Using Flowise with Local LLMs.
 Brian King
Brian King
TL;DR.
Using Flowise, with local LLMs like Ollama, allows for the creation of cost-effective, secure, and highly customizable AI-powered applications. Flowise provides a versatile environment that supports the integration of various tools and components, enhancing AI workflows and enabling the development of local chatbots and AI agents. This setup offers benefits in terms of data privacy and operational security, making it ideal for both business and personal AI projects.
Attributions:
A YouTube video produced by Leon van Zyl↗:
An Introduction.
Low-code GUI solutions like Flowise allows developers to focus on the big picture while maintaining an eye on the details:
The purpose of this post is to demonstrate how to build Chatflows.
The Big Picture.
This post is a continuation of the Langflow and Flowise installation post.
Flowise is an excellent low-code GUI for creating AI workflows and agents. It simplifies the use of LangChain and LlamaIndex solutions. LangChain is a Python library that makes it easier to develop, produce, and deploy applications using large language models (LLMs). It offers open-source components, integrations, and tools for different purposes, like question answering, chatbots, and more.
Prerequisites.
Updating my Base System.
- From the (base) terminal, I update my (base) system:
sudo apt clean && \
sudo apt update && \
sudo apt dist-upgrade -y && \
sudo apt --fix-broken install && \
sudo apt autoclean && \
sudo apt autoremove -y
NOTE: The Ollama LLM manager is already installed on my (base) system.
What is Flowise?
Flowise is an open-source, low-code platform that helps me easily create customized AI workflows and agents. It simplifies the development of AI applications, which usually require many iterations, by allowing for quick changes from testing to production. Chatflows link AI models with various tools like memory, data loaders, and cache, along with over a hundred other integrations including LangChain and LlamaIndex. This setup enables the creation of autonomous agents and assistants that can perform diverse tasks using custom tools. I can build functional agents and OpenAI assistants, or opt for local AI models to save costs. Flowise supports extensions and integrations through APIs, SDKs, and embedded chat features. It is platform-agnostic, meaning Flowise can work with local, open-source AI models in secure, offline environments using local data storage. It is compatible with various platforms and technologies like Ollama, HuggingFace, AWS (Amazon Web Services), Azure, and GCP (Google Cloud Platform), offering flexibility in deployment.
Running the Flowise UI.
- From the Terminal, I activate the Flow environment:
conda activate Flow
- I run Flowise:
npx flowise start
- I open the Flowise UI in the browser:
Example 1: Local Chatbot.
- I click
Chatflowsbutton in the Main Menu, found on the left of the Flowise UI:
At the top-right of the UI, I click the blue
+ Add Newbutton.At the top-right of the
Untitled chatflowcanvas, I click the Save (💾) button:

- I name the canvas
Local Chatbotand and click the blueSavebutton:
NOTE: On the left of the UI is a round, blue button with a plus symbol (+). This is the
Add Nodesbutton. Clicking theAdd Nodesbutton causes the blue button to change to a minus symbol (-) and a drop-down menu to display. Clicking the blue minus symbol (-) closes the drop-down menu. Within the drop-down menu are closed sub-menus (˅) that twirl open (˄) when clicked. Click an open sub-menu to close it again. The convention is to follow the path (>) to a node. All paths start withAdd Nodes >and end with nodes being dragged onto the current canvas.
