Day 31 Task: Launching your First Kubernetes Cluster with Nginx running
 Vaishnavi Shivde
Vaishnavi Shivde
What is minikube?
Minikube is a tool which quickly sets up a local Kubernetes cluster on macOS, Linux, and Windows. It can deploy as a VM, a container, or on bare-metal.
Minikube is a pared-down version of Kubernetes that gives you all the benefits of Kubernetes with a lot less effort.
This makes it an interesting option for users who are new to containers, and also for projects in the world of edge computing and the Internet of Things.
Features of minikube
Supports the latest Kubernetes release (+6 previous minor versions)
Cross-platform (Linux, macOS, Windows)
Deploy as a VM, a container, or on bare-metal
Multiple container runtimes (CRI-O, containerd, docker)
Direct API endpoint for blazing fast image load and build
Advanced features such as LoadBalancer, filesystem mounts, FeatureGates, and network policy
Addons for easily installed Kubernetes applications
Supports common CI environments
What is Pod?
Pods are the smallest deployable units of computing that you can create and manage in Kubernetes.
A Pod (as in a pod of whales or pea pod) is a group of one or more containers, with shared storage and network resources, and a specification for how to run the containers. A Pod's contents are always co-located and co-scheduled, and run in a shared context. A Pod models an application-specific "logical host": it contains one or more application containers which are relatively tightly coupled.
TASK-01
How to install minikube on AWS EC2 machines?
To install minikube on AWS EC2 machines, you need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Update System Packages
Update your package lists to make sure you are getting the latest version and dependencies.
sudo apt update
Step 2: Install Required Packages
Install some basic required packages.
sudo apt install -y curl wget apt-transport-https
Step 3: Install Docker
Minikube can run a Kubernetes cluster either in a VM or locally via Docker. This guide demonstrates the Docker method.
sudo apt install -y docker.io
Start and enable Docker.
sudo systemctl enable --now docker
Add current user to docker group (To use docker without root)
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER && newgrp docker
Now, logout (use exit command) and connect again.
Step 4: Install Minikube
First, download the Minikube binary using curl:
curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64
Make it executable and move it into your path:
chmod +x minikube
sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin/
Step 5: Install kubectl
Download kubectl, which is a Kubernetes command-line tool.
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
Make it executable and move it into your path:
chmod +x kubectl
sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/
Step 6: Start Minikube
Now, you can start Minikube with the following command:
minikube start --driver=docker
This command will start a single-node Kubernetes cluster inside a Docker container.
Step 7: Check Cluster Status
Check the cluster status with:
minikube status
Congratulations! You have successfully installed minikube on AWS EC2 machines and launched a local Kubernetes cluster.
TASK-02
How to create a pod on Kubernetes using minikube?
To create a pod on Kubernetes using minikube, you need to follow these steps
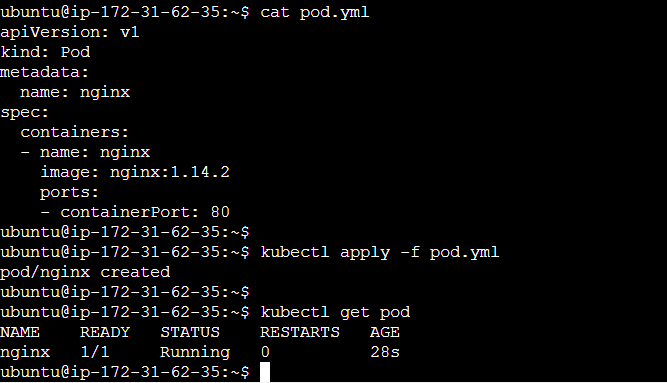
Create a YAML file that defines the pod specification.
Apply the YAML file to the cluster.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Vaishnavi Shivde directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
Vaishnavi Shivde
Vaishnavi Shivde
Aspiring DevOps Engineer | Linux | Git & Github | Shell Scripting | Docker | CI/CD Jenkins | Kubernetes | AWS | Terraform | JIRA | Python |