The Beginner's Guide to Proxies: Proxy Server
 BrowserScan
BrowserScanNavigating the internet securely and efficiently is more important than ever. Proxy servers are crucial tools that act as intermediaries between your device and the internet, directing your web requests and responses.
Whether you're a business aiming to protect sensitive data or an individual seeking more private browsing, understanding proxy servers is essential.
This guide breaks down how proxy servers work, the different types, and the benefits they provide, along with the potential risks involved.
What Is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server serves as a gateway between you and the internet. It is an intermediary server that separates users from the websites they browse. Depending on how you plan to use it, your specific needs, or the policies of your organization, a proxy server can offer different levels of functionality, security, and privacy.
When you use a proxy server, your internet traffic passes through this server on its way to the destination you've requested. The same proxy server will handle the returning data from the website, forwarding it back to you.
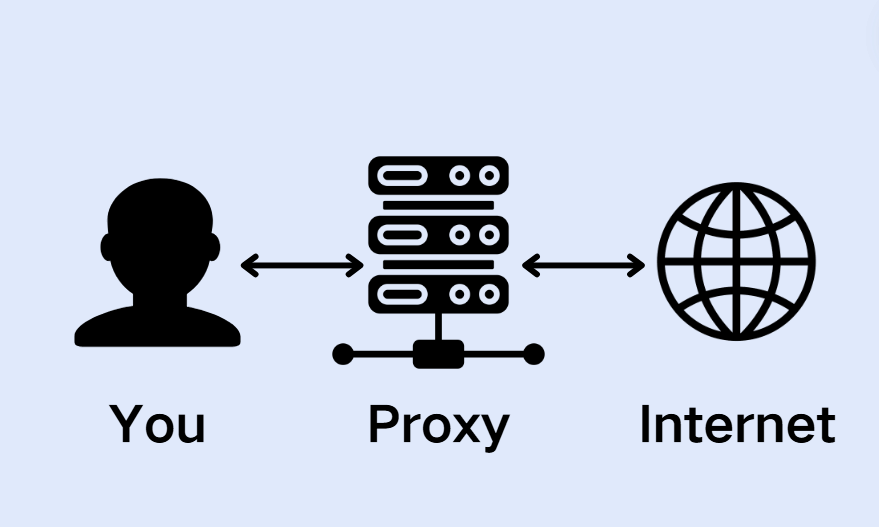
These servers can act as firewalls, filter web content, facilitate shared network connections, and store commonly requested data to quicken response times. A well-configured proxy server not only safeguards users and internal networks from potential threats found online but also boosts privacy significantly.
How Does a Proxy Server Work?
Usually, when you access a website, you send a request from your browser to the web server using your own IP address. The web server then responds by sending back the data for the website directly to you.
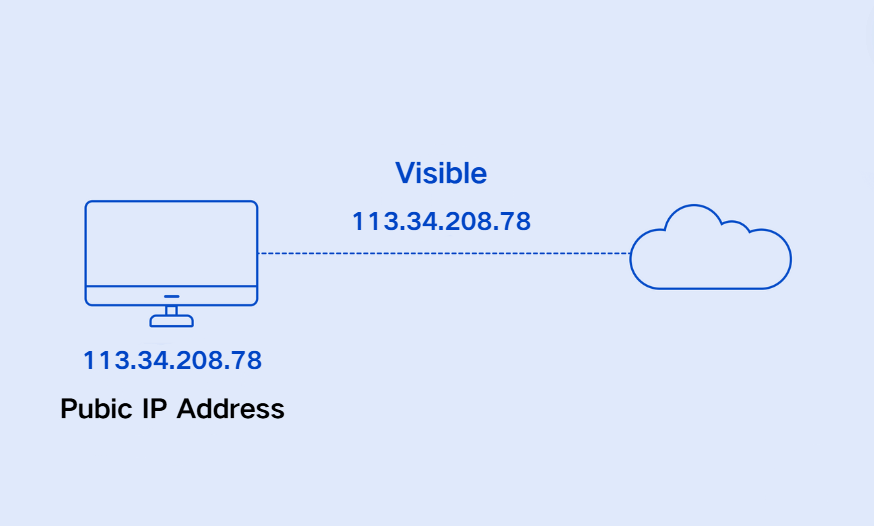
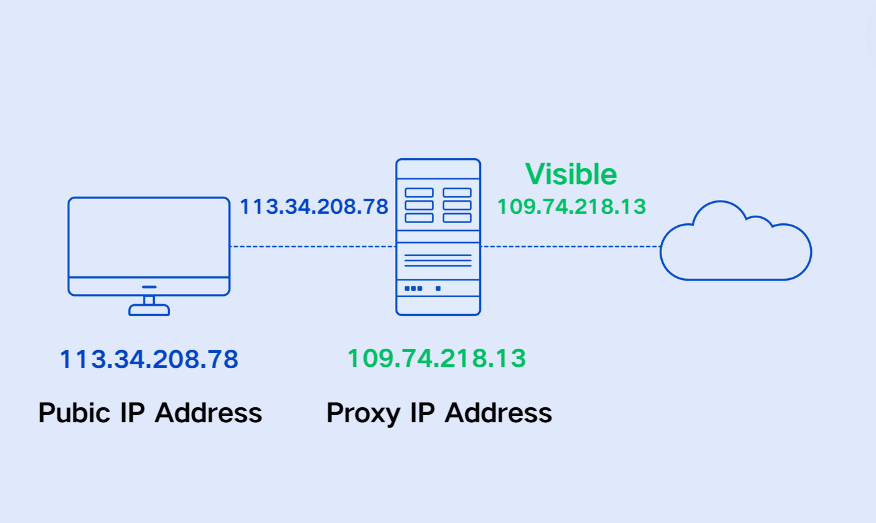
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between you and the web server. Proxy servers represent users with a different IP address, effectively concealing their actual IP addresses from web servers.