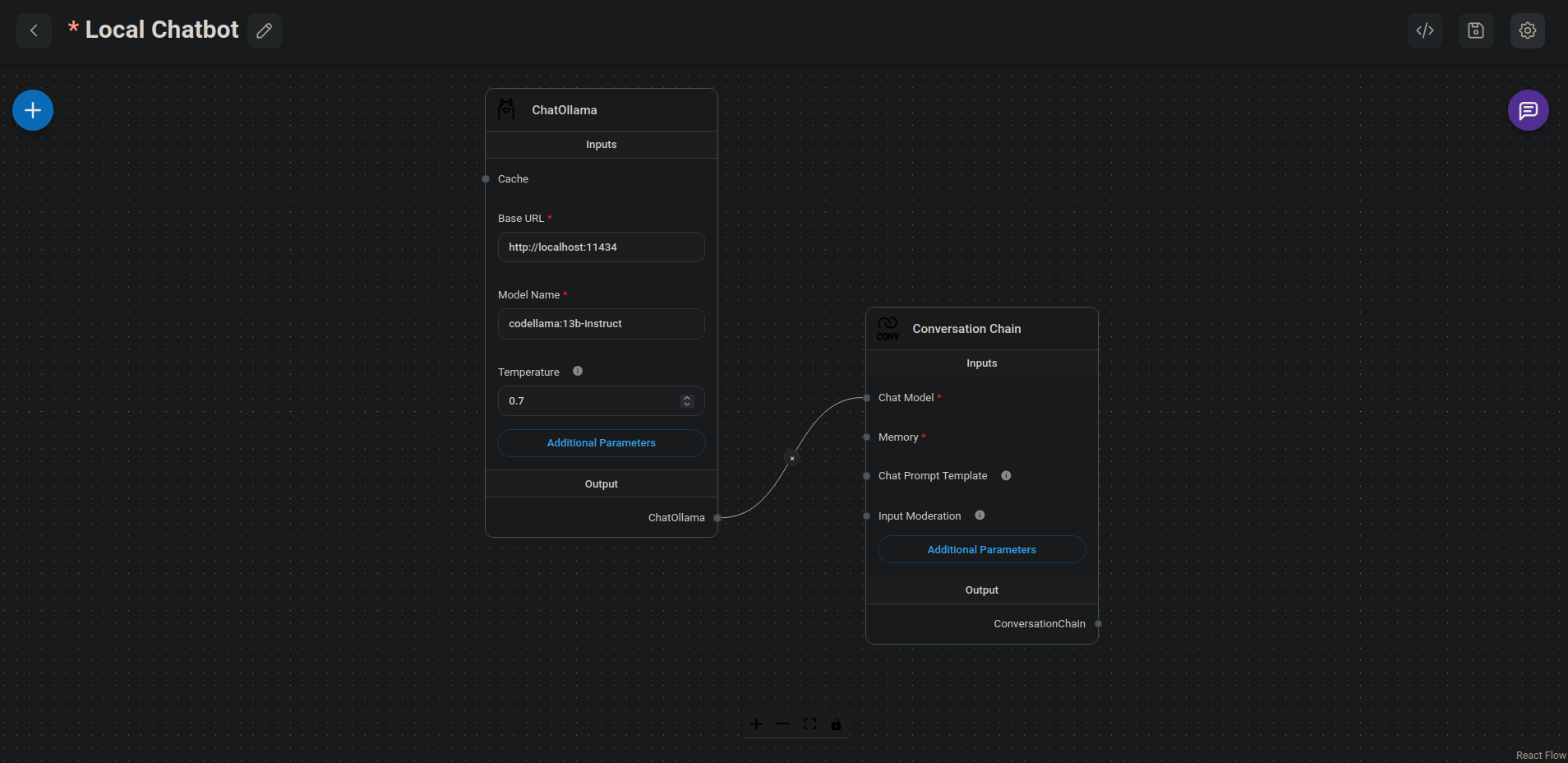
- I drag the
Add Nodes > Chains > Conversation Chainonto theLocal Chatbotcanvas:
I drag the
Add Nodes > Chat Models > ChatOllamanode onto the canvas.In the
ChatOllamanode, I I define the following settings:
| Setting | Value |
| Base URL * | http://localhost:11434 |
| Model Name * | codellama:13b-instruct |
| Temperature | 0.7 |
- I connect the
ChatOllamaOutput to theChat Model *Input of theConversation Chainby clicking-and-dragging a connector from one node to the other node:
