Day 68 - Scaling with Terraform 🚀
 Nilkanth Mistry
Nilkanth Mistry
Welcome to Day 68 of the 90DaysOfDevOpsChallenge! Yesterday, we learned how to create an AWS S3 Bucket with Terraform. Today, we will explore how to scale our infrastructure with Terraform. 🌟
Understanding Scaling
Scaling is the process of adding or removing resources to match the changing demands of your application. 📈 As your application grows, you need more resources to handle the increased load. When the load decreases, you can remove the extra resources to save costs. 💸
Terraform simplifies scaling by providing a declarative way to define your resources. 📝 You specify the number of resources you need, and Terraform handles the creation or destruction of those resources. Let's dive into scaling with Terraform! 🚀
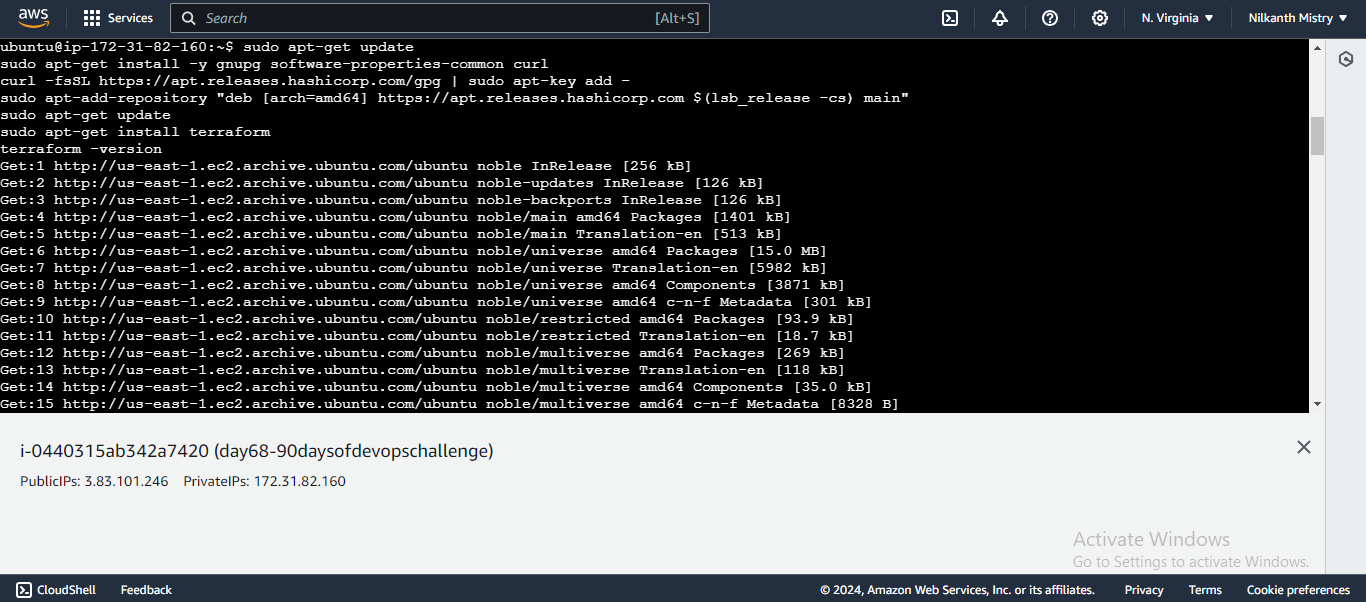
- Install Terraform on your local machine.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y gnupg software-properties-common curl
curl -fsSL https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-add-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(lsb_release -cs) main"
sudo apt-get update
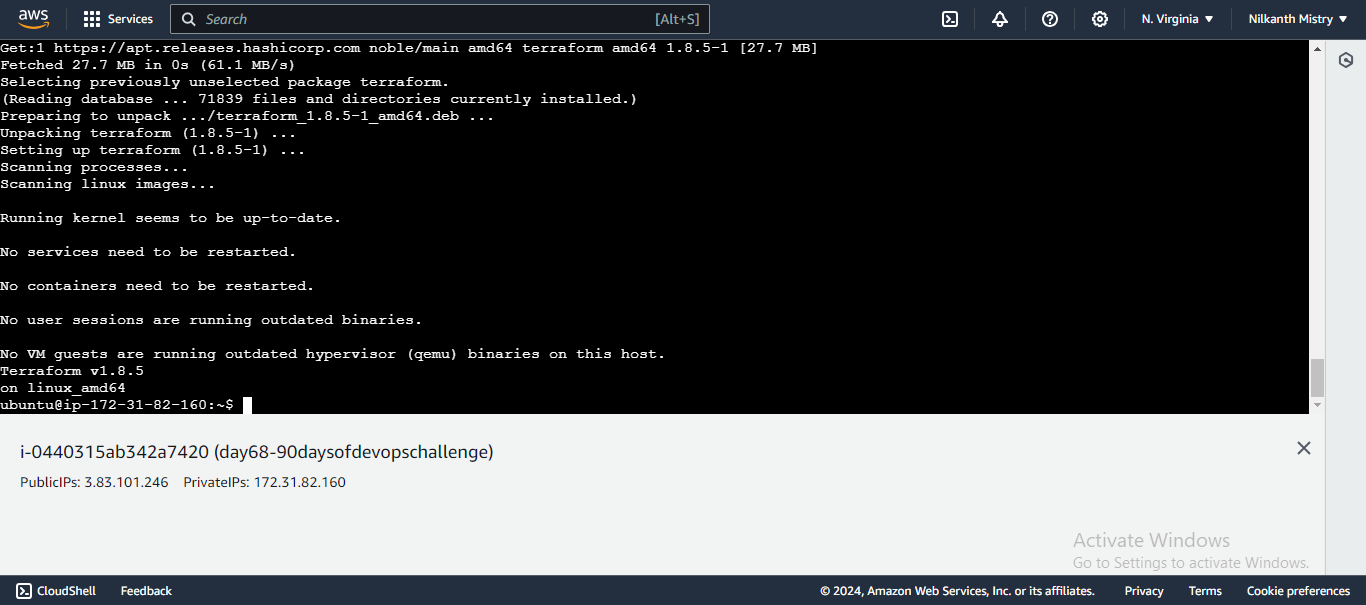
sudo apt-get install terraform
terraform -version
Install AWS CLI:
sudo apt-get update sudo snap install aws-cli --classic aws --version aws configureTask 1: Create an Auto Scaling Group 🔧
Auto Scaling Groups are used to automatically add or remove EC2 instances based on the current demand. Follow these steps to create an Auto Scaling Group:
📝 In your
