Understanding the Five Stages of the Design Thinking Process
 Subashini S
Subashini S
Design Thinking: A User-Centered Approach
The design thinking approach emphasizes a hands-on, user-centric methodology for solving complex problems. It addresses unclear or undefined problems by understanding people's needs, defining the problem, brainstorming creative solutions, prototyping, and testing the ideas to identify the optimal solution.
Importance of Design Thinking in Problem-Solving
Design thinking has emerged as a critical methodology in problem-solving, particularly for tackling complex and ambiguous challenges. Its importance can be attributed to several key aspects:
User-Focused
Design thinking places the needs and experiences of users at the forefront of the problem-solving process. This user-centric focus ensures that solutions are designed to meet the real needs of people, leading to more relevant and effective outcomes.
Iterative Process
The iterative nature of design thinking involves continuous prototyping, testing, and refinement. This cycle allows for the early identification and resolution of issues, ensuring that solutions are continually improved and validated through real-world feedback.
Collaborative Approach
Design thinking promotes collaboration across diverse teams, bringing together different perspectives and expertise. This collaborative nature enhances creativity and ensures a more holistic approach to problem-solving, as insights from various disciplines contribute to more robust solutions.
Works Within Constraints
Design thinking embraces constraints, viewing them as opportunities rather than obstacles. Working within specific limits can inspire creative solutions and innovative problem-solving. Constraints help focus efforts and encourage thinking outside the box to find effective and efficient ways to overcome challenges.
Problem Framing
One of the first steps in design thinking is problem framing, which involves defining and understanding the problem from the user's perspective to ensure teams address the right issues and develop relevant, effective solutions.
Overview of the Five Stage
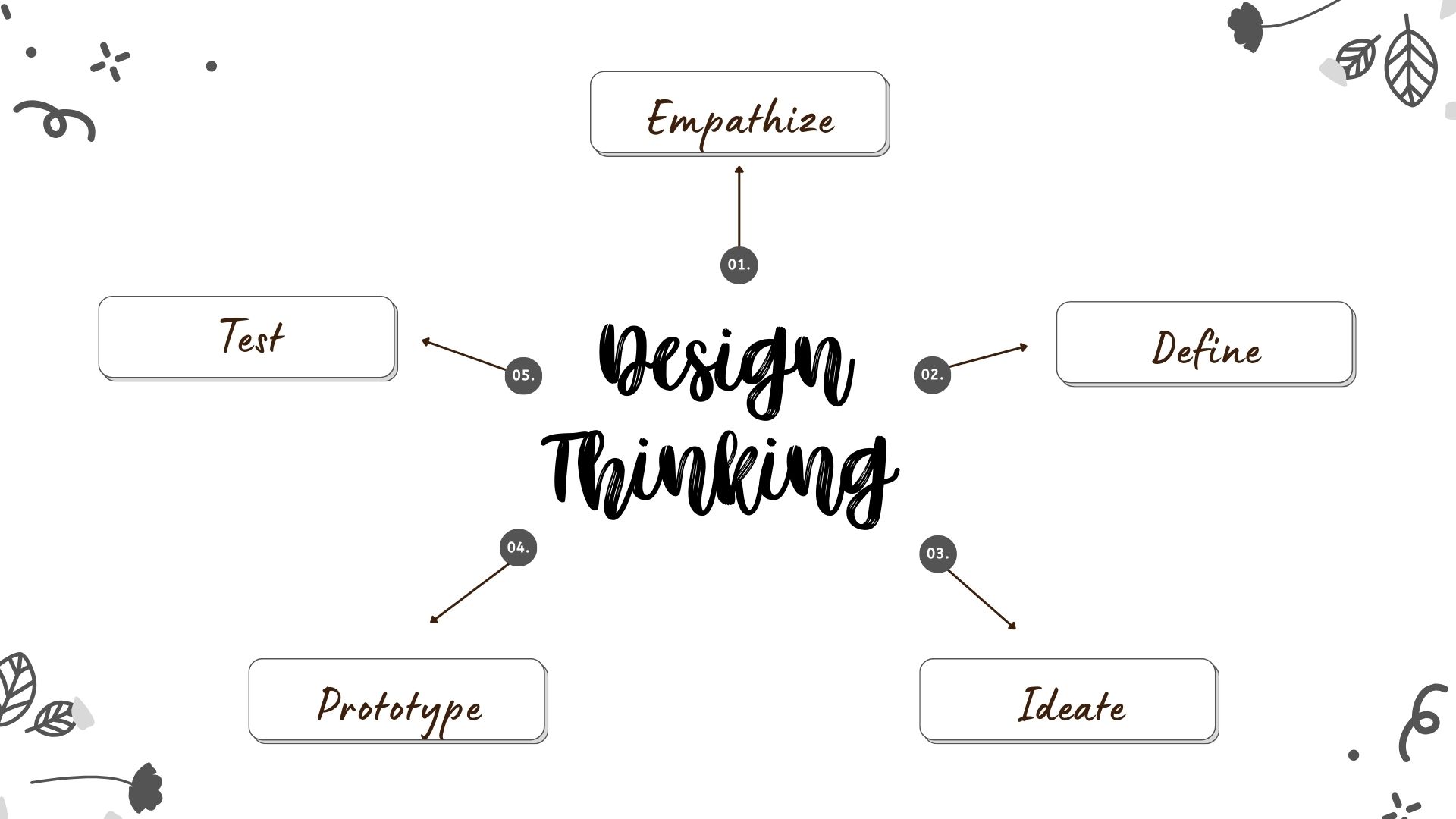
Empathize
This is the initial stage where you seek to understand the problem deeply from the perspective of the people experiencing it. Here's how you can gain an empathetic understanding:
Connect with People: Engage directly with the individuals or communities facing the challenge you aim to solve. Listen actively to their stories, concerns, and experiences.
Ask Questions: Pose open-ended questions to encourage them to share their thoughts, feelings, and experiences related to the problem. Avoid leading questions that might bias their responses.
Deep Insights: Dive deeper into their responses to uncover underlying emotions, motivations, and pain points. Look for patterns and contradictions to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Perspective-taking: Put yourself in their shoes to understand their needs better. This involves not just understanding what they say, but also their unspoken needs and desires.
Define
This stage involves refining your understanding of the problem by analyzing insights gathered during the empathize stage. Here's how you can clarify and redefine the problem into a concise statement, guiding further problem-solving efforts:
