flow. It lets me easily create, and test, different setups by dragging and dropping components and using a chat box. Each part of the graph in Langflow works on its own. It's designed to help me quickly try out new ideas and build AI applications without needing to write much code. Langflow comes with ready-to-use components that I can mix and match to build AI apps. It fits perfectly with the tools I already use and makes it simple to develop basic, or advanced, AI applications. Langflow is all about making AI integration straightforward and expanding what I can do with AI in both tests and real-life uses.
Installing Langflow.
- I use pip to install Langflow:
pip install langflow[local] -U --force-reinstall
- I run Langflow:
langflow run
- Langflow is accessed using a browser:
What is Flowise?
Flowise is an open-source, low-code platform that helps me easily create customized AI workflows and agents. It simplifies the development of AI applications, which usually require many iterations, by allowing for quick changes from testing to production. Chatflows link AI models with various tools like memory, data loaders, and cache, along with over a hundred other integrations including LangChain and LlamaIndex. This setup enables the creation of autonomous agents and assistants that can perform diverse tasks using custom tools. I can build functional agents and OpenAI assistants, or opt for local AI models to save costs. Flowise supports extensions and integrations through APIs, SDKs, and embedded chat features. It is platform-agnostic, meaning Flowise can work with local, open-source AI models in secure, offline environments using local data storage. It is compatible with various platforms and technologies like Ollama, HuggingFace, AWS, Azure, and GCP, offering flexibility in deployment.
Installing Flowise.
I open a new Terminal tab.
I activate the Flow environment:
conda activate Flow
- I use NPM to install Flowise globally:
npm install -g flowise
- I use NPX to start Flowise:
npx flowise start
- Flowise is accessed using a browser:
Differences are Good.
NOTE: The differences between Langflow and Flowise results in broader, more diverse solutions.
1 of 3: Agent Differences.
| Langflow Agents | Flowise Agents |
| Auto GPT: A complete conversational agent built on the React framework, providing a wide range of language processing capabilities. | CSV Agent: Enables data retrieval and manipulation from CSV files. |
| Baby AGI: A pre-trained conversational agent designed for efficient language understanding and response generation. | JSON Agent: Facilitates JSON data extraction, transformation, and manipulation. |
| Conversational Agent: Allows users to define conversational flows and logic to create interactive conversations. | SQL Agent: Interacts with databases using SQL queries to retrieve and update data. |
| LLM (Language Model Memory) Agent: Incorporates memory and context to enable more context-aware language processing. | Vector Store Router: Provides a routing mechanism for directing requests to different vector stores based on predefined rules. |
2 of 3: Chain Differences.
| Langflow Chains | Flowise Chains |
| Conversation Chain: Facilitates multi-turn conversations and supports complex dialogue flows. | Conversation Chain: Enables seamless conversations with users, supporting back-and-forth interactions. |
| Retrieval QA Chain: Allows retrieval-based question-answering capabilities using predefined responses. | Retrieval QA Chain: Retrieves answers to user queries from predefined knowledge bases. |
| LLM Chain: Utilizes Language Model Memory to enhance language understanding and generate context-aware responses. | SQL Database Chain: Integrates SQL databases for data retrieval and manipulation. |
| Maths Chain: Provides mathematical computation capabilities within language processing pipelines. | Vector DB Chain: Accesses and manipulates data stored in vector databases. |
3 of 3: Tooling Differences.
| Langflow Tools | Flowise Tools |
| Text Splitters: Splits text into meaningful units for further processing or analysis. | Wrappers: Offers a text request wrapper, allowing seamless integration with external request libraries. |
| Embeddings: Generates vector representations of text for various natural language processing tasks. | Vector Stores: Manages and organizes vector representations of data for efficient retrieval and comparison. |
| LMS (Language Model Store): Stores and manages pre-trained language models for efficient access and utilization. | Metadata Filter: Filters data based on specific metadata criteria, enabling efficient data processing and retrieval. |
| Prompts: Provides pre-defined prompts to initiate and guide user interactions. |
Further Details.
Please visit the excellent post from Apoorva Gosain to discover more details about Langflow and Flowise:
Attributions:
The Results.
The exploration of Langflow and Flowise offers a revealing look into the capabilities and distinctions of modern AI tools designed for language processing and workflow automation. While Langflow focuses on ease of use and modular integration for rapid prototyping of AI applications, Flowise caters more to creating customizable AI workflows with a robust set of features for scalability and integration across different platforms. Both tools demonstrate their unique strengths, making them valuable depending on my specific needs and technical environments. Ultimately, the choice between Langflow and Flowise should be guided by the my specific requirements in terms of ease of use, customization, and the scope of deployment. This comparison not only highlights the individual features of each tool but also underscores the broad spectrum of possibilities that AI-driven platforms offer to innovators and developers in the tech industry.
In Conclusion.
As an AI enthusiast and developer, I am always looking to streamline my AI application development with powerful tools. Let's dive into the capabilities of Langflow and Flowise, two cutting-edge platforms that are transforming the landscape of AI-driven applications.
Langflow is a user-friendly interface built on react-flow, perfect for creating and testing AI setups with minimal coding. It is designed to integrate seamlessly into my existing toolkit, enhancing my ability to develop simple, or complex, AI applications.
Flowise, on the other hand, is an open-source, low-code platform that simplifies the creation of customized AI workflows. It supports numerous integrations and can operate in secure, offline environments, making it incredibly flexible for different deployment scenarios.
Both platforms offer unique features:
Langflow focuses on ease of use and rapid prototyping.
Flowise excels in creating customizable workflows with extensive features for scalability.
As a startup looking to innovate, or a large enterprise aiming to enhance my AI capabilities, these tools provide substantial value.
For a deeper comparison and more insights, check out the full article here: [Link to the full article]
What has been your experience with AI tools in your projects? Have you tried Langflow or Flowise yet? Let's discuss in the comments below!
Until next time: Be safe, be kind, be awesome.
#Langflow #Flowise #AI #ArtificialIntelligence
#AIIntegration #AIApplications #LowCodePlatforms
#WorkflowAutomation #Innovation #SoftwareDevelopment
#TechCommunity #TechTools
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Brian King directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Brian King
Brian King
Thank you for reading this post. My name is Brian and I'm a developer from New Zealand. I've been interested in computers since the early 1990s. My first language was QBASIC. (Things have changed since the days of MS-DOS.) I am the managing director of a one-man startup called Digital Core (NZ) Limited. I have accepted the "12 Startups in 12 Months" challenge so that DigitalCore will have income-generating products by April 2024. This blog will follow the "12 Startups" project during its design, development, and deployment, cover the Agile principles and the DevOps philosophy that is used by the "12 Startups" project, and delve into the world of AI, machine learning, deep learning, prompt engineering, and large language models. I hope you enjoyed this post and, if you did, I encourage you to explore some others I've written. And remember: The best technologies bring people together.