main.tffile, add the following code to create an Auto Scaling Group:resource "aws_launch_configuration" "web_server_as" { image_id = "ami-02bf8ce06a8ed6092" instance_type = "t2.micro" security_groups = [aws_security_group.web_server.name] user_data = <<-EOF #!/bin/bash echo "<html><body><h1>You're doing really Great</h1></body></html>" > index.html nohup python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 & EOF } resource "aws_autoscaling_group" "web_server_asg" { name = "web-server-asg" launch_configuration = aws_launch_configuration.web_server_as.name min_size = 1 max_size = 3 desired_capacity = 2 health_check_type = "EC2" vpc_zone_identifier = [aws_subnet.public_subnet_2a.id, aws_subnet.public_subnet_2b.id] }🛠️ This Terraform code creates two AWS resources: an Auto Scaling Group and a launch configuration.
aws_launch_configuration: This resource creates a launch configuration for EC2 instances that we are going to deploy as part of our Auto Scaling Group.
image_id: The EC2 image ID to launch. 🖼️instance_type: The size of instance to launch. 📏security_groups: A list of associated security group IDs. 🛡️user_data: The script to be executed when an instance is launched, which starts a simple web server. 🌐
aws_autoscaling_group: Provides an Auto Scaling Group resource.
max_size: Maximum size of the Auto Scaling Group. 🚀min_size: Minimum size of the Auto Scaling Group. 📉desired_capacity: Number of Amazon EC2 instances that should be running in the group. 📈


🔧 This Terraform script creates an AWS VPC with two public subnets in different availability zones, an internet gateway, a public route table, and route table associations. It also creates an AWS security group that allows SSH and HTTP traffic, a launch configuration that uses user data to start a Python HTTP server on port 80, and an Auto Scaling Group with a minimum of 1, maximum of 3, and desired capacity of 2 instances, spread across the two subnets.
