Understanding the Decentralized Digital Ledger in the Web3 World
 Lokesh Jha
Lokesh JhaTable of contents
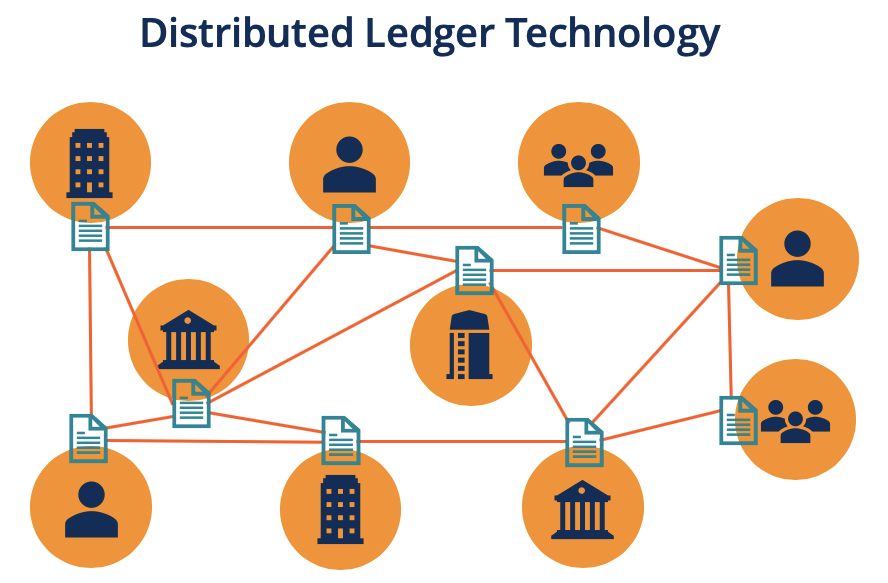
In the rapidly evolving landscape of Web3, one term that frequently comes up is "decentralized digital ledger." This fundamental concept underpins many of the innovations driving the new wave of internet technologies. But what exactly is a decentralized digital ledger, and how does it function in the Web3 ecosystem? Let's explore this concept with a real-world example to illustrate its practical implications.
What is a Decentralized Digital Ledger?
A decentralized digital ledger is a type of database that is distributed across multiple nodes or computers, rather than being stored on a central server. Each participant in the network has a copy of the entire ledger, and updates to the ledger are agreed upon through a consensus mechanism. This decentralization ensures transparency, security, and resilience, as no single entity controls the entire system, and it is inherently resistant to tampering.
Key Features of Decentralized Digital Ledgers
Distributed Architecture: The ledger is maintained across a network of computers (nodes), each holding an identical copy of the ledger.
Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This is achieved through cryptographic techniques.
Transparency: All participants in the network can view the entire ledger, promoting openness and trust.
Security: The decentralized nature and cryptographic methods make it difficult for unauthorized parties to manipulate the ledger.
Real-World Example: Supply Chain Management
To better understand the concept of a decentralized digital ledger, let's consider its application in supply chain management.
Scenario: Tracking Coffee Beans from Farm to Cup
Imagine a coffee company that wants to ensure the quality and authenticity of its coffee beans, from the farm where they are grown to the consumer's cup. Traditionally, this process involves multiple intermediaries, each maintaining their own records. This can lead to inefficiencies, increased costs, and potential for fraud or errors.
Implementation with a Decentralized Digital Ledger
Step 1: Initial Record Creation
Farmer: The coffee journey begins at a farm in Colombia. The farmer harvests the coffee beans and records the details on a blockchain-based ledger, including the date of harvest, type of beans, and farm location.
Blockchain Entry: This entry is timestamped and stored across all nodes in the network, ensuring it cannot be altered.
Step 2: Transportation and Processing
Transporter: The beans are transported to a processing plant. Each stage of transportation is logged into the ledger, recording details like transit times and conditions.
Processor: At the processing plant, the beans are roasted and packaged. These actions are also recorded on the blockchain, including details of the roasting process and quality checks.
Step 3: Distribution and Retail
Distributor: The processed coffee beans are then shipped to various retailers. Each shipment is logged, detailing the quantity and destination.
Retailer: Finally, the retailer records the arrival of the coffee beans and their availability for sale.
Step 4: Consumer Access
- Consumer: When a consumer purchases the coffee, they can scan a QR code on the packaging to access the entire journey of the coffee beans, from farm to cup, as recorded on the blockchain.
Benefits of Using a Decentralized Digital Ledger
Enhanced Transparency: Consumers can trace the origin and journey of their coffee, building trust in the product.
Improved Efficiency: Eliminating intermediaries and reducing paperwork streamlines the supply chain, lowering costs and speeding up processes.
Increased Security: The immutable nature of the ledger prevents tampering and fraud, ensuring the integrity of the product's history.
Real-Time Updates: All participants have access to the latest information, enabling better decision-making and coordination.
Conclusion
A decentralized digital ledger transforms traditional systems by providing a transparent, secure, and efficient way to record and track transactions. In the context of Web3, this technology empowers industries to enhance their operations and build trust with consumers. The example of tracking coffee beans from farm to cup illustrates how decentralized ledgers can revolutionize supply chain management, ensuring authenticity and quality at every step.
As we continue to explore and innovate within the Web3 space, the applications of decentralized digital ledgers will undoubtedly expand, unlocking new possibilities and driving us towards a more transparent and interconnected future.
Connect on https://x.com/Lokesh1jha && https://www.linkedin.com/in/lokesh-jha-088549136/
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Lokesh Jha directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Lokesh Jha
Lokesh Jha
I am a senior software developer and technical writer who loves to learn new things. I recently started writing articles about what I've learned so that others in the community can gain the same knowledge. I primarily work with Node.js, TypeScript, and JavaScript, but I also have past experience with Java and C++. Currently, I'm learning Go and may explore Web3 in the future.