Microsoft Entra ID / Azure Active Directory Roles
 Ibikunle ayobami
Ibikunle ayobami
Introduction
Sometimes, we may have confusion between two terms - Azure AD roles and Azure roles i.e. role-based access control in Azure. In this article, I will explain some of the core differentiation between those two terms.
Step 1; Explain the difference between Azure AD Roles and Azure Roles Step 2: Create the Admin Department and add two users to it Step
3: Assign the Global Administrator Role to User A Step
4: Show all the steps it took the Global Admin to Log in into the Azure Portal with his new credentials Step
5:Let the Global Administrator create/onboard a new member to the Admin Department
What are Azure AD Roles?
Azure AD is nothing but an identity store in Azure. Here we can define users, groups, applications, and service principles. These users can authenticate onto Azure and they can access resources that are part of Azure subscription.
We can assign Azure AD roles to a user and these permissions are normally given to manage the various aspects of Azure AD.
Let’s say we want to give a user the ability to register applications in Azure, then we can assign them as application administrator role or let's say we want to give the ability for a user to manage groups, then we can assign the group's administrator role to the user.
Azure AD roles are used to manage access to Azure AD resources. These resources include Azure AD itself and other Microsoft 365 platforms such as Exchange and SharePoint
The scope of Azure AD roles is at the tenant level. In other words, these roles apply to the entire Azure AD environment for a specific organization or subscription.
Examples of Azure AD Roles:
Global Administrator: Has full access to all Azure AD resources.
User Administrator: Manages user accounts and groups.
Application Administrator: Manages applications registered in Azure AD.
Security Administrator: Manages security-related settings.
What is Azure Roles (Role-Based Access Control - RBAC):