Run
terraform initto initialize the Terraform project. ⚙️Run
terraform planto see the execution plan. 📝




Run
terraform applyto create the Auto Scaling Group. 🚀terraform apply


🔍 Below, two new EC2 instances created as desired capacity set to 2:

✅ Launch configuration successfully created:

📊 Auto Scaling Group is created with group details:

🚀 Two instances are running in the Auto Scaling Group:

Task 2: Test Scaling 📈📉
Go to the AWS Management Console and select the Auto Scaling Groups service. 🌐
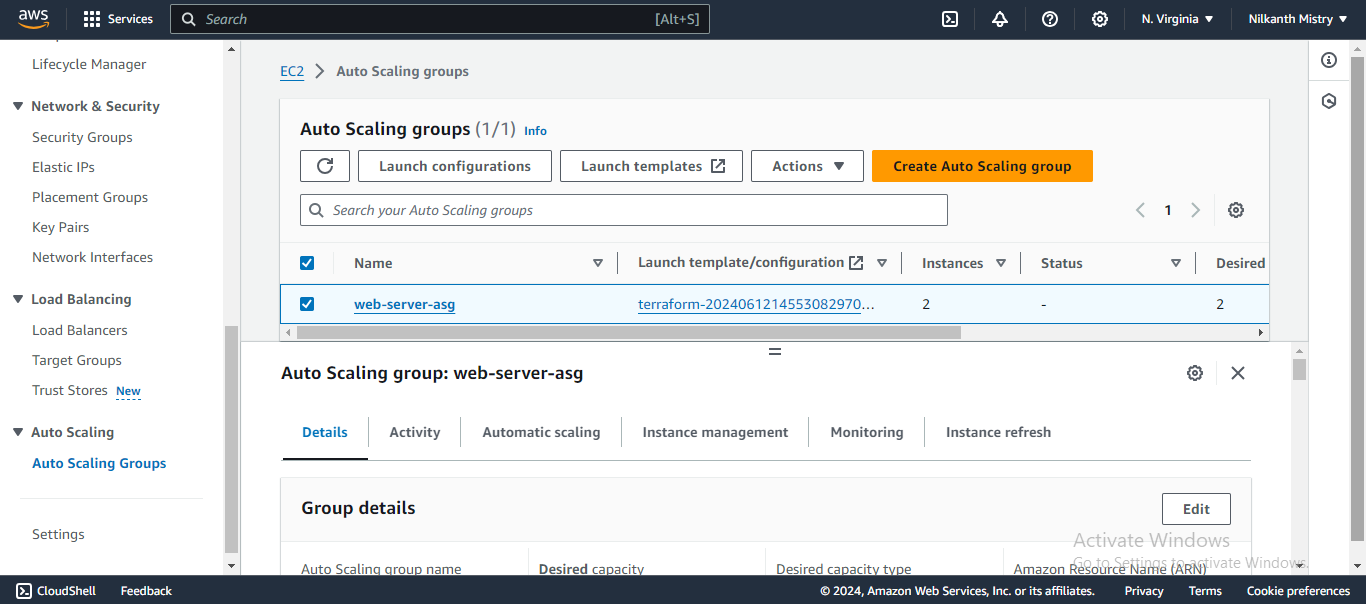
Select the Auto Scaling Group you just created and click on the "Edit" button. ✏️
Increase the "Desired Capacity" to 3 and click on the "Save" button. 💾
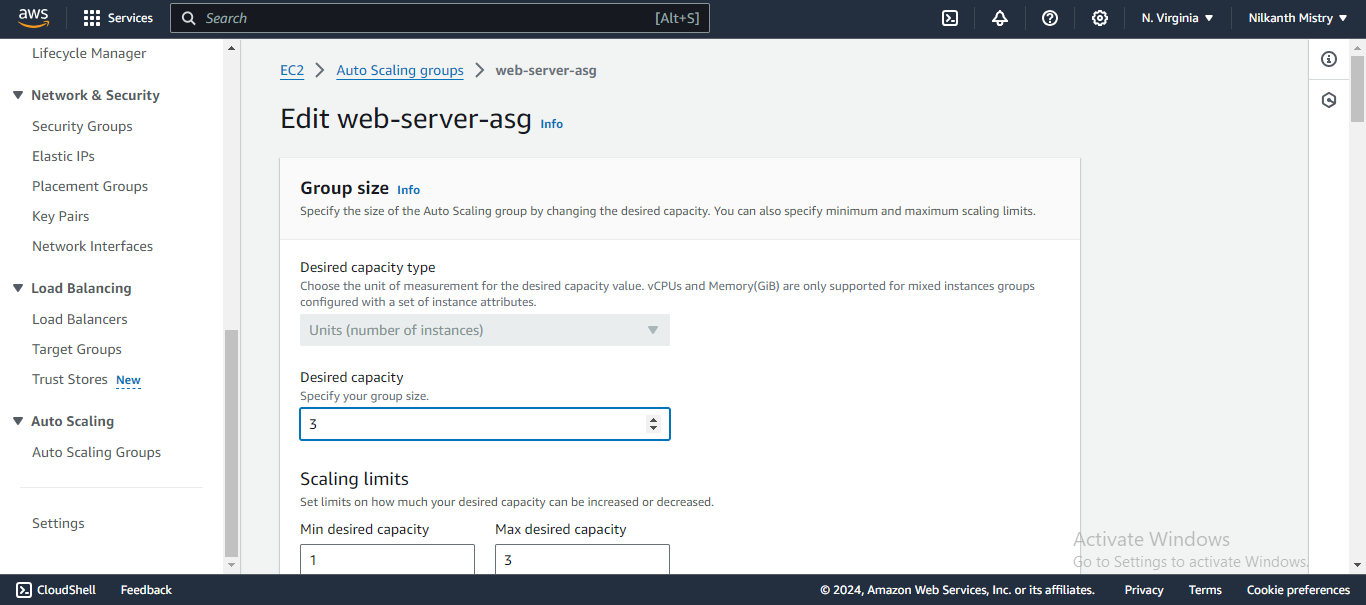
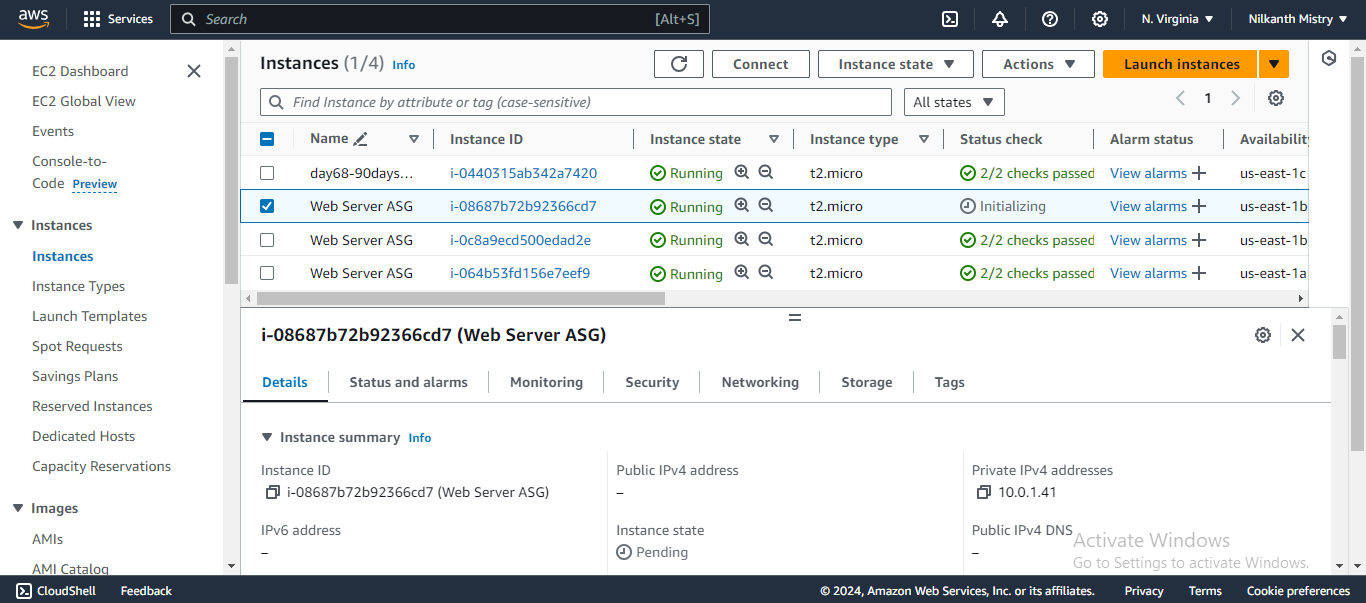
Wait a few minutes for the new instances to be launched. ⏳
Go to the EC2 Instances service and verify that the new instances have been launched. 🖥️✅
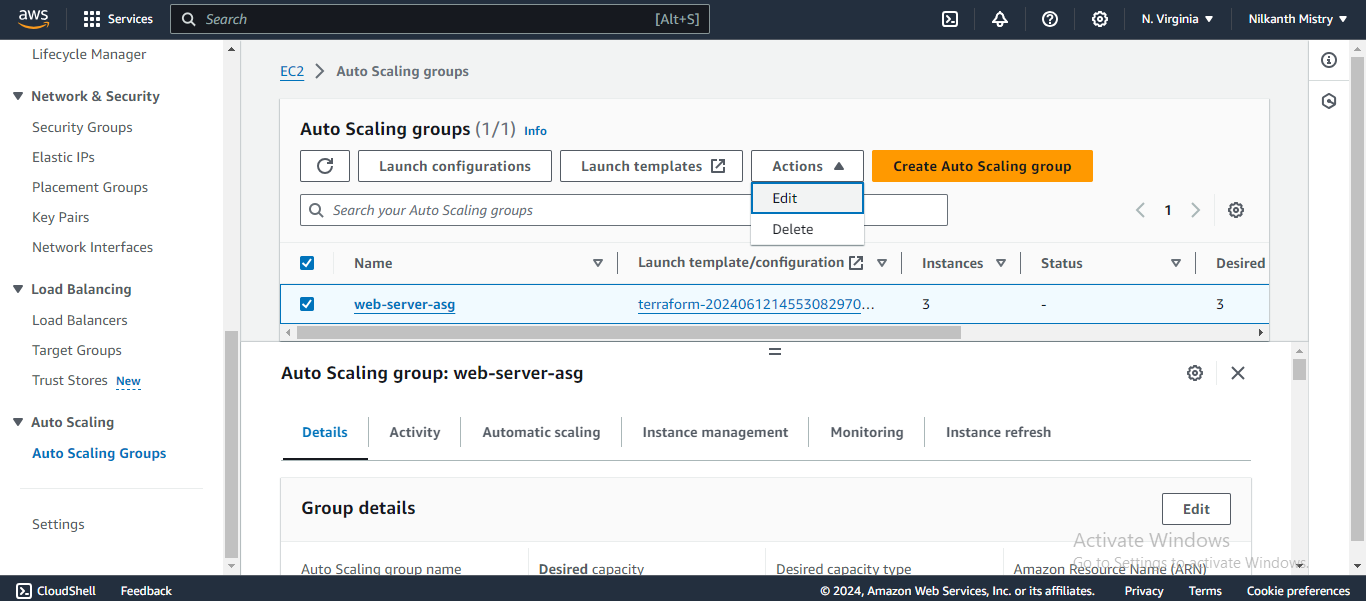
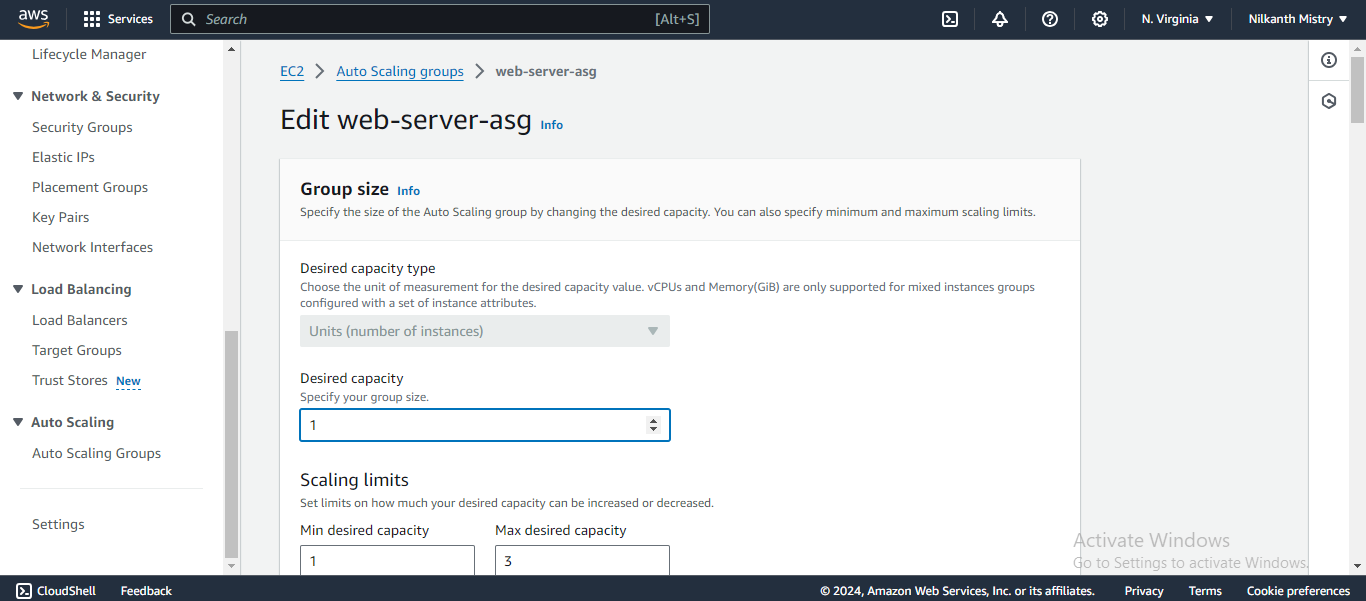