I drag the
Add Nodes > Memory > Buffer Memoryonto the canvas.I connect the
Buffer MemoryOutput to theMemory *Input of theConversation Chain:
I save the changes to the
Local Chatbot.On the right of the UI, I click the round, purple Chat icon to send the "Tell me a joke" message to the LLM:
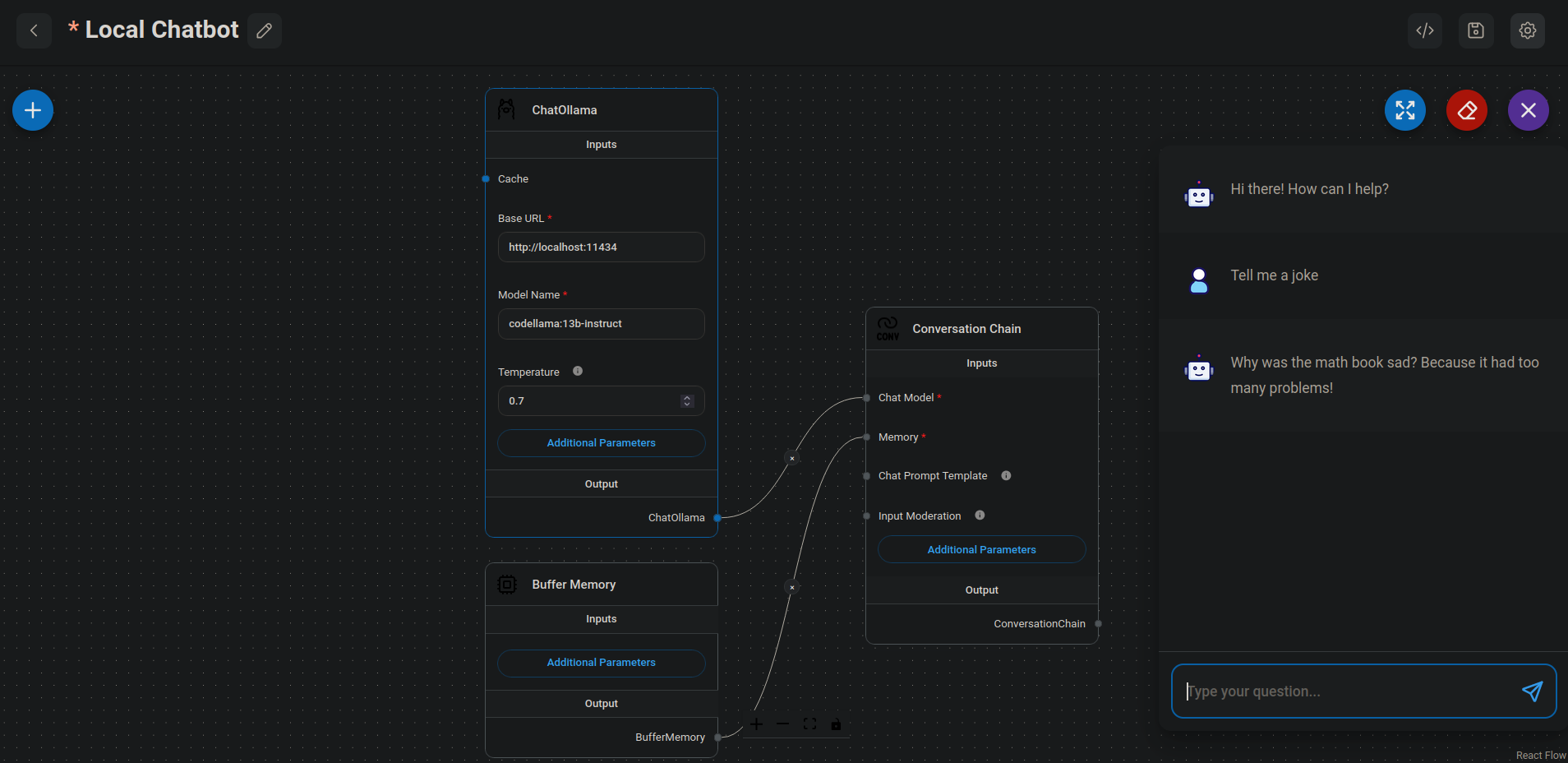
- At the top-left of the UI, I click the left-pointing arrow to return to the Main Menu.
Example 2: Local RAG Chatbot.