Azure roles are used to manage access to Azure resources. These resources include virtual machines, storage accounts, subscriptions, and more. On the other hand, role-based access control (RBAC) is meant to authorize a user to use resources in Azure.
So for example, you could give a role for a user to go ahead and give them the ability to create a storage account or to manage resource groups.
Role-based access control can be given at the management group level, subscription level, resource group level, or at the resource level.
Management Group: Applies to a group of subscriptions.
Subscription: Applies to a specific subscription.
Resource Group: Applies to resources within a resource group.
Resource: Applies to individual resources.
Examples of Azure Roles:
Owner
This role has full access to all the resources and can delegate access to others.
Contributor
This role can create and manage all types of resources, but can’t grant access to other users and groups.
Reader
This role can view existing Azure resources.
Custom Roles: Organizations can create custom roles with specific permissions.
2: Create the Admin Department and add two users to it Step search for “Microsoft Entra ID” and click on it, first we be creating users and proceed to create a group that will represent the admin department:
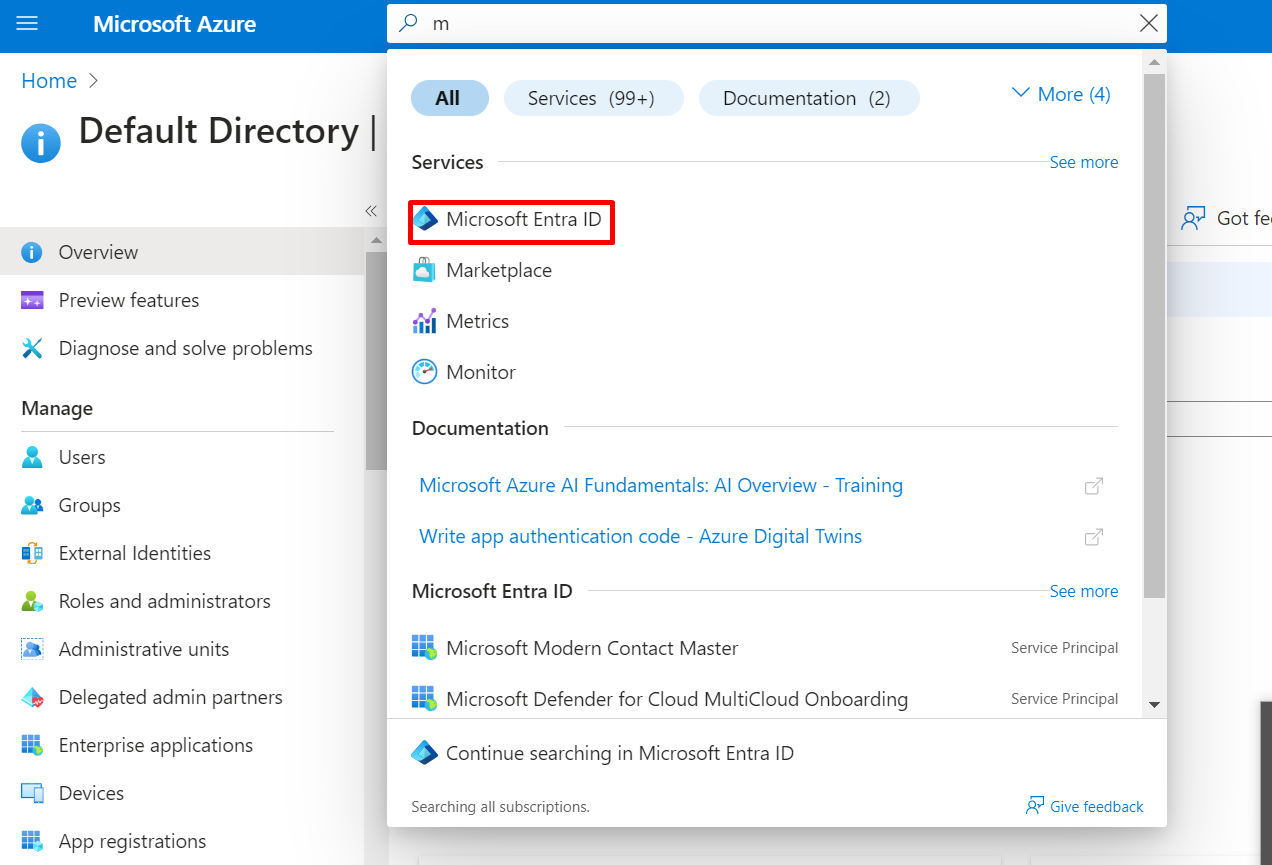
CREATE USER;
1 Click on the user under overview
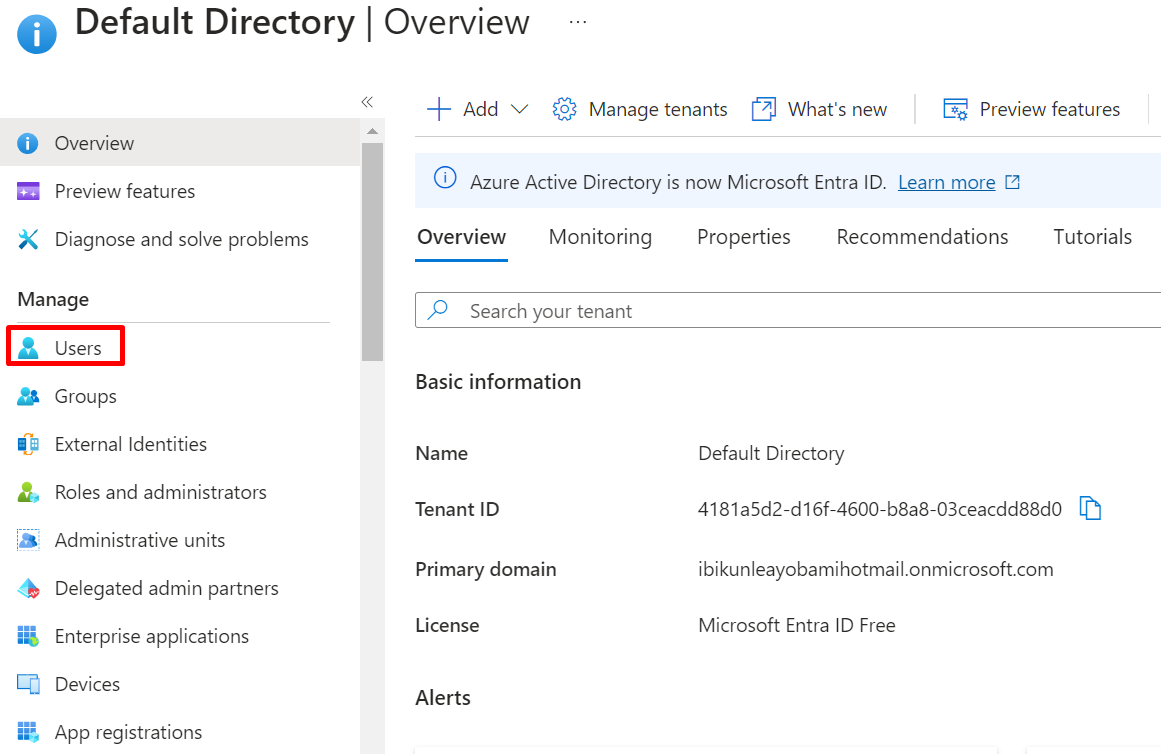
2 Select new user and click on create new user
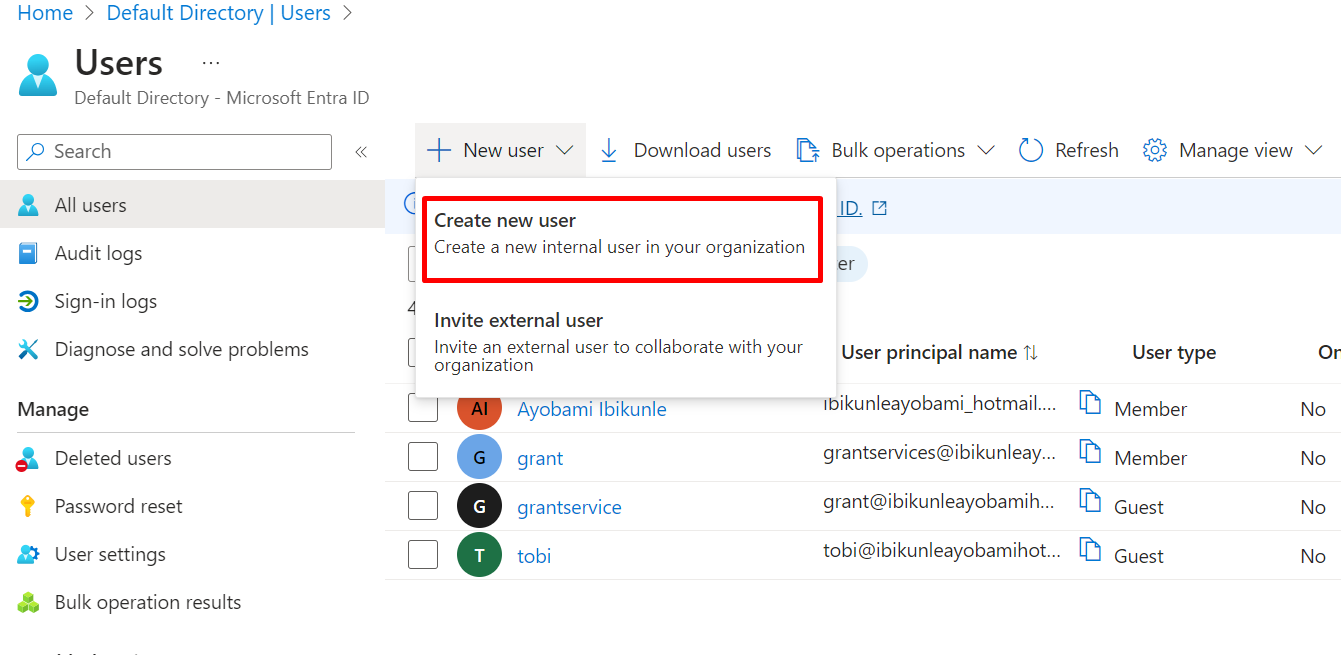
3: Basic; under basic proceed to identity and give your user “User principal name”
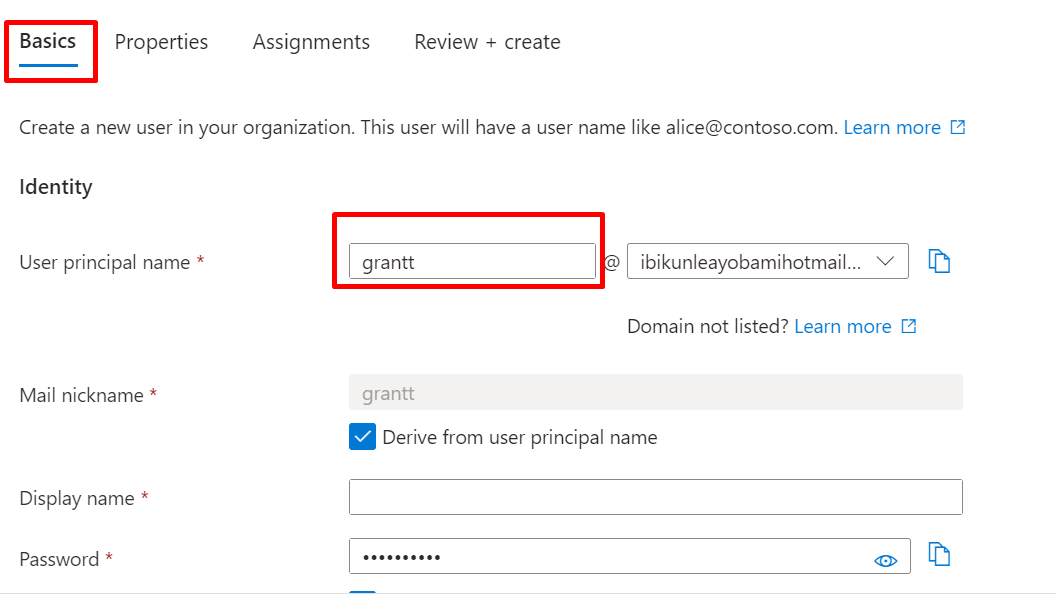
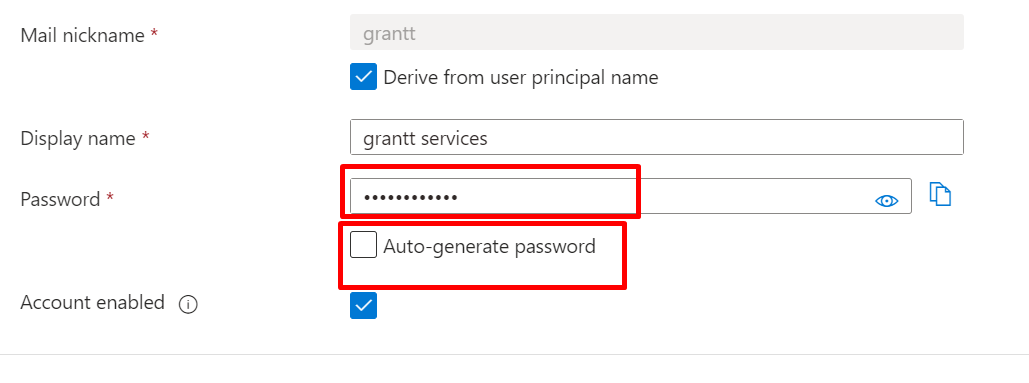
4: Display name you want and click on Auto-generate password to create your own password or you leave it to the generated one.
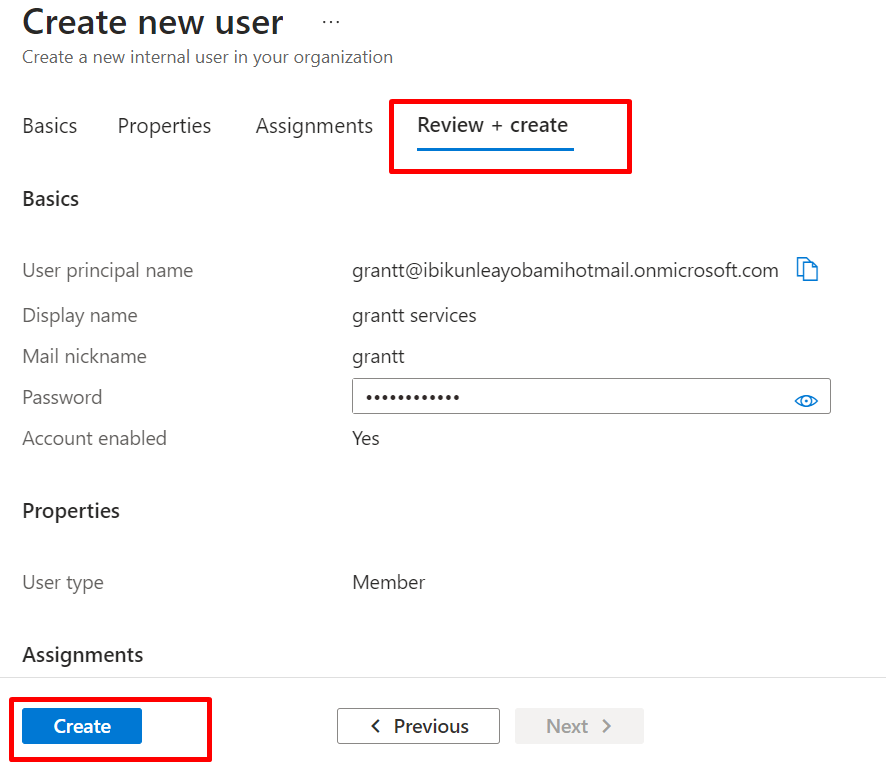
5: Click on Review and create
6: Creating a group
creating group is the first steps to take before creating admin department
Search for and select Azure Active Directory
On the Active Directory page, click on Groups and then select + New group.
Fill Out the New Group Form:
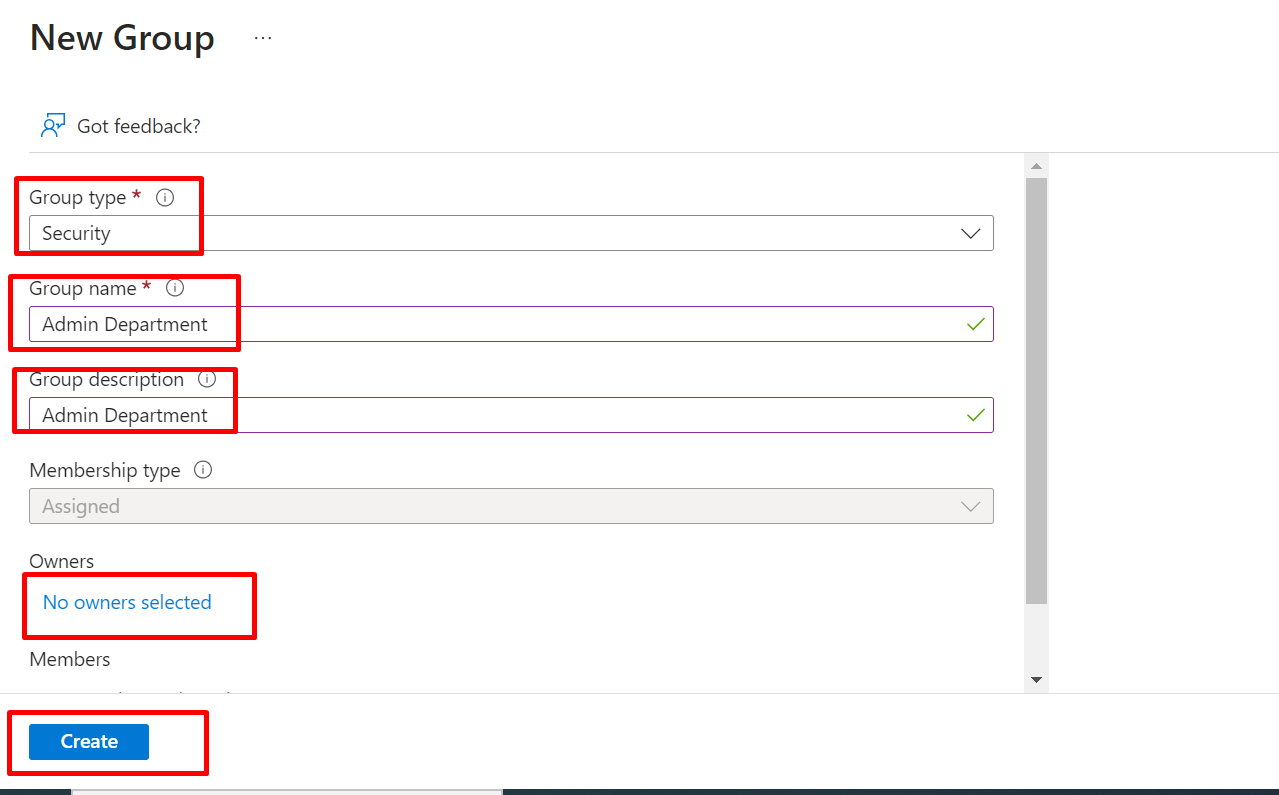
Click Create:
Your group will be created, and you can now add members to it.