Here's a straightforward breakdown of how a proxy server operates:
You type a website’s URL into your browser.
The proxy server receives your request.
The proxy server forwards the request to the web server.
The web server responds with the requested data, sending it back to the proxy server.
The proxy server relays the web server's response back to you.
Types of Proxy Servers
HTTP Proxy Server
An HTTP proxy server uses the HTTP protocol to manage web content. It's typically configured by the browser or website, not by the user. This server changes the user's IP address for browsing but doesn't hide their online activities.
HTTPS Proxy Server
An HTTPS proxy server, also known as an SSL proxy, handles web content securely using the HTTPS protocol. It is designed to work only with web content, not other types of data.
This server ensures that all web traffic is encrypted, enhancing privacy and security for users. When accessing HTTPS websites, which already have SSL encryption, the use of an HTTPS proxy provides an additional layer of security, making the connection even more secure.
SOCKS Proxy Server
A SOCKS proxy, specifically the SOCKS5 version, handles all types of internet traffic through a third-party server, ensuring that data moves through a safe pathway using the TCP (Transmission Control Protocol).
This type of proxy doesn't encrypt traffic by itself; it relies on the encryption provided by the website or application it interacts with.
While SOCKS proxies can work with SHH (Secure Shell) to create secure connections, they do not offer anonymity. This means that while the connection can be secure, it may still be possible to identify the user.
Find out the differences of HTTP(S) vs SOCKS here.
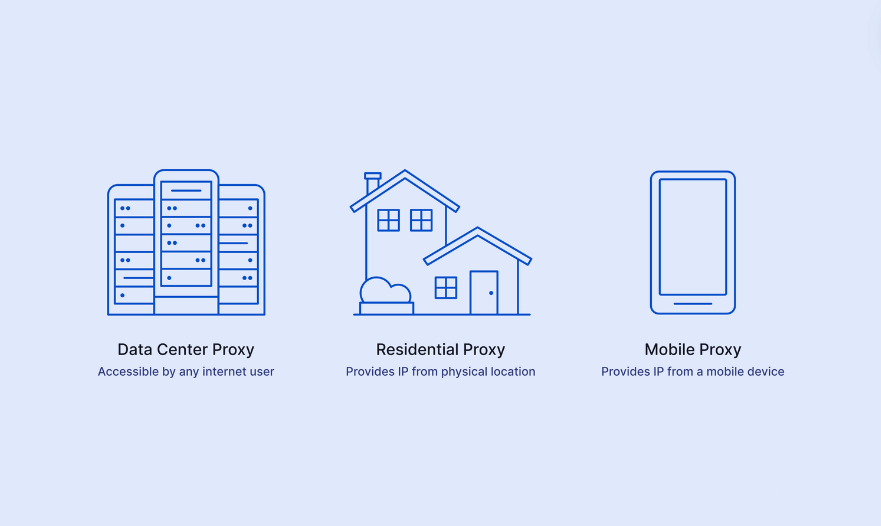
Datacenter Proxy Server
A datacenter proxy server is independent of any Internet Service Provider (ISP). It uses artificial IP addresses to help users stay anonymous online.