From the Main Menu ( on the left of the UI), I click
Chatflows.In the
Untitled chatflowcanvas, I click theSavebutton (that looks like a floppy disk.)I rename the canvas
Local RAG Chatbot.
NOTE: Remember, the
Add Nodesbutton on the left is round, blue, and has a (+) symbol.
I drag the
Add Nodes > Chains > Conversational Retrieval QA Chainnode to the canvas.I drag the
Add Nodes > Chat Models > ChatOllamanode to the canvas.I connect the
ChatOllamanode Output to theConversational Retrieval QA ChainnodeChat ModelInput.In the
ChatOllamanode, I define the following settings:
| Setting | Value |
| Base URL * | http://localhost:11434 |
| Model Name * | codellama:13b-instruct |
| Temperature | 0.4 |
I drag the
Add Nodes > Vector Stores > In-Memory Vector Storenode to the canvas.I connect the
In-Memory Vector Storenode Output to theConversational Retrieval QA ChainnodeVector Store RetrieverInput.I drag the
Add Nodes > Embeddings > Ollama Embeddingsnode to the canvas.I connect the
Ollama Embeddingsnode Output to theIn-Memory Vector StorenodeEmbeddingsInput.In the
Ollama Embeddingsnode, I define the following settings:
| Setting | Value |
| Base URL * | http://localhost:11434 |
| Model Name * | codellama:13b-instruct |
| Additional Parameters | Number of GPU: 1 |
| Use MMap: On |
I drag the
Add Nodes > Document Loaders > Cheerio Web Scrapernode to the canvas.I connect the
Cheerio Web ScraperOutput to theIn-Memory Vector StorenodeDocumentInput.In the
Cheerio Web Scrapernode, I define the following settings:
| Setting | Value |
| URL * | https://www.langchain.com/langsmith |
I save the changes to the
Local RAG Chatbot.I insert data from the
Cheerio Web Scraperinto theIn-Memory Vector Storeby clicking the green DB button at the top-right of the screen.Once completed, I can chat with the results, e.g. "What is LangSmith?"
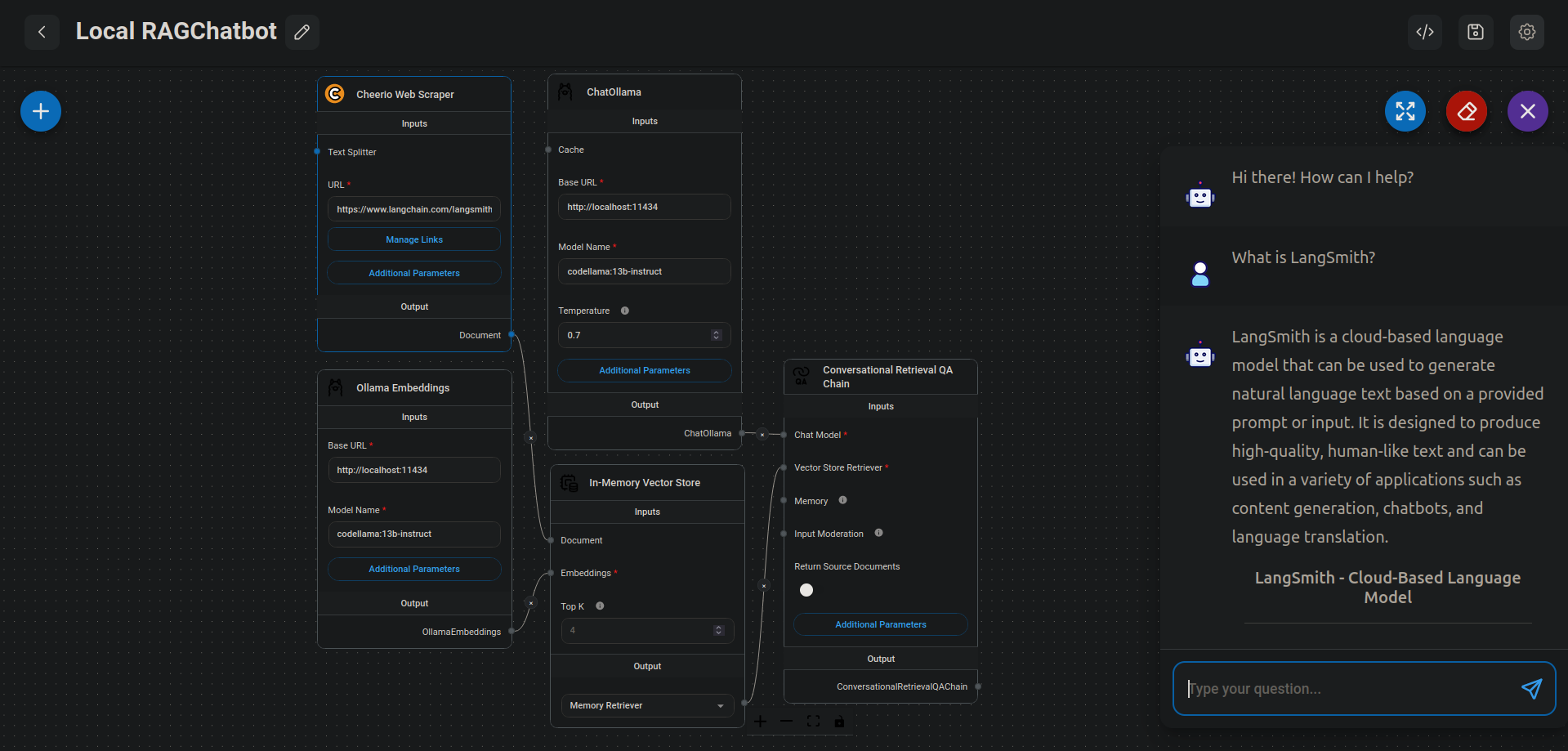
The Results.
Using Flowise with local LLMs offers a robust and flexible environment for developing advanced, AI-powered applications. By integrating tools like Ollama, and various Flowise components, I can create efficient, cost-effective, local chatbots and AI agents capable of performing a wide range of tasks. This setup enhances data privacy, operational security, and allows for extensive customization to meet specific needs. Whether for business processes, customer service, or personal projects, the ability to build and manage local AI models with Flowise opens up new possibilities for innovation and efficiency in AI application development.