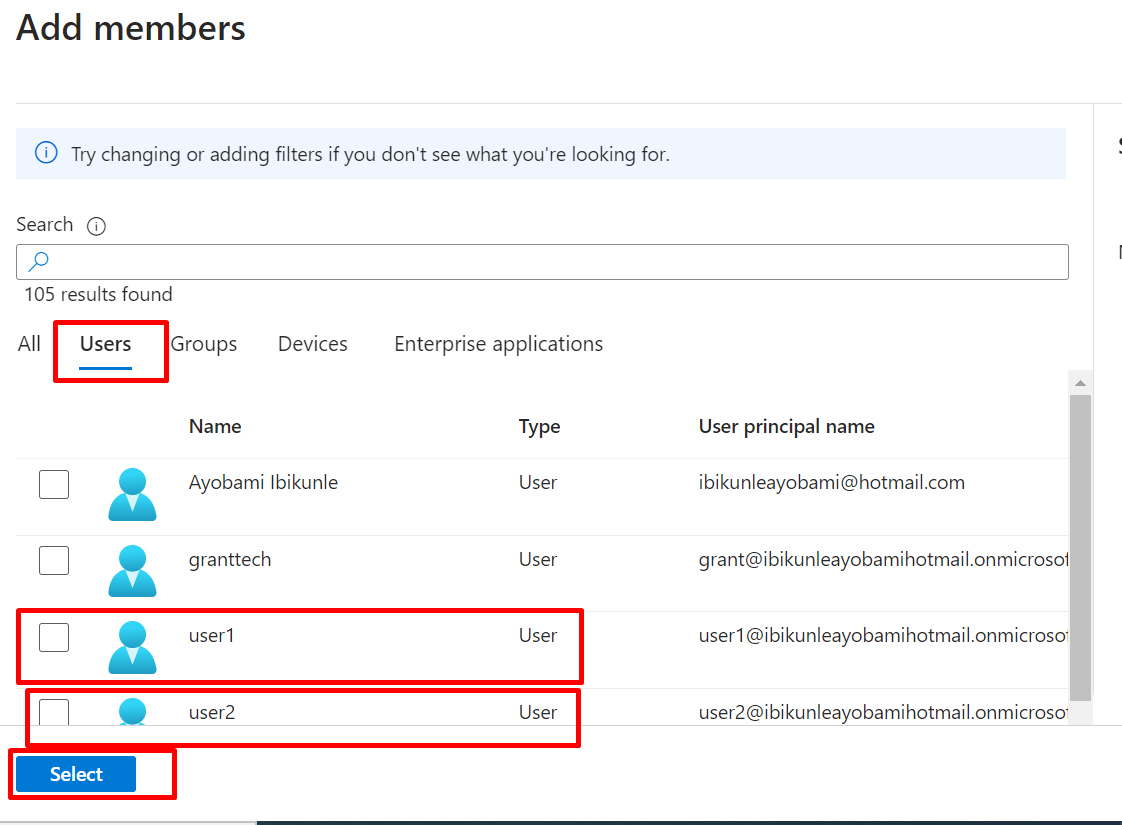
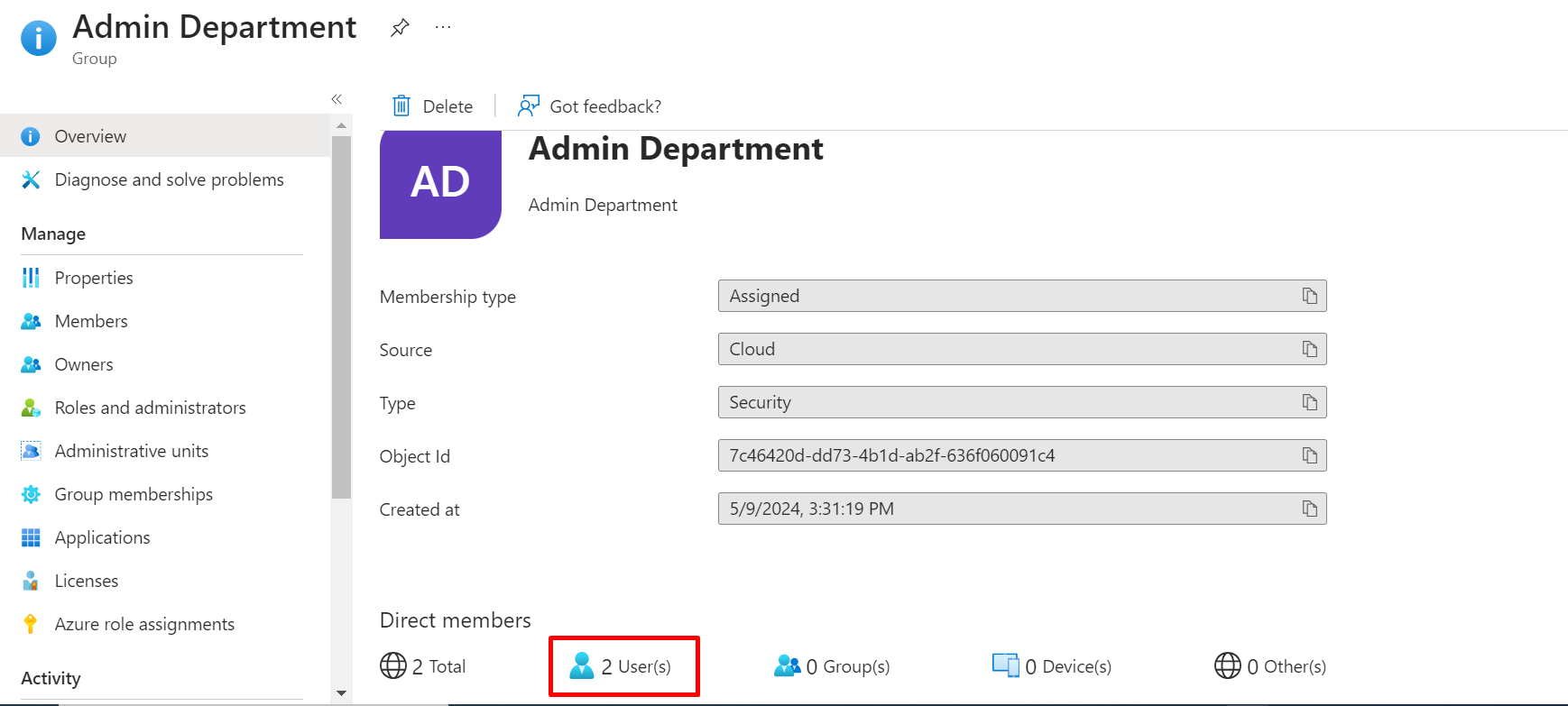
Click on member and see the user we create
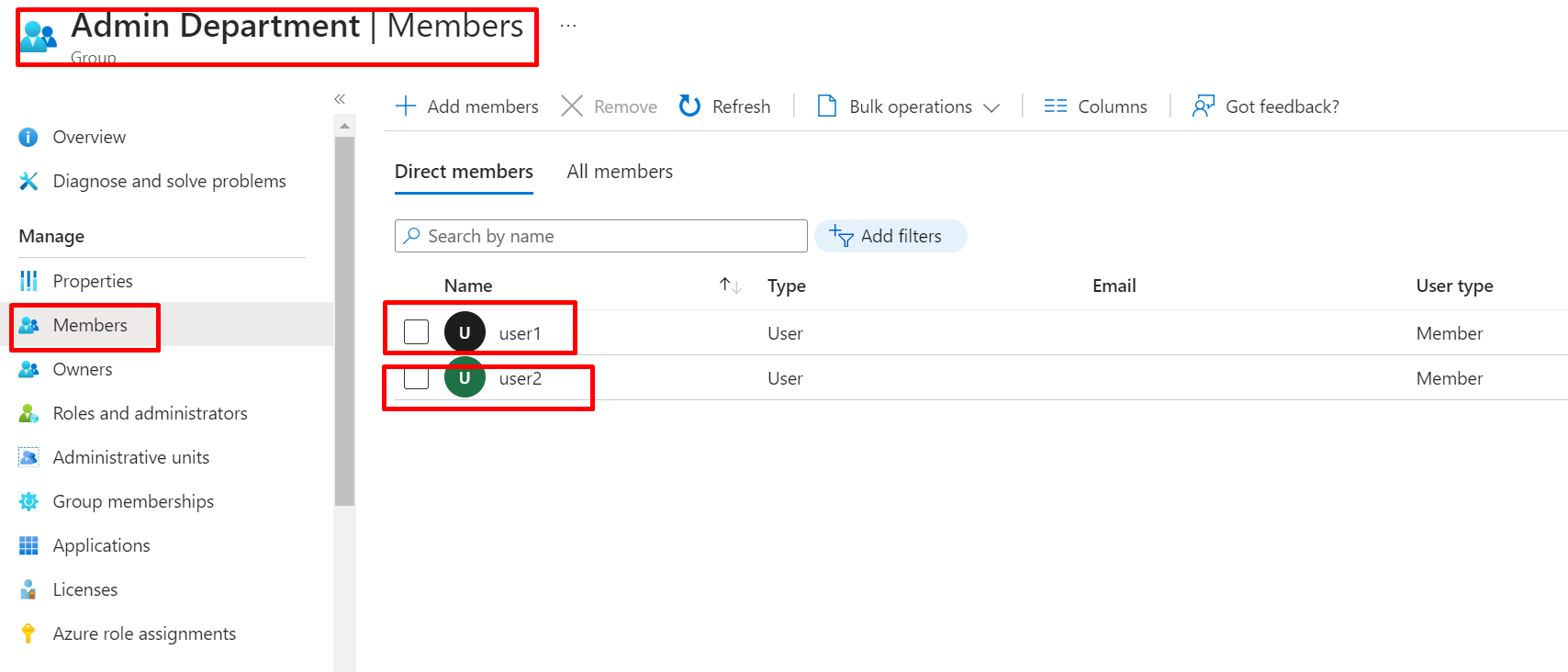
3: Assign the Global Administrator Role to User A Step
Let’s walk through the steps to assign the Global Administrator role to a user in Microsoft Entra ID
As a Global Admin, you have the authority to assign roles to users
Navigate to Users > Active users
Choose the user you want to make an admin.