Decrease the "Desired Capacity" to 1 and wait a few minutes for the extra instances to be terminated. ⏳
Go to the EC2 Instances service and verify that the extra instances have been terminated. 🖥️❌
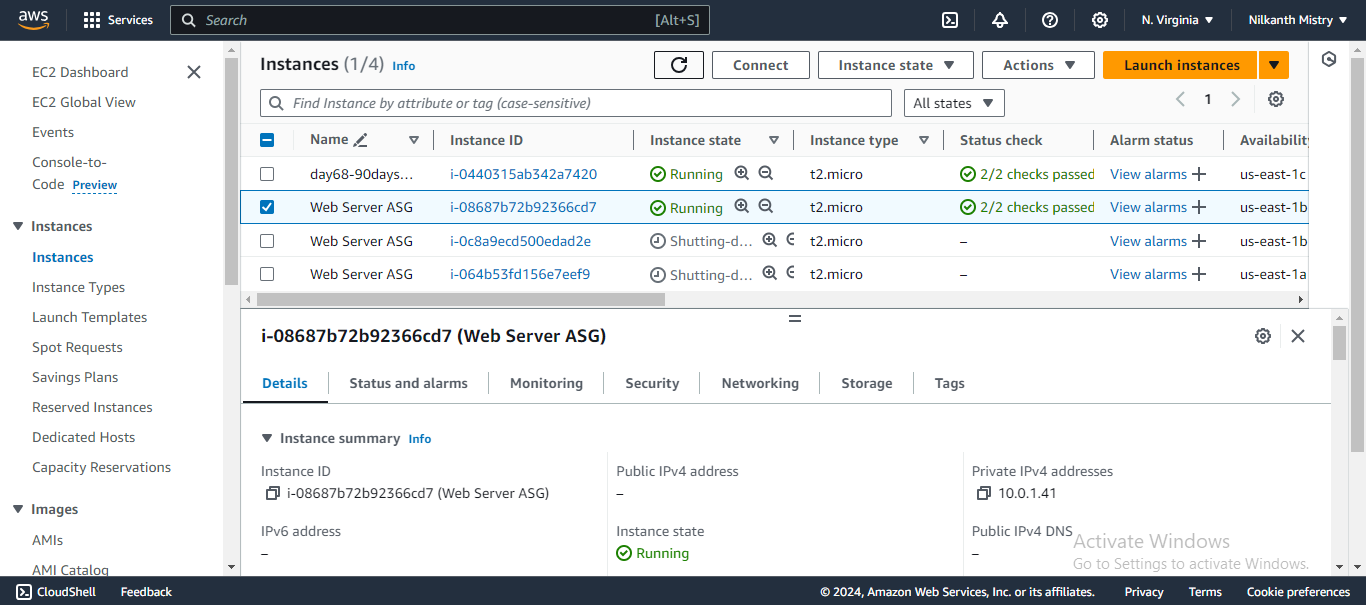
🎉 Congratulations! You have successfully scaled your infrastructure with Terraform. Keep up the great work and happy learning! 📚🚀
Happy Learning! 😊
Keep experimenting and learning. Tomorrow, we'll explore more exciting topics in our DevOps journey. See you then! 👋
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nilkanth Mistry directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Nilkanth Mistry
Nilkanth Mistry
Embark on a 90-day DevOps journey with me as we tackle challenges, unravel complexities, and conquer the world of seamless software delivery. Join my Hashnode blog series where we'll explore hands-on DevOps scenarios, troubleshooting real-world issues, and mastering the art of efficient deployment. Let's embrace the challenges and elevate our DevOps expertise together! #DevOpsChallenges #HandsOnLearning #ContinuousImprovement