Understanding VPC: Your Private Space in the Cloud
 TechDevotion
TechDevotion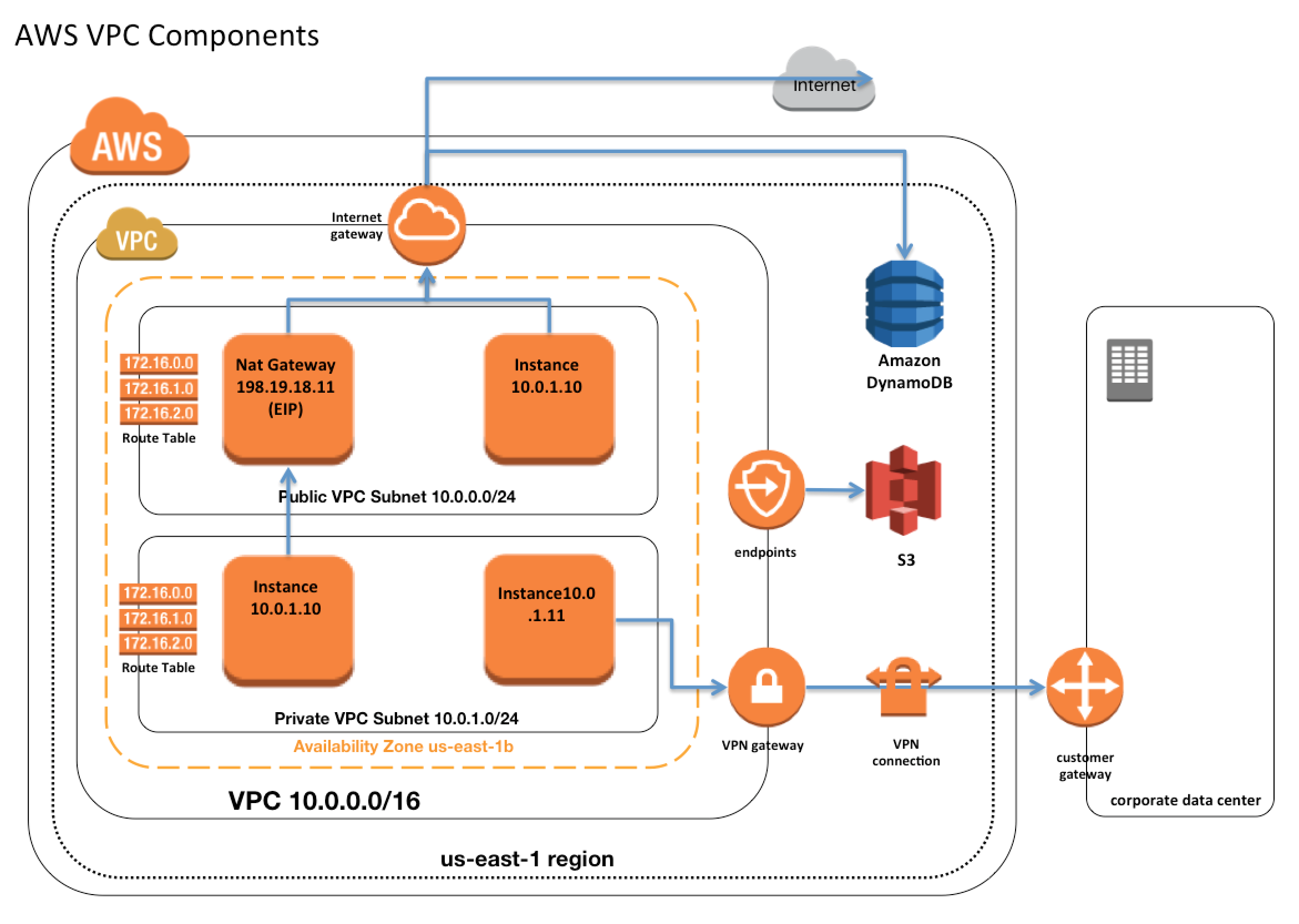
Welcome back, amazing people!
If you read my "Beginner's Guide to Cloud Computing" blog, then you'll catch on quickly.
Let's revisit that rental home analogy: imagine a big building with lots of flats for rent. The building represents the public cloud, like AWS, Azure, GCP, or IBM. Your flat in this building is your VPC (Virtual Private Cloud). Just as you can sing, dance, and do whatever you want in your flat, the VPC lets you control your own space in the cloud.
Now, let's get a bit more technical: A VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) is a fundamental component of AWS. It allows you to create a logically isolated private network within the AWS cloud. With VPC, you can customize your network environment, choosing IP address ranges, creating subnets, configuring route tables, and setting up network gateways. Crucially, you can also connect your VPC to your on-premises data center via a VPN connection, enhancing your overall security on the public cloud.
Key Components of a VPC:
Subnet
Private Subnet
Public Subnet
Route Table
NAT Gateway
Internet Gateway
Network ACLs (Access Control Lists)
Security Groups
Why Use a VPC?
Customization: Tailor your network setup to fit your specific needs. Security: Enhance security by isolating your resources from other users in the cloud. Connectivity: Seamlessly connect your on-premises data center with your VPC. Flexibility: Create multiple subnets for better organization and security.
With a VPC, you have full control over your cloud environment, just like you have control over your own flat. This isolation and control are crucial for securely managing your resources and ensuring smooth operations.
Stay tuned for more insights and tips!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from TechDevotion directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by