Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): An Essential Guide
 Vikram
Vikram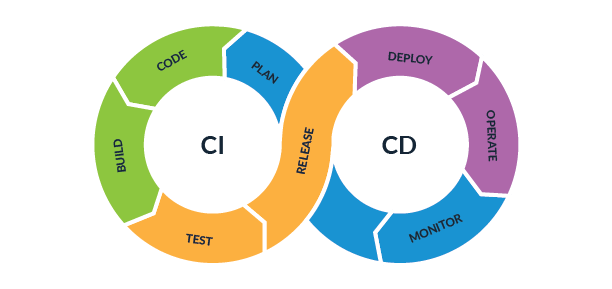
Introduction
In the world of modern software development, speed, efficiency, and reliability are paramount. Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) are practices that address these needs by streamlining the software development and deployment processes. This article will delve into the concepts of CI/CD, their benefits, tools, and best practices.
What is CI/CD?
Continuous Integration (CI) is a software development practice where developers frequently merge their code changes into a central repository. Automated builds and tests are run on each merge to ensure the new code integrates well with the existing codebase and that no new bugs are introduced.
Continuous Delivery (CD) extends CI by automatically deploying all code changes to a staging or production environment after the build stage. This ensures that the code is always in a deployable state and can be released at any time.
Together, CI/CD automates the entire software release process, from code integration to deployment, enabling faster and more reliable releases.
Benefits of CI/CD
Faster Time to Market:
- Automated build and test processes reduce the time taken to detect and fix bugs, allowing new features and updates to be released more quickly.
Improved Code Quality:
- Frequent integration and testing ensure that code quality is consistently high. Automated tests catch issues early, reducing the likelihood of bugs in production.
Reduced Manual Effort:
- Automation of repetitive tasks like building, testing, and deploying frees up developers to focus on writing code and developing new features.
Enhanced Collaboration:
- CI/CD practices encourage collaboration among team members, as everyone integrates their code frequently and works with a shared codebase.
Early Detection of Bugs:
- Automated tests run on every code change help in catching bugs early in the development process, making them easier and cheaper to fix.
CI/CD Workflow
Code Commit:
- Developers write code and commit it to a version control system like Git.
Build:
- A CI server (e.g., Jenkins, Travis CI) detects the code commit and triggers a build process to compile the code and check for syntax errors.
Automated Testing:
- After the build, automated tests (unit tests, integration tests, etc.) are run to validate the new code changes.
Artifact Creation:
- If the tests pass, the CI server packages the application into deployable artifacts (e.g., Docker images, JAR files).
Deployment:
- The artifacts are automatically deployed to staging environments for further testing. In a CD pipeline, they can be automatically or manually promoted to production.
Monitoring:
- After deployment, the application is monitored for performance, errors, and other metrics to ensure it runs smoothly.
CI/CD Tools
There are numerous tools available to implement CI/CD pipelines. Some of the popular ones include:
Jenkins:
- An open-source automation server that supports building, deploying, and automating any project.
GitLab CI/CD:
- Integrated with GitLab, it provides a complete CI/CD solution, including version control, CI/CD, and monitoring.
Travis CI:
- A hosted CI service for open-source and private projects that integrates well with GitHub.
CircleCI:
- A CI/CD service that automates the software development process using continuous integration and delivery.
GitHub Actions:
- Integrated with GitHub, it allows automation of workflows, including CI/CD, directly in the repository.
Bamboo:
- A CI/CD server by Atlassian that integrates with other Atlassian products like Jira and Bitbucket.
Azure DevOps:
- A set of development tools by Microsoft that includes CI/CD pipelines, version control, and project management.
Best Practices for CI/CD
Version Control:
- Use a robust version control system like Git to manage your codebase and ensure all code changes are tracked.
Automated Testing:
- Write comprehensive automated tests to catch bugs early and ensure code quality. Include unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests.
Small, Frequent Commits:
- Encourage developers to commit small, frequent changes to make it easier to identify and fix issues.
Consistent Environments:
- Use containers or infrastructure as code (IaC) to ensure consistency between development, staging, and production environments.
Monitor and Log:
- Implement monitoring and logging to track the performance and health of your application in real-time.
Feedback Loops:
- Establish quick feedback loops to notify developers of build, test, or deployment failures promptly.
Security:
- Integrate security checks into your CI/CD pipeline to ensure code is secure and vulnerabilities are caught early.
Conclusion
CI/CD is a crucial practice in modern software development, enabling teams to deliver high-quality software faster and more reliably. By automating the integration, testing, and deployment processes, CI/CD allows developers to focus on what they do best—writing code and innovating. Implementing CI/CD requires the right tools, a collaborative culture, and adherence to best practices, but the payoff in terms of efficiency and code quality is well worth the effort. Embrace CI/CD to transform your development workflows and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced software landscape.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Vikram directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
