ELASTIC COMPUTE CLOUD ( EC2 ) Part - I
 N Chandra Prakash Reddy
N Chandra Prakash ReddyTable of contents

Introduction
Cloud computing resources that are scalable are available through Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud).
Amazon EC2 allows you to launch as many or as few virtual servers as needed.
Storage management, networking, and security are all adjustable.
Instances can be dynamically scaled up or down with Amazon EC2.
There are two types of storage options: instance store and elastic block store (EBS).
Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) are preconfigured templates that are provided.
Two high I/O instances are included in the maximum 20 instances per region that are restricted to new EC2 accounts by default.
There are four sizes for EC2 instances: Nano, Small, Medium, and Large.
Types of EC2 instances
General Purpose
Suitable for a variety of applications, general-purpose instances provide a balanced combination of memory, networking, and processing capability.
There are two series of general-purpose instances.
M series : M4, M5, M5a, M5n, M5zn, M6a, M6g, M6i, M6in, Mac, M7a, M7g, M7i, M7i-flex
T series : T2 (free tier eligible), T3, T3a, T4g
Each series here indicates different things like
M4 : Older generation, balanced compute, memory, and networking.
M5 : Latest generation, optimized for general-purpose workloads.
M5a : M5 instances powered by AMD processors.
M5n : M5 instances with enhanced networking capabilities.
M6a : M6 instances powered by 3rd generation AMD processors.
M6g : M6 instances powered by AWS Graviton2 processors, with additional memory optimizations.
M6i : M6 instance powered by 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors.
M6in : M6 instances powered by 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors and also for network-intensive workloads.
Mac : Mac instances designed for macOS workloads.
M7a : M7a instance powered by 4th Generation AMD EPYC processors and also delivered upto to 50% high performance compared to M6a instance.
M7g : M7g instance powered by Arm-based AWS Graviton3 processors.
M7i : M7i instance powered by 4th Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors and deliver 15% better price performance than M6i instances.
M7i-flex : M7i instance powered by 4th Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors with flexible configurations.
As for the same T series , each series denotes various aspects like, generations , architecture, network.
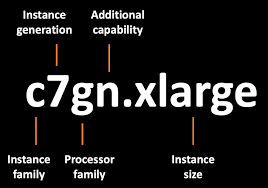
- Some instance types support 'arm based architecture' and some are '64bit (x86) architecture'. I'm not included some instance type like 'A series'. It's only support arm based architecture. So, choose carefully based on our requirements.
Compute Optimized
High-performance CPUs are advantageous for applications that strongly depend on processing power, and compute-optimized instances are suitable for them.
Compute-optimized instances are only available in the C series.
- C Series : C4, C5, C5a, C5n, C6a, C6i, C6in, C6g, C6gn, C7a, C7g, C7gn, C7i, C7i-flex
As you have read above instance types series i.e., M Series, You know what does 'a', 'n', 'i', 'in', 'g', 'gn' and flex denotes.
Memory Optimized
Memory-optimized instances are made to run quickly when processing vast amounts of data that are kept in memory.
There are four different series of memory-optimized instances.
R Series : R4, R5, R5a, R5n, R5b, R6a, R6g, R6i, R6in, R7a, R7g, R7i, R7iz, R8g
X Series : X1, X1e, X2iedn, X2iezn, X2idn, X2gd
High Memory Series : like u-3tb1.56xlarge, u-6tb1.56xlarge, u-6tb1.112xlarge, u-9tb1.112xlarge etc.
Z Series : z1d
Here, few series denotes various aspects like
R5b instances 3x EBS performance compared to R5 instances of the same size.
R7iz instances are equipped with 4th Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors, making them perfect for tasks that demand a lot of CPU power and memory.
X1e instances are specifically designed for big databases, in-memory databases, and other memory-heavy business applications like enterprise level.
z1d instances offer high compute capacity and memory, with high-frequency variants delivering up to 4.0 GHz, the fastest in the cloud.
Storage Optimized
Workloads requiring high-throughput read and write access to large datasets on local storage are supported by storage-optimized instances.
These instances are designed to give applications tens of thousands of random, low-latency I/O operations per second (IOPS).
Storage optimized instances come in three different series.
H Series : H1
D Series : D2, D3, D3en
I Series : I3, I3en, I4g, I4i, Im4gn, Is4gen
Accelerated Computing
Hardware co-processors or accelerators are used in situations of accelerated computing instances.
They perform more effectively than CPUs alone on tasks like data pattern matching, graphics processing, and floating-point calculations.
Accelerated Computing instances come in Seven different series.
P Series : P2, P3, P4, P5
G Series : G3, G4ad, G4dn, G5, G5g, G6
Trn Series : Trn1
Inf Series : Inf1, Inf2
DL Series : DL1, DL2q
F Series : F1 ( Field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs)
VT Series : VT1 ( Video Transcoding )
Here, few series denotes various aspects like
Trn1 instance with AWS Trainium chips are designed for high-performance deep learning training, offering up to 50% cost savings.
- AWS created the machine learning (ML) chip known as AWS Trainium specifically for deep learning (DL) training of models with more than 100 billion parameters.
Inf2 instance powered by AWS Inferentia2 offering 3x compute, 4x memory, 4x throughput, and 10x lower latency than Inf1.
- For deep learning (DL) and generative AI inference applications, AWS inferentia offer the best performance at the lowest cost on Amazon EC2.