In Conclusion.
I discovered how Flowise can transform my AI development process and revolutionize my AI workflows with local LLMs.
In today's tech-driven world, efficiency and customization in AI are crucial. That's why I'm excited to share my journey using Flowise with local LLMs, a robust platform that simplifies the creation of AI-powered applications.
With Flowise, I've built powerful local chatbots and AI agents that are not only cost-effective but also prioritize data privacy and operational security. This setup is perfect for businesses and individual developers looking to innovate, while also maintaining control over their data.
From integrating tools like Ollama to utilizing components like Chatflows and Memory Buffers, Flowise has allowed me to seamlessly transition from testing to production, ensuring my AI solutions are both dynamic and scalable.
Have you considered using local LLMs for your AI projects? What has been your biggest challenge in AI development?
Until next time: Be safe, be kind, be awesome.
#Flowise #AI #AIdevelopment #AIWorkflow #AIApplications #LocalLLMs #Chatbots #MachineLearning #TechInnovation #DataPrivacy #OperationalSecurity
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Brian King directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Brian King
Brian King
Thank you for reading this post. My name is Brian and I'm a developer from New Zealand. I've been interested in computers since the early 1990s. My first language was QBASIC. (Things have changed since the days of MS-DOS.) I am the managing director of a one-man startup called Digital Core (NZ) Limited. I have accepted the "12 Startups in 12 Months" challenge so that DigitalCore will have income-generating products by April 2024. This blog will follow the "12 Startups" project during its design, development, and deployment, cover the Agile principles and the DevOps philosophy that is used by the "12 Startups" project, and delve into the world of AI, machine learning, deep learning, prompt engineering, and large language models. I hope you enjoyed this post and, if you did, I encourage you to explore some others I've written. And remember: The best technologies bring people together.