These proxies are less expensive and faster than residential proxies, but they are also less reliable. Websites can easily recognize data center proxies and often block them from accessing their content.
Residential Proxy Server
A residential proxy server is linked to an Internet Service Provider (ISP) and offers real IP addresses based on physical locations. This allows users to browse the internet anonymously.
Residential proxies are more expensive than data center proxies but are more trusted. They use real residential addresses, making web servers less likely to block them.
Residential proxy servers come in two forms:
Static Proxy Server: This type assigns a single residential IP address to users. Static proxies are less secure because they are easier for hackers to target and easier to trace since they always use the same IP address.
Rotating Proxy Server: This type provides a different IP address from a pool of addresses with each new connection. Rotating proxies are safer because their constantly changing IPs are harder to track.
Find out the differences of datacenter proxies vs residential proxies here.
Mobile Proxy Server
A mobile proxy server utilizes IP addresses from devices like smartphones and tablets that connect via mobile data (3G, 4G, or 5G). Users on desktop devices can use mobile proxies to make it look like their internet requests come from mobile devices.
These proxies are particularly useful for testing ads, apps, user experiences, and other product development activities. They help ensure that everything works smoothly for mobile users.
Benefits of Proxy Servers
Proxy servers are simple tools that provide big benefits to businesses. They are especially valuable in these ways:
Improved Security
Proxy servers are crucial for improving a company's security. Cybercrime, which cost the world over $6 trillion in 2021, is expected to top $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
By filtering out harmful data before it reaches a company’s network, proxy servers offer an extra layer of protection. They help prevent cyberattacks, phishing, identity theft, DDoS attacks, and other threats.
Anonymity
Proxies provide anonymity by standing between a company's network and the internet. This means the external servers cannot see the company's own IP address. This protects a company’s research and sensitive data from being exposed or stolen, especially if someone is trying to spy on their network activities.
Faster Speed
Proxy servers improve internet speeds by caching frequently visited web pages. This means the proxy does not have to request information from the internet every time, speeding up access.
They also compress internet traffic and remove ads, which further boosts speed.
Control Internet Usage
Companies use proxies to control which websites employees can access and to monitor internet requests, ensuring that no inappropriate or illegal activities are conducted online.
Bypass Restrictions
Sometimes, websites restrict access to users from certain locations. Proxies help businesses bypass these restrictions by masking their real IP addresses, allowing them to access the needed online content regardless of geographical barriers.
Risks of Proxy Servers
Proxy servers offer many advantages, but they also come with certain risks. Here's what users need to be aware of:
Lack of Encryption
If a proxy server isn't set up with encryption, it operates over an unsecured connection. This means attackers can easily intercept data like usernames and passwords, putting sensitive information at risk.
To stay safe, users should use proxies that offer encryption.
Data Logging
Proxy servers log information such as users' IP addresses and the websites they visit. Some proxies might not secure this data and could even sell it, increasing the risk of data breaches.
It's important for users to check the privacy policies of proxies before using them.
Open Ports
Proxies typically operate on open ports, which can be a security risk. These open ports might be targets for attacks, making the network more vulnerable.
Limited Privacy
Although proxies hide your IP address, this privacy might not cover everything you do online.
Free proxies, in particular, might use unsecured networks and display ads, which could be risky.
Inconsistent Speeds
Free proxy servers can become overloaded with traffic, leading to slow internet speeds. They often lack the bandwidth to handle many users at once, resulting in a sluggish experience.
Proxy Server vs VPN
Proxy servers share some similarities with VPNs, such as hiding users' IP addresses and helping bypass geo-restrictions..
However, the differences between them are more obvious than their similarities.
The main differences between proxy servers and VPNs are how they work and which protocols they support, which affects their privacy and security capabilities.
VPNs typically work at the device level, managing all sorts of traffic—such as web browsing, music streaming, and online gaming—through their secure networks. Generally, VPNs allow users to adjust settings so specific apps can bypass the VPN, although the default configuration directs all traffic through the VPN.
Proxy servers need individual setups for each application. This means that if a user doesn't specify that an app should use the proxy, it will directly connect to the internet, independent of any other proxy connections on the same device.
Conclusion
If you're using proxy servers, you can quickly