DL2q instance powered by Qualcomm AI 100, cost-efficiently deploy and validate deep learning ( DL ) workloads.
HPC Optimized
On AWS, HPC instances are made to perform at the best possible cost.
Ideal for workloads involving deep learning and big, complex models.
Designed to handle large-scale high-performance computing (HPC) workloads.
High-performance CPUs installed for demanding use.
Below are the series that HPC Optimized instance have
Hpc6a
Hpc6id
Hpc7a
Hpc7g
Here, Hpc means High Performance Computing ( HPC )
EC2 Purchasing options
AWS EC2 instances offer six purchasing options.
On-Demand Instances
Virtual servers available in AWS at a set hourly price are called AWS On-Demand instances.
Suggested for continuous or unpredictable workloads that cannot be interrupted.
Ideal for EC2 application development and testing.
When using On-Demand instances, you only pay for the EC2 instances that you use.
By eliminating the need for hardware planning and maintenance, On-Demand instances turn fixed expenses into unpredictable expenses.
For Linux instances, pricing is calculated per second; for other instance types, pricing is calculated per full hour.
Saving Plans
Flexible pricing is provided by Savings Plans, which can reduce AWS consumption costs by up to 72% on computing workloads.
Compute Savings Plans offer discounted costs for using AWS Lambda, AWS Fargate, and Amazon EC2, regardless of the type, size, tenancy, or AWS Region of the instance.
For Amazon SageMaker instance usage, SageMaker Savings Plans provide reduced costs irrespective of the kind, size, component, or AWS Region of the instance.
Savings Plans, which demand a commitment to a certain amount of compute power usage for one or three years, offer savings above and above On-Demand rates.
Reserved Instances
When compared to On-Demand pricing, Amazon EC2 Reserved Instances (RIs) offer savings of up to 75%.
In addition, RIs offer a capacity reserve when used within a designated availability zone.
When compared to On-Demand pricing, Reserved Instances enable you to reserve a Database instance for one or three years, saving a significant amount of money.
Spot Instances
Up to 90% less than On-Demand rates are available for unused capacity in the AWS cloud with Amazon EC2 Spot Instances.
Suitable for various test and development workloads.
Options to let EC2 know when to reclaim capacity and to hibernate, stop, or terminate Spot Instances with a two-minute warning.
Spot Instances can save you up to 90% over On-Demand costs, but AWS may interrupt them.
To the extent of your spot limit for each region, request Spot Instances.
Using the EC2 console, check the status of a Spot request by message and status code.
While stopping clears RAM, hibernation maintains RAM data.
Hibernate enables instances to easily pause and resume in response to disruptions.
Dedicated Hosts
A physical server that is only yours to utilize is called an Amazon EC2 dedicated host.
Dedicated hosts use pre-existing server-bound software licenses to help save money and meet regulations.
To save money, purchase a dedicated physical host for your instances and bring your current software licenses.
Over time, maintain consistent deployment by having visibility and control over where instances are placed on physical servers.
Dedicated hosts satisfy regulation requirements and allow the usage of current server-bound software licenses.
Using the XEN Hypervisor, instances on a dedicated host are identical to those on regular EC2 instances.
There is only one instance size and type such as C3.XLARGE that each dedicated host supports.
On dedicated hosts, you can only launch AWS Marketplace AMIs, BYOL, and Amazon Linux.
Dedicated Instance
In a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), dedicated instances operate on hardware that is assigned to just one customer.
At the host hardware level, they are physically separated from instances that are part of other AWS accounts.
Even though dedicated instances are separated, they could share hardware with non-dedicated instances from the same account.
Cover the cost of dedicated instances Reserved Instances can save you up to 70% on-demand, and Spot Instances can save you up to 90%.
Capacity Reservations
You can reserve compute capacity for Amazon EC2 instances in a particular Availability Zone by using capacity reservations.
Different use cases are served by two different types of capacity reservations.
Conclusion
Instance Flexibility : Launch and control virtual servers with networking, storage, and security configurations that you may customize.
Instance Selection : Based on your unique requirements, select the instance type and size that are appropriate.
Dynamic Scaling : Easily adjust instances size to suit your needs.
Storage Options : Depending on how much storage you need, pick between Elastic Block Store (EBS) and instance store.
Purchasing Options : Take advantage of a variety of buying options, each providing special chances for cost savings: On-Demand, Savings Plans, Reserved Instances, Spot Instances, Dedicated Hosts, and Dedicated Instances.
References
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from N Chandra Prakash Reddy directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

N Chandra Prakash Reddy
N Chandra Prakash Reddy
-> I'm an enthusiastic DevOps professional with over 3+ years of hands-on expertise in cloud infrastructure management and orchestrating the deployment of applications which are ready for production. -> Excellent problem-solving skills and a proactive learner, staying updated with the latest trends in DevOps and Cloud Computing. 𝐆𝐞𝐭 𝐢𝐧 𝐓𝐨𝐮𝐜𝐡 -> 𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐜𝐭 𝐨𝐧 𝐋𝐢𝐧𝐤𝐞𝐝𝐢𝐧 : If you're interested in engaging in technical discussions or connecting professionally, please feel free to connect with me on LinkedIn. -> 𝐄𝐦𝐚𝐢𝐥 : ncpr.0912@gmail.com