Click on Assigned roles
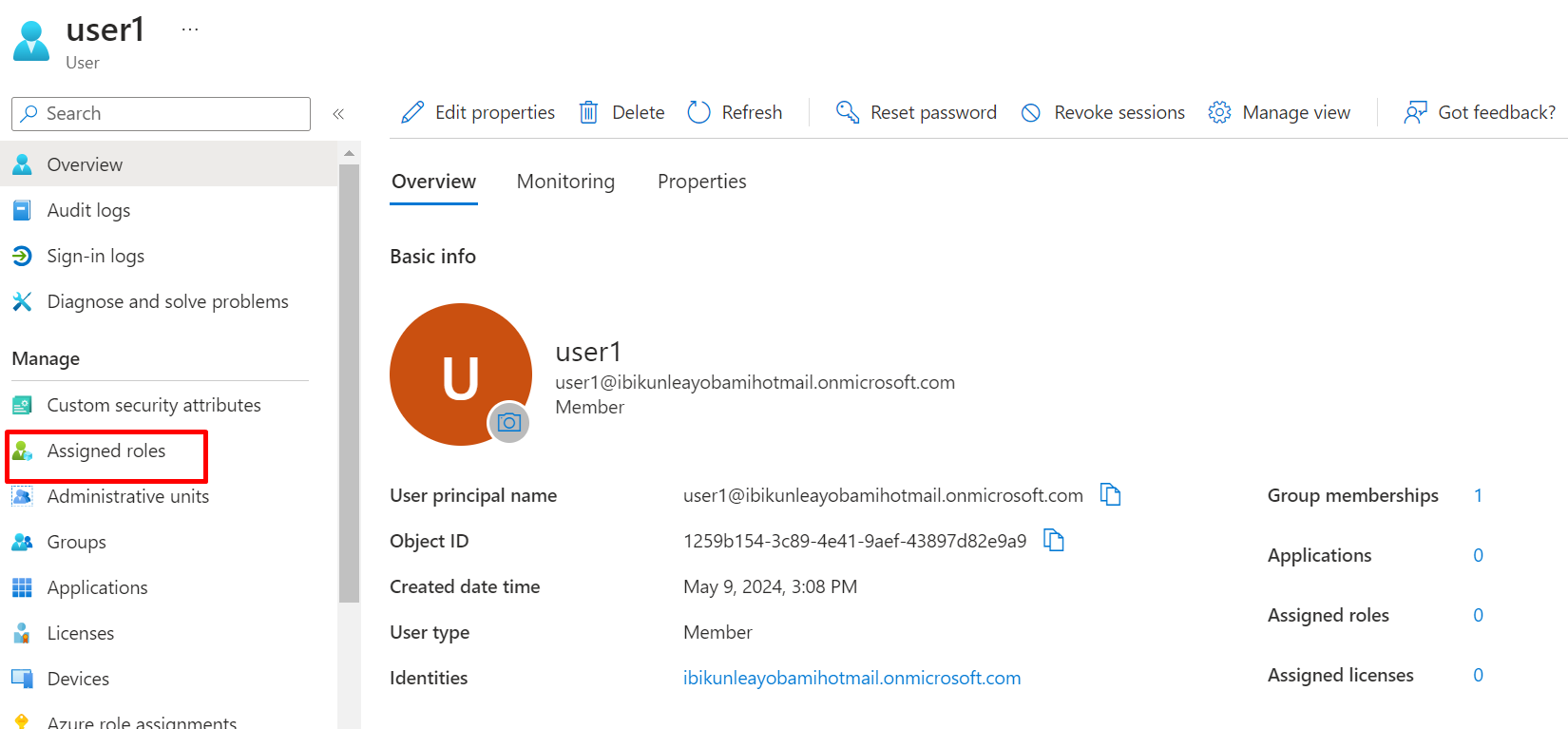
Click on add assignment
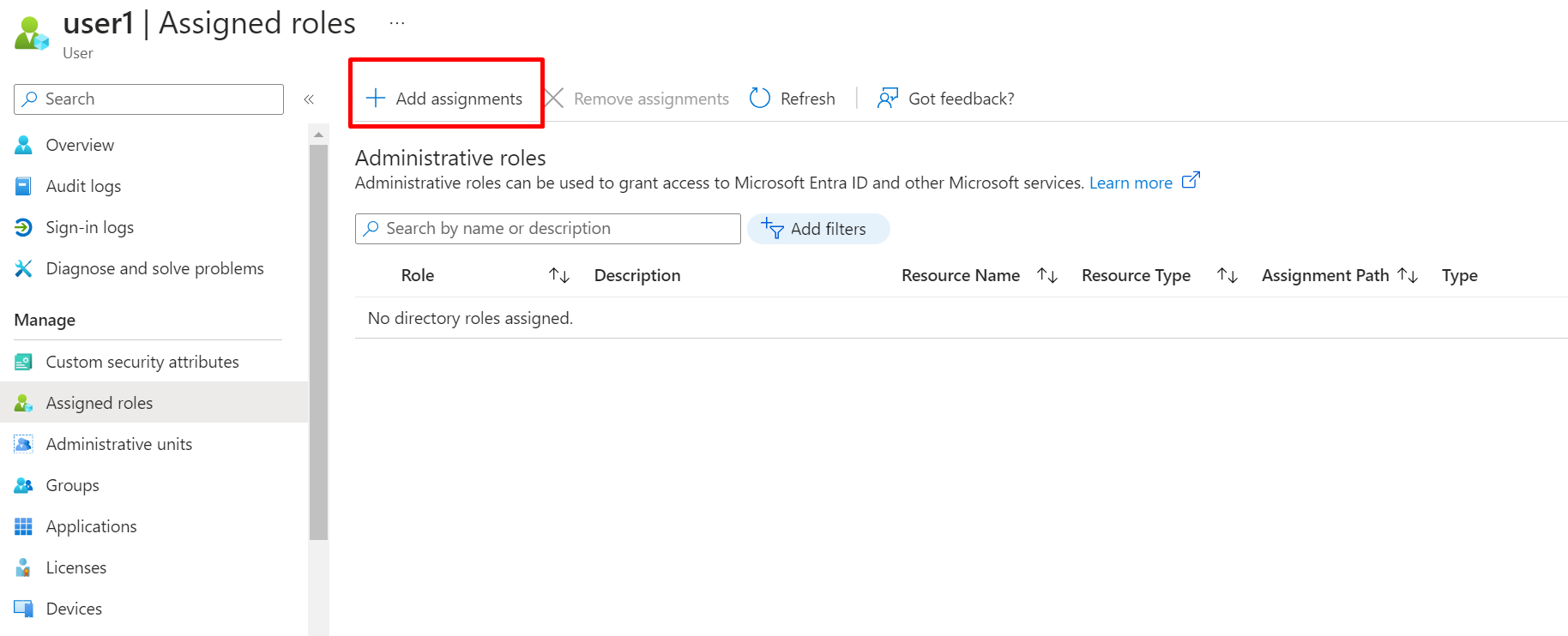
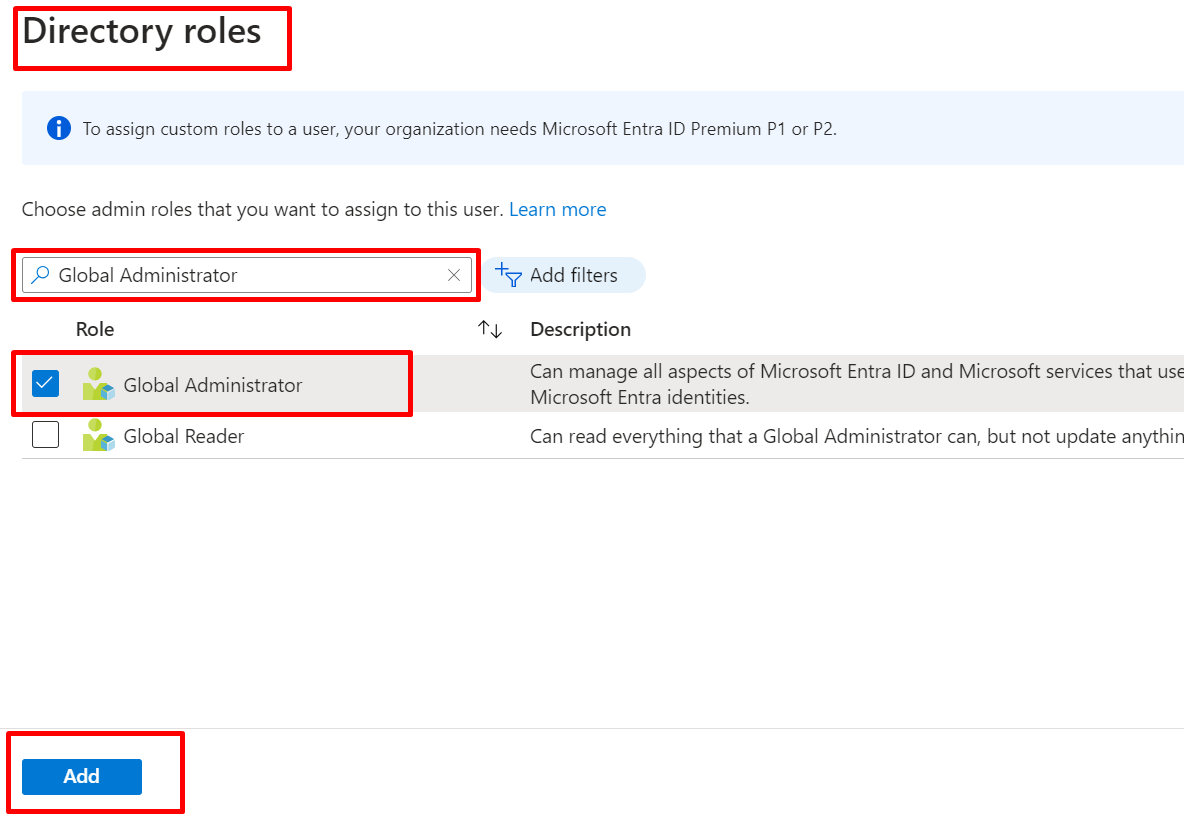
Select Manage roles:
Pick the admin access you want the user to have (e.g., Global Administrator) and click add.
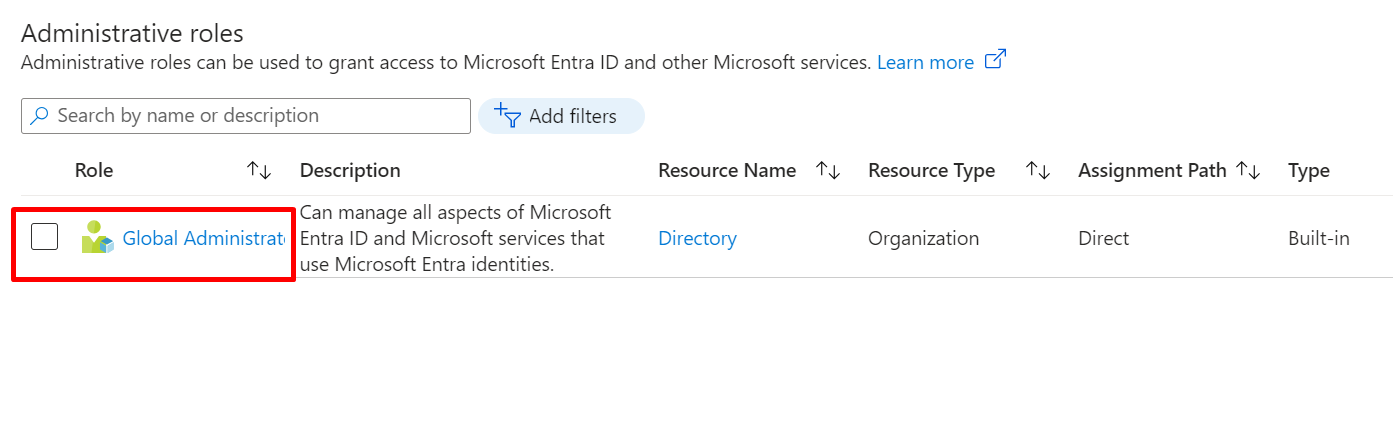
4: Show all the steps it took the Global Admin to Log in into the Azure Portal with his new credentials Step.
Let’s simplify the sign-in process for a Global Admin to access the Azure Portal https://portal.azure.com/ with new credentials.
Open your web browser and go to the Azure Portal or Incognito window
On the sign-in page, type your email address
using the credentials that’s the user-email and password that was selected when the user was created that was used during the creation process.
Click the Sign In button, and you’re authenticated

Sign in on with the User principal name
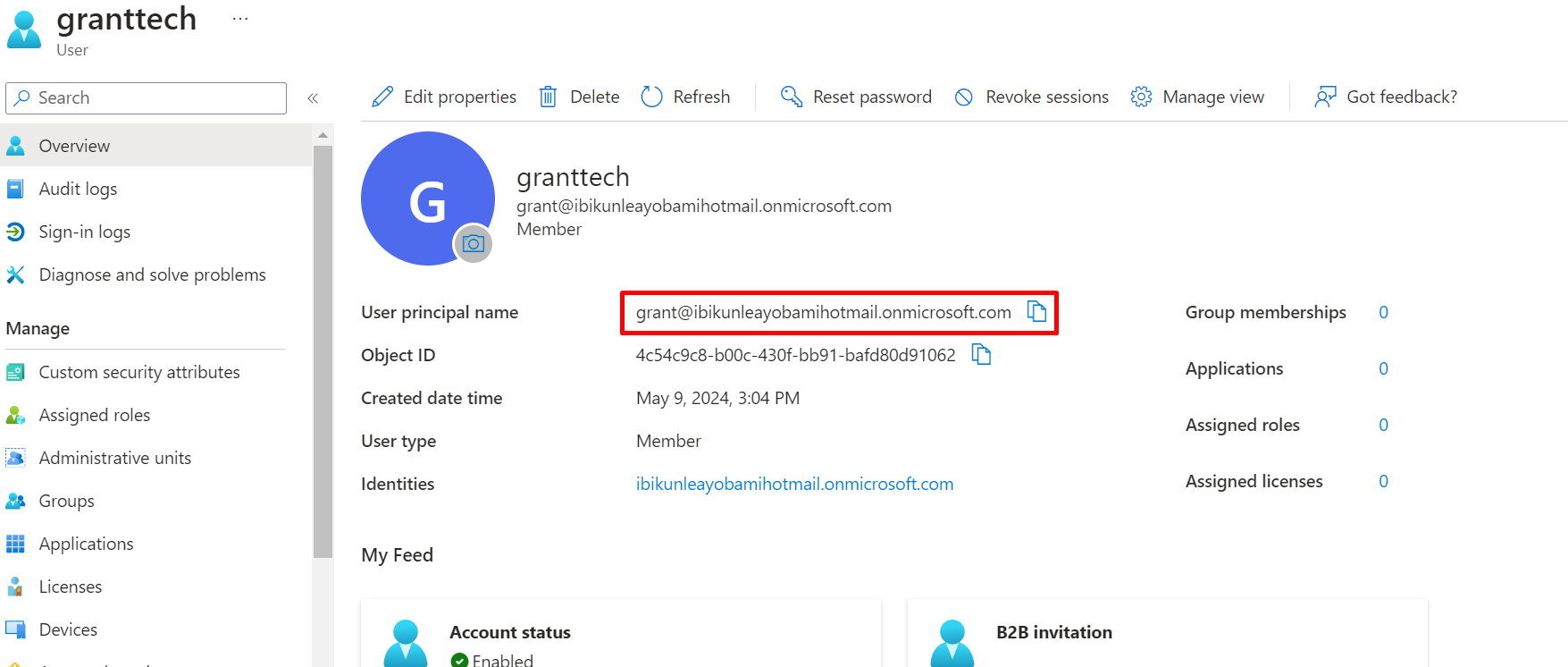
sign in the password you create or the generated one

then update your password
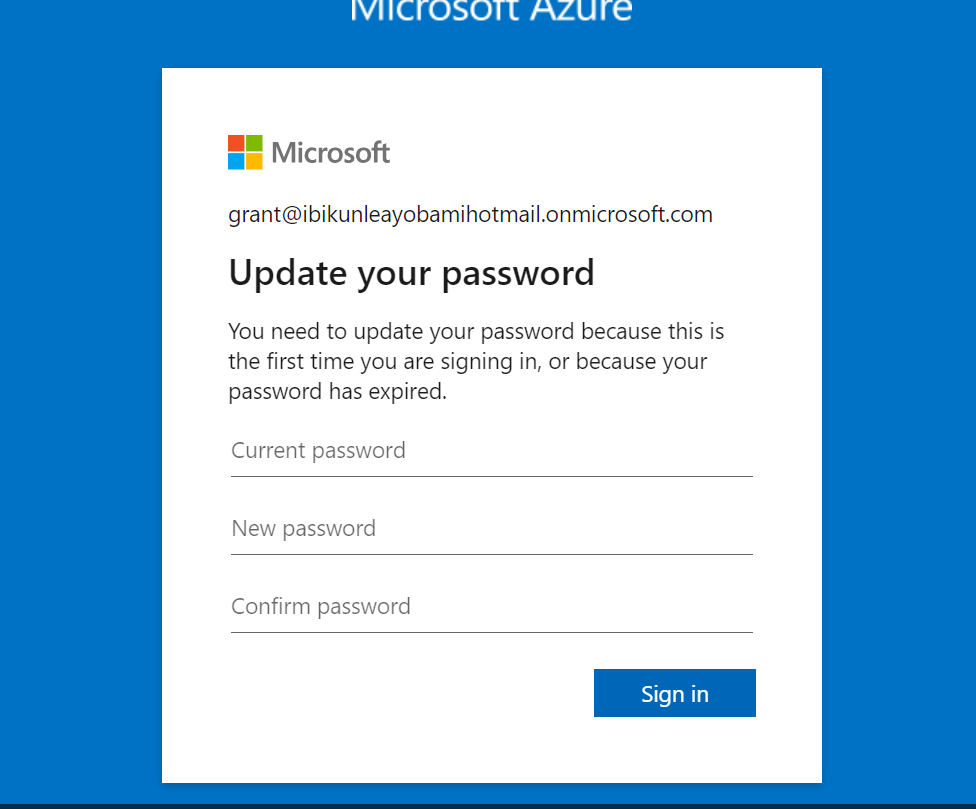
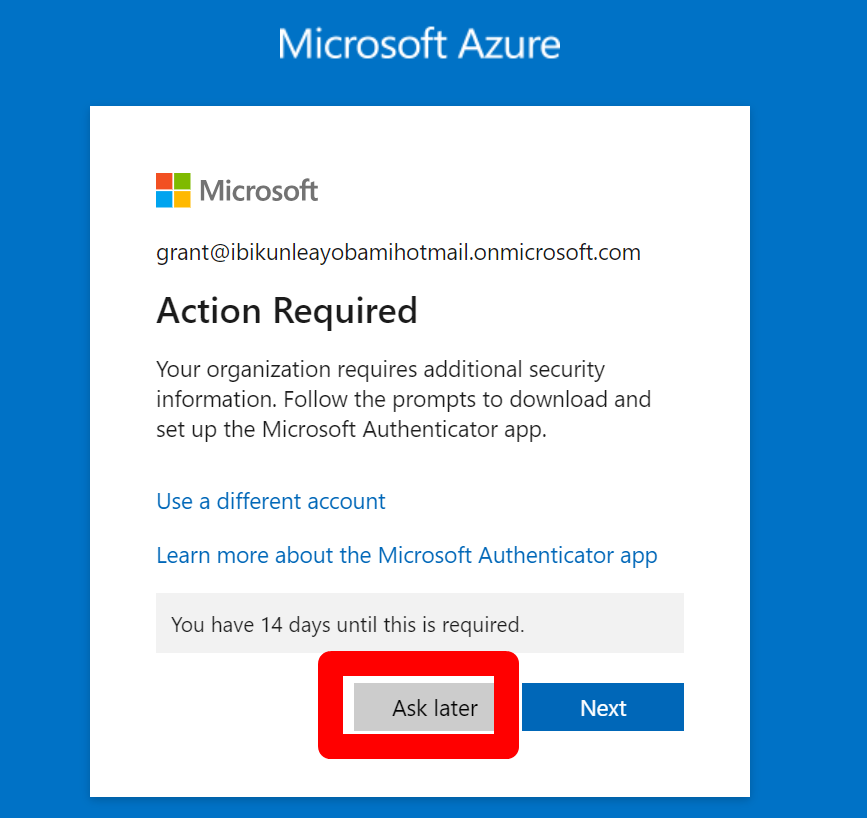
Ask later
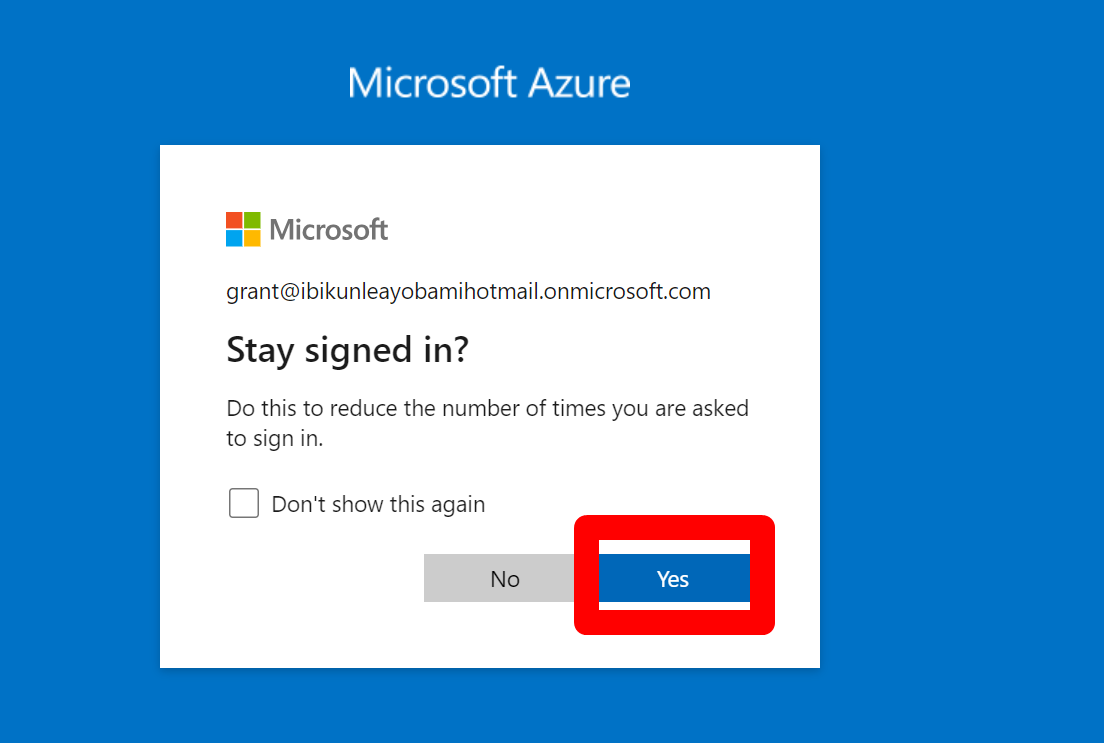

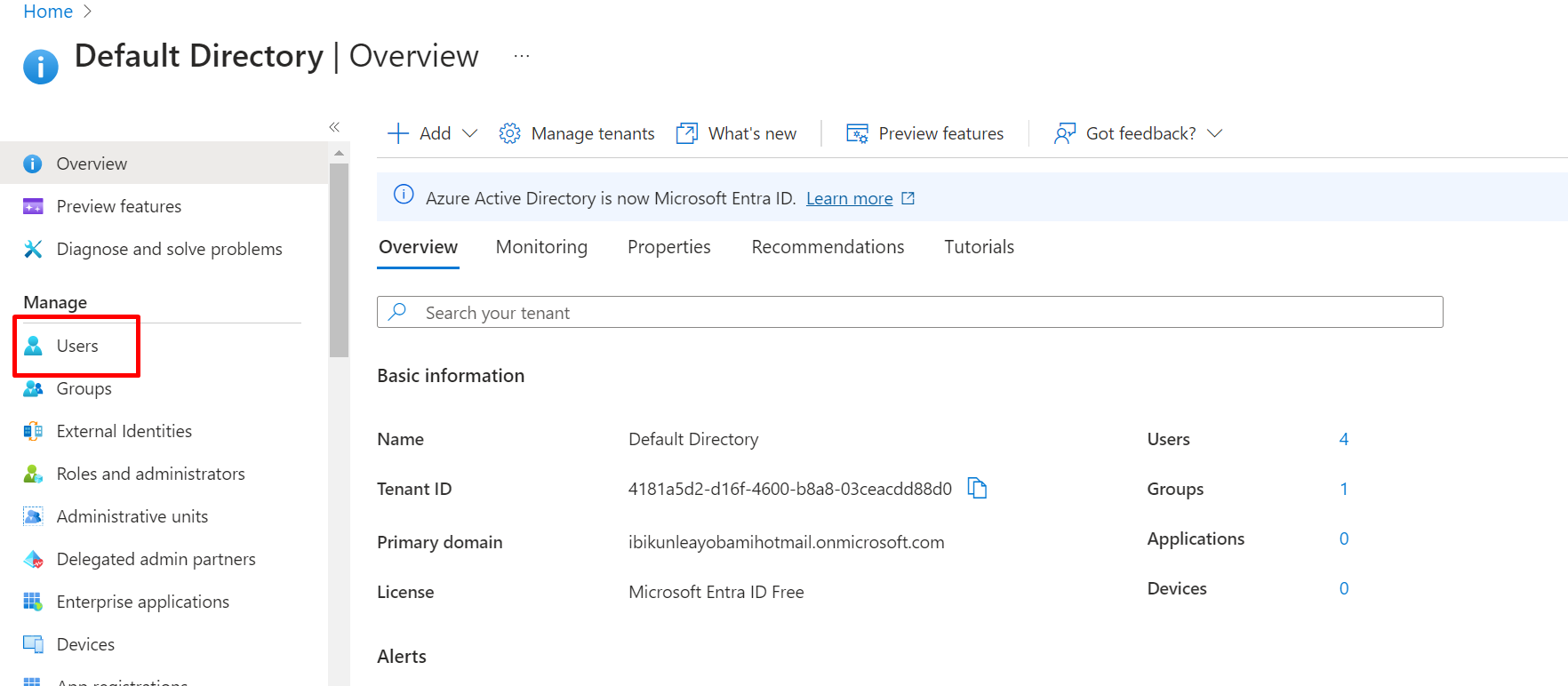
5: Let the Global Administrator create/onboard a new member to the Admin Department.
Navigate to Users: From the left navigation pane, click on Users.
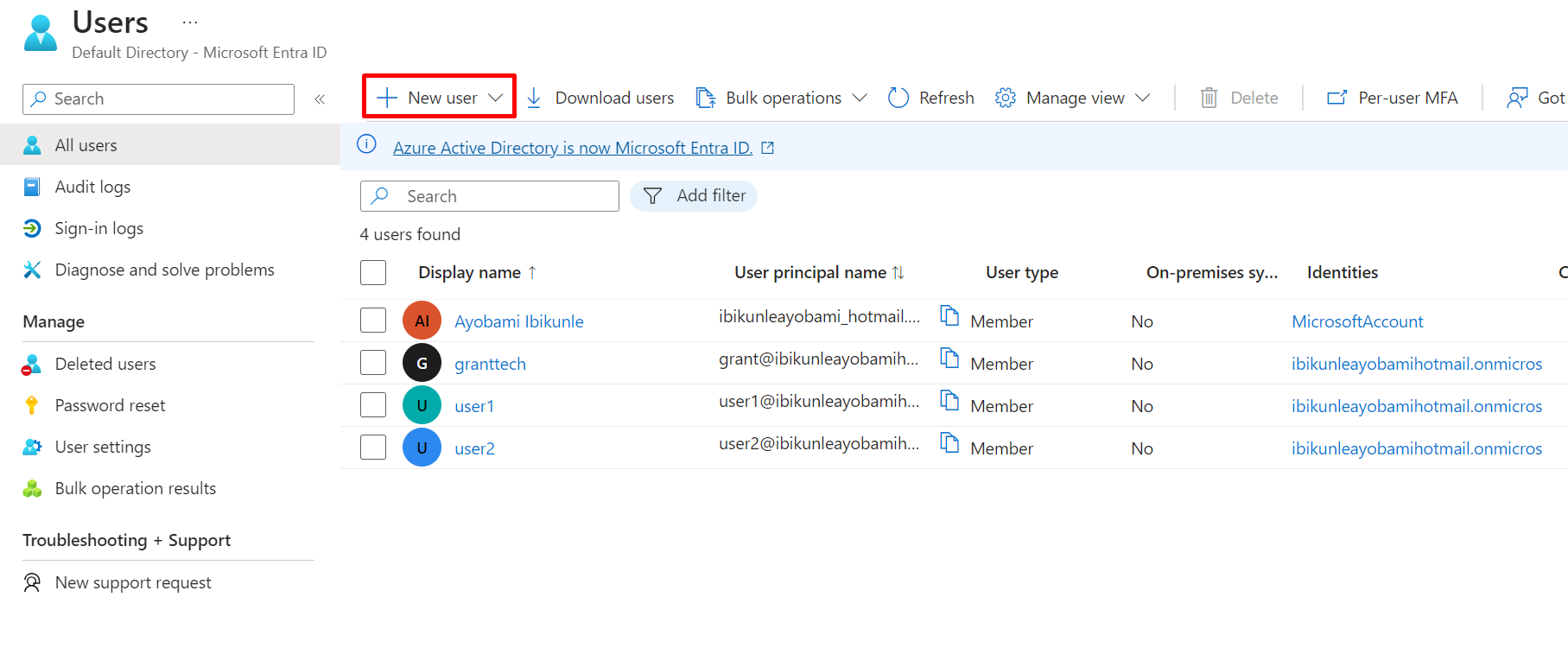
Click on + Add a user
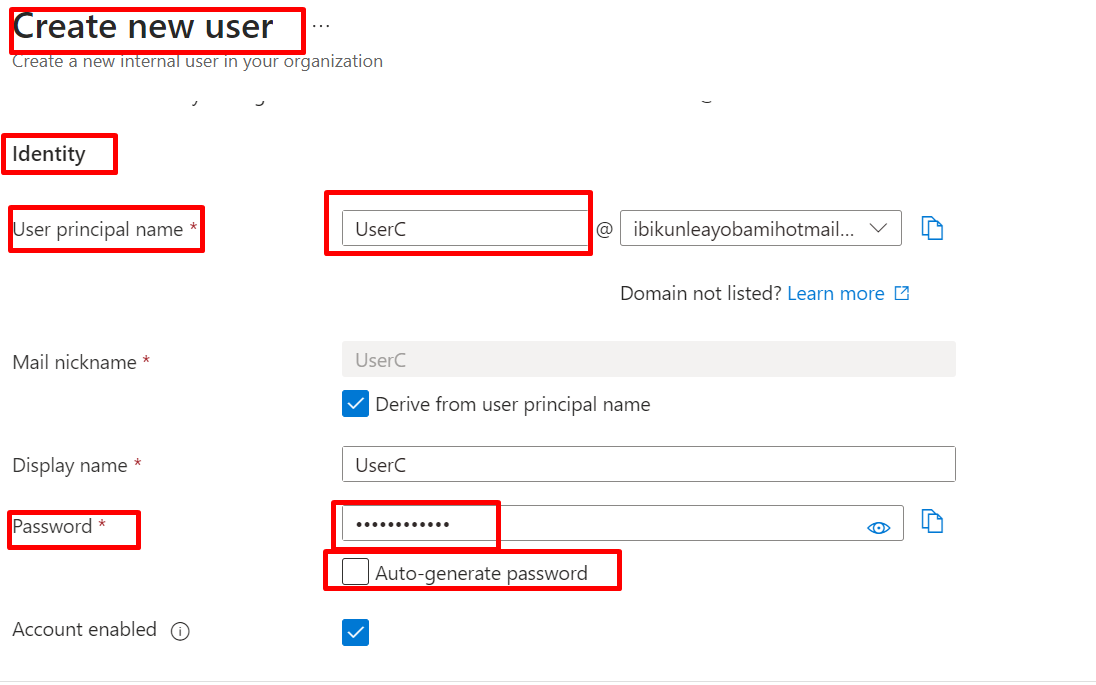
Fill in the required details for the new user
select assignment, click on group
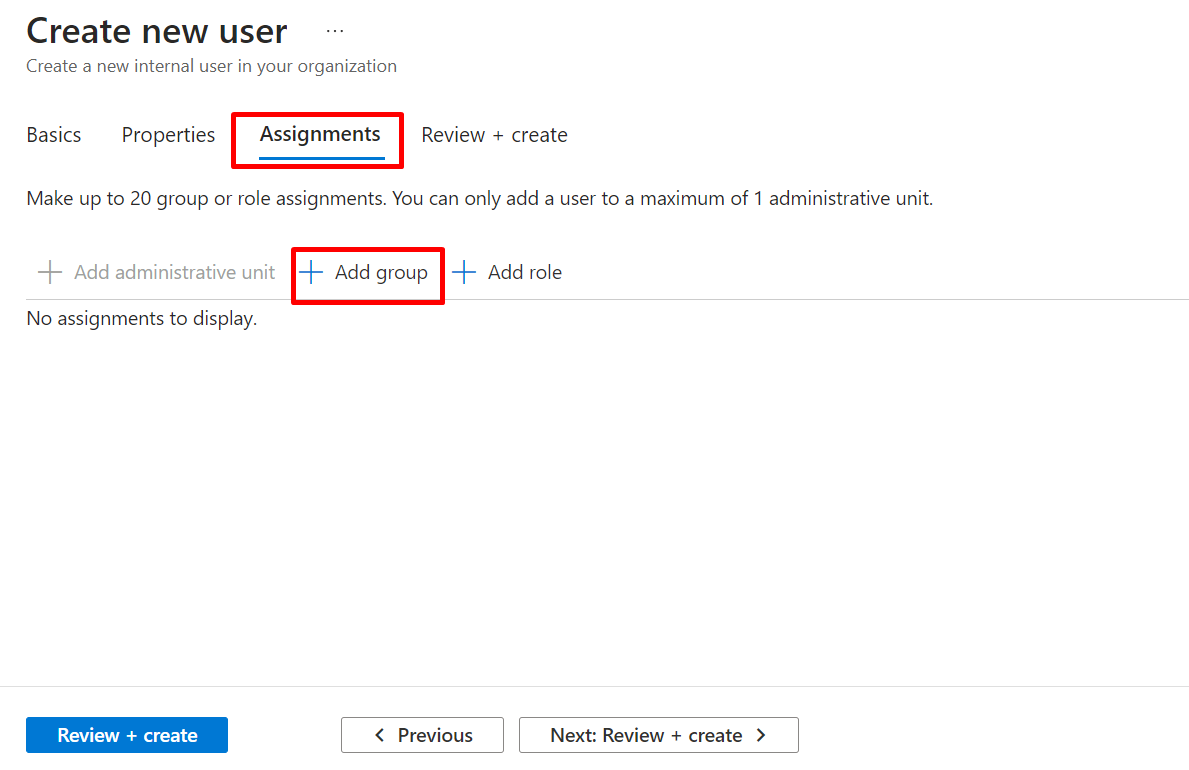
Under select group, click on the group we are adding to, and Assign the appropriate role.
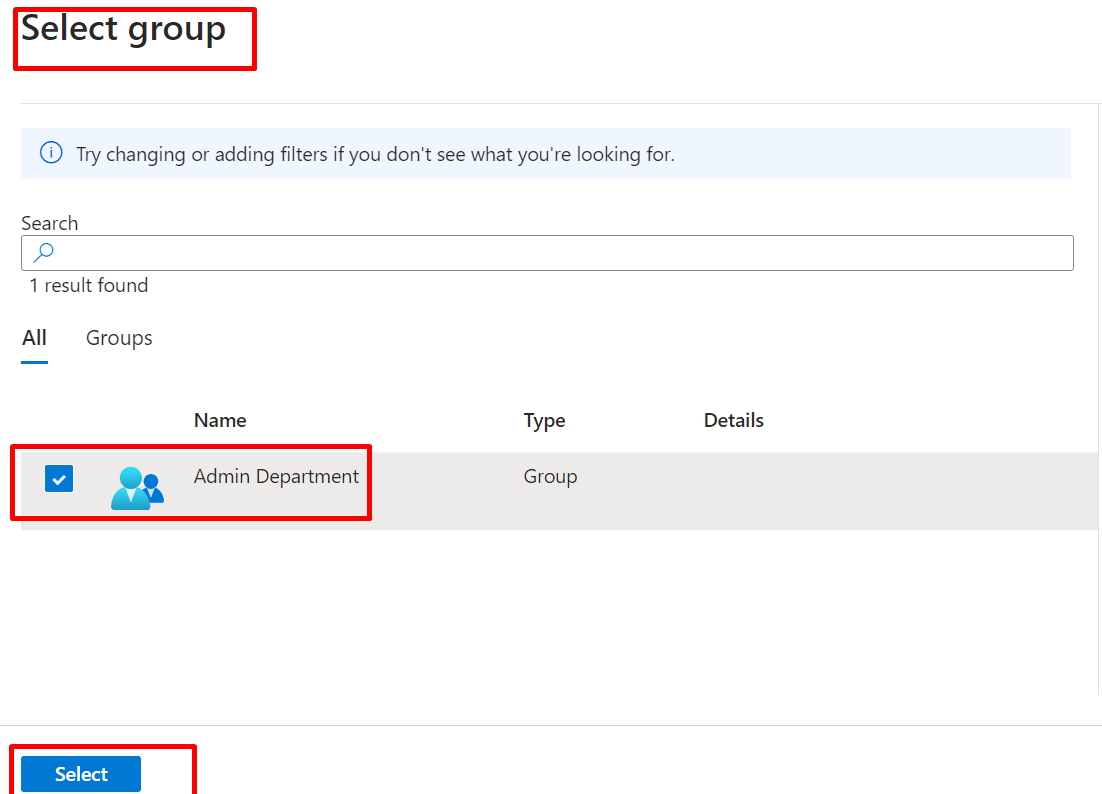
Click on Review + create and CREATE
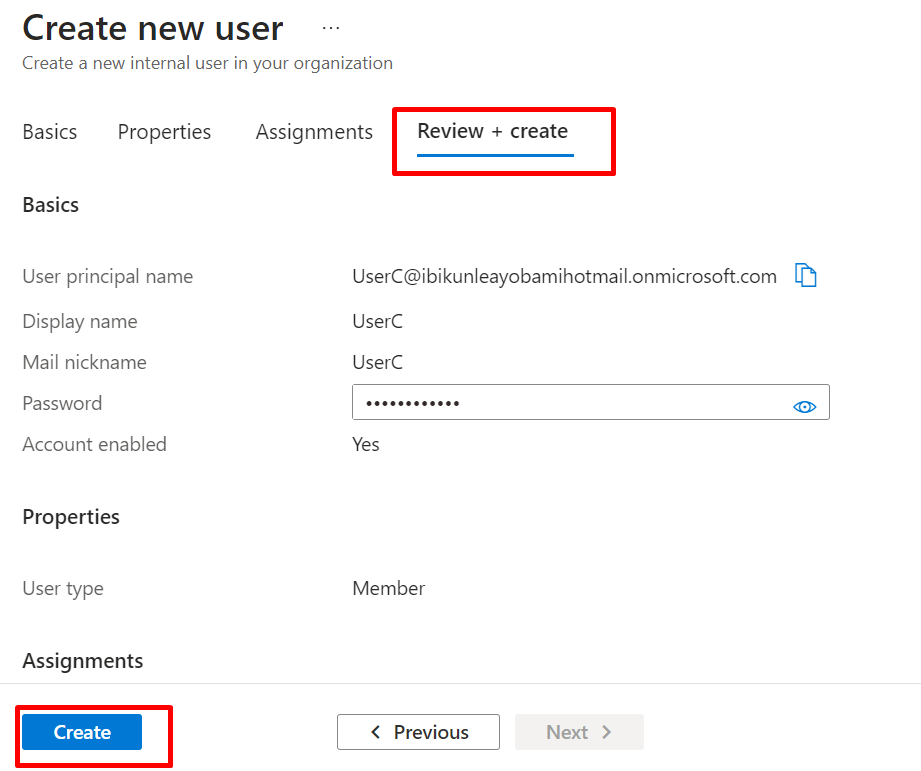
Navigate to All user and see all the user, new user as been added under member
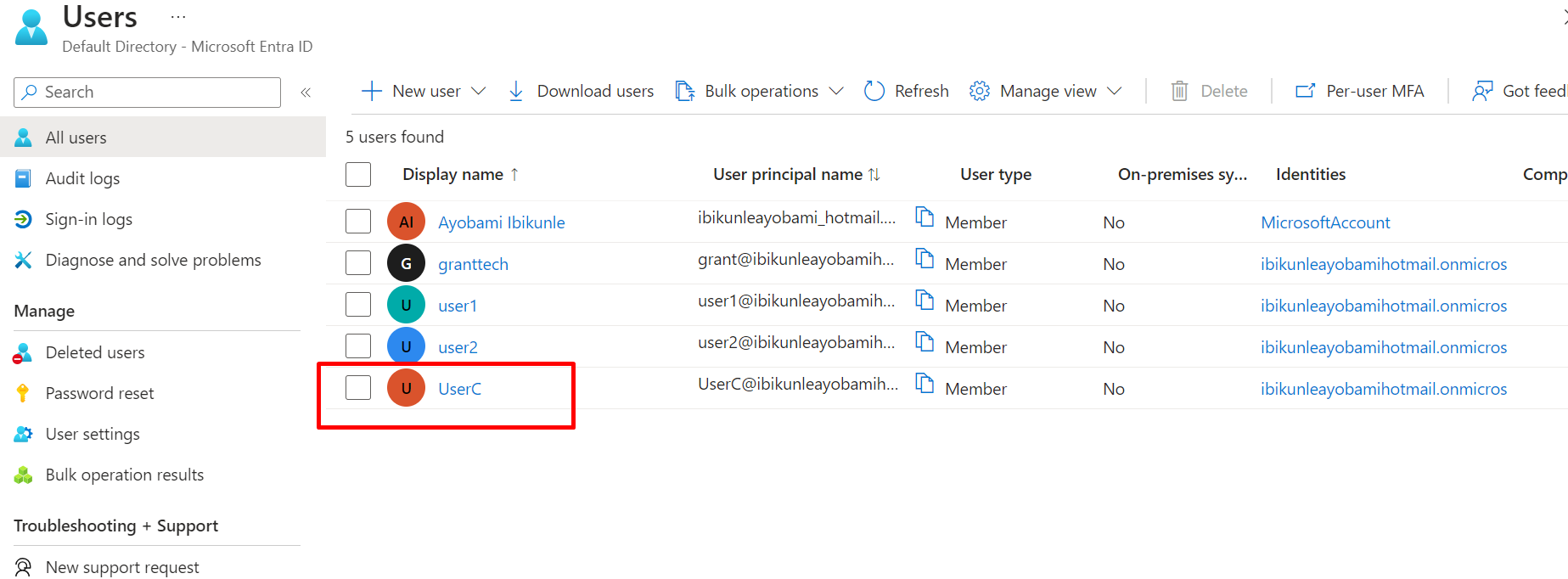
New member under Admin Department Member group Create.
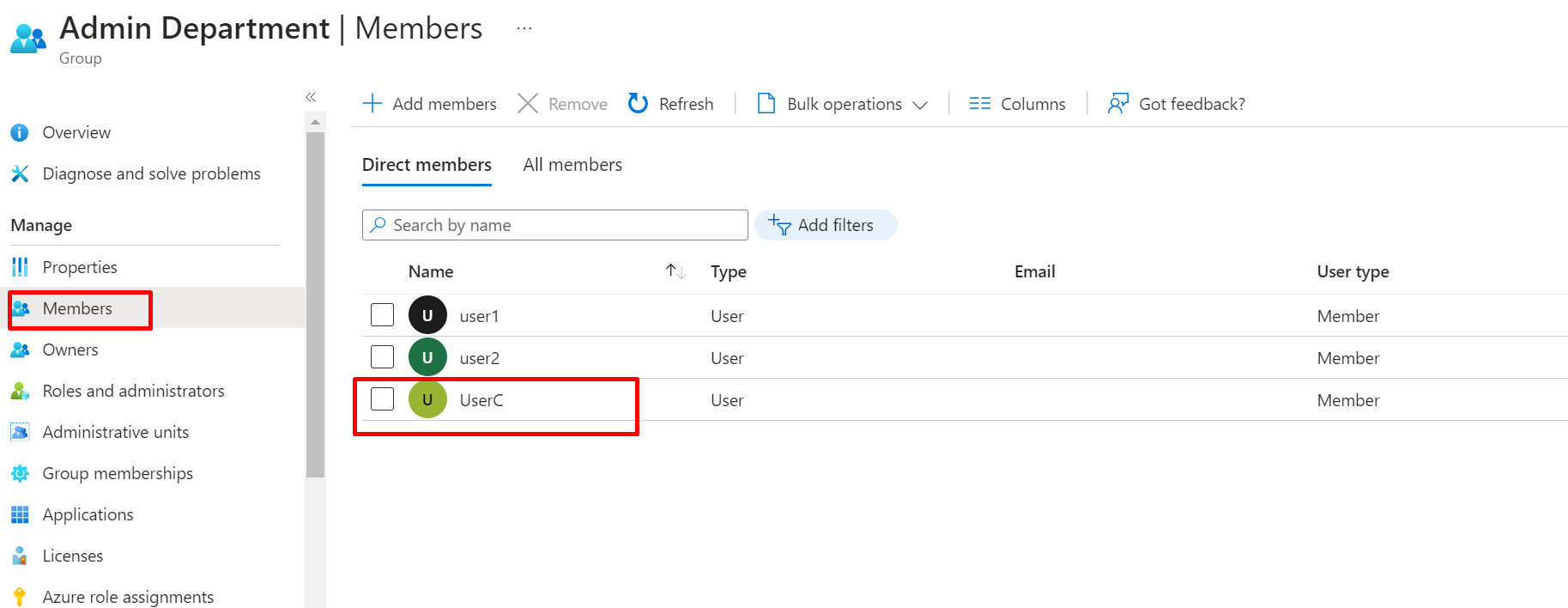
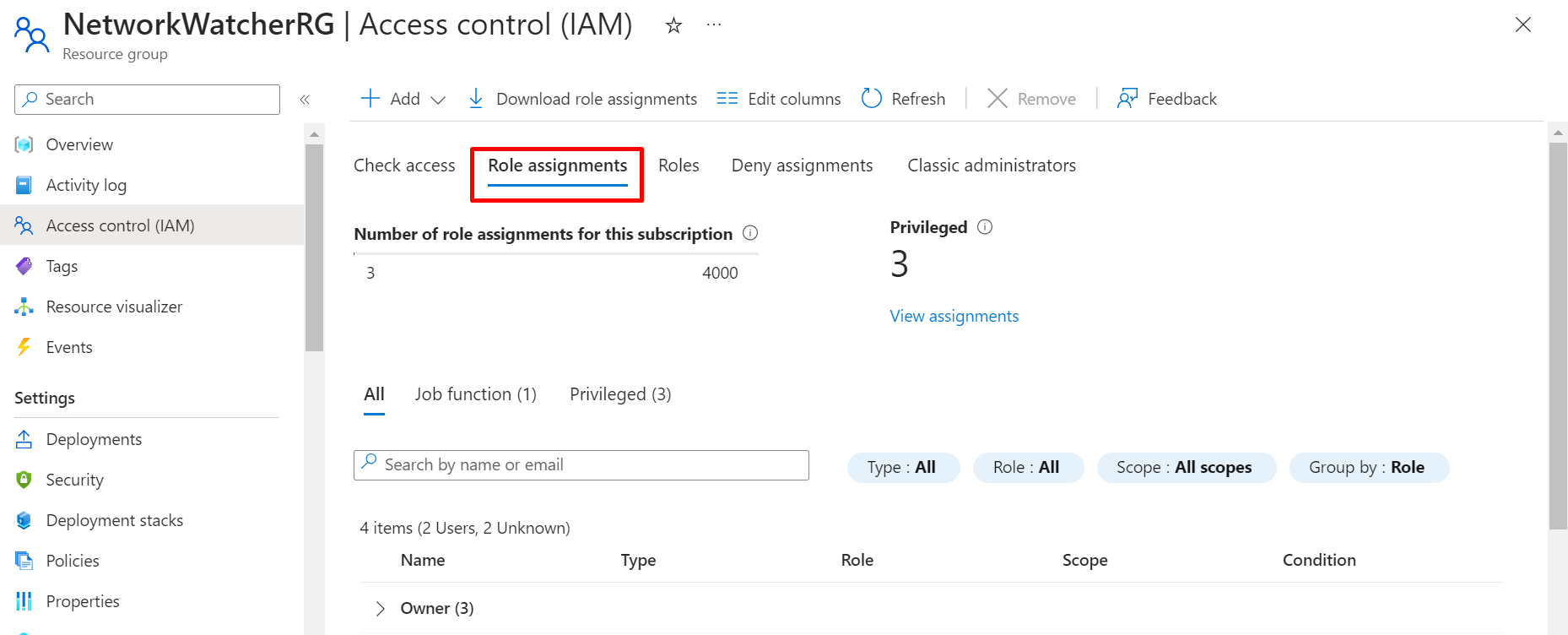
If you now go to the Role assignments tab, you will now see the role assigned to the user as a Reader.
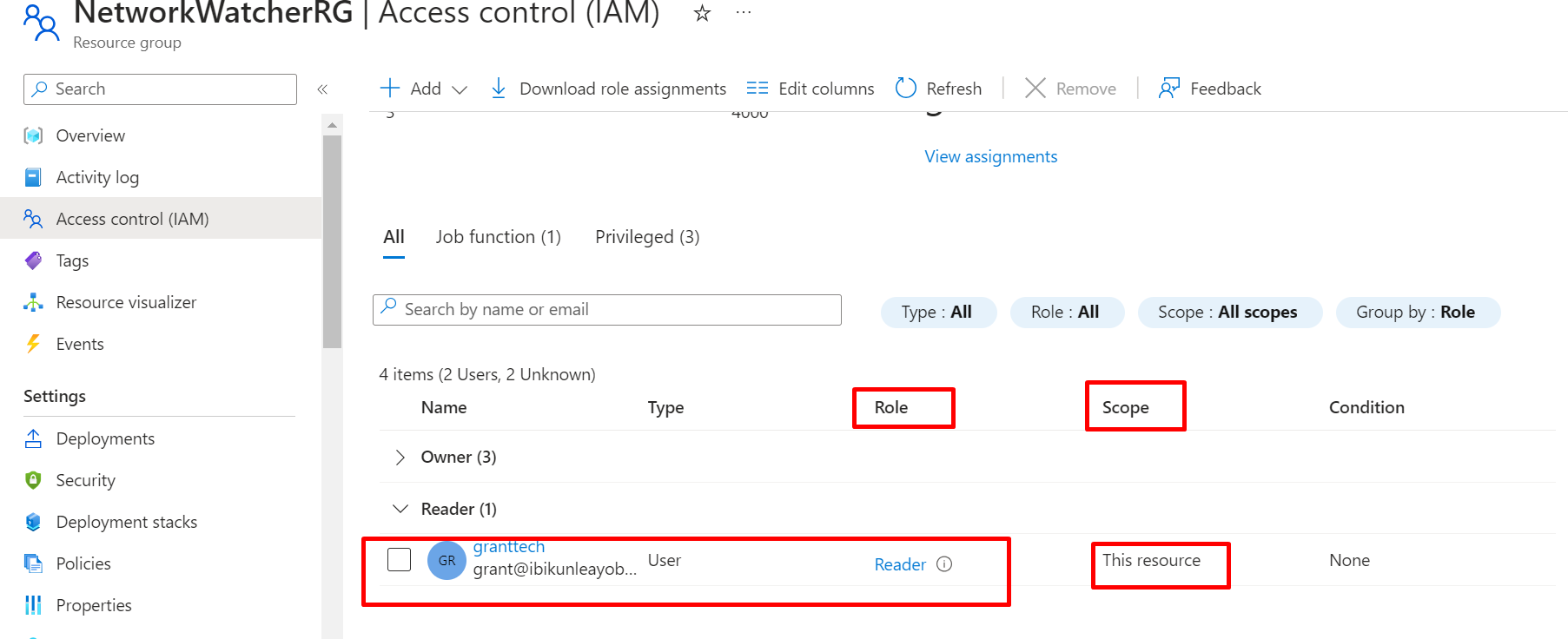
As a Global Administrator, you can grant additional permissions or roles to the new user as needed ( granting admin roles, access to specific resources, etc.).
Summary
Azure AD roles are used to manage access to Azure AD resources, whereas Azure roles are used to manage access to Azure resources.
The scope of Azure AD roles is at the tenant level, whereas the scope of Azure roles can be specified at multiple levels including management group, subscription, resource group, resource.
I hope you found this information useful!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ibikunle ayobami directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