Define the Problem: Utilize the information collected during the empathize stage to pinpoint the primary issue.
Reframe the Problem: Clarify and redefine the problem concisely, guiding further problem-solving efforts.
Generate Ideas: Use the defined problem to inspire creative thinking and develop potential solutions.
Establish Future Functions: Plan the features and elements essential for effectively addressing the identified problem.
Ideate
In this stage, you focus on generating a wide range of potential solutions to the defined problem. Embrace creativity and collaboration to explore various approaches and perspectives. Here’s how to foster innovative thinking and develop diverse solutions:
Brainstorming Sessions: Engage in brainstorming sessions to generate many ideas from different perspectives. Write down every idea that comes to mind, no matter how unconventional. Utilize sticky notes to jot down and organize ideas and concepts, building an information architecture and user flow.
Explore Various Approaches: Consider various methods and strategies for solving the problem to expand your thinking and promote an environment that supports creative thinking.
Foster Collaboration: Foster a collaborative atmosphere where team members can inspire each other with innovative ideas.
Refine and Iterate: Continuously refine and iterate on ideas based on feedback and insights gained during the ideation process.
Prototype
In this stage, you validate your ideas by constructing low-fidelity wireframes and prototypes to explore the best solutions for the identified problems. Here's how to effectively create and test your prototypes:
Create Low-Fidelity Wireframes: Start by constructing low-fidelity wireframes using pencil sketches or digital tools to visualize your ideas.
Second Round of Prototyping: After the initial wireframes, proceed to a more detailed second round of prototyping to refine your solutions.
Experimental Approach: Treat the prototype stage as an experimental phase, aiming to find the best solutions for the problems identified in earlier stages.
Implement Solutions: Integrate individual solutions into the prototype to see how they function.
Test
In this stage, you evaluate your prototype with real users to ensure it meets their needs and improves their experiences. Accept, enhance, or reevaluate solutions as needed, and be ready to reject those that don't improve the user experience. Here’s how to conduct effective testing:
User Needs Assessment: Ask yourself if the solution meets users' needs and enhances their experiences.
Collect Feedback: Evaluate the prototype with real users to gather valuable feedback.
Goal Verification: Verify if the prototype achieves your initial goals and solves the identified problem.
Adjust Based on Feedback: Revise the prototype according to the feedback received from users.
Continuous Improvement: Test and refine the prototype until it effectively meets users' needs. Aim to create a final product that is user-friendly and solves the problem.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Subashini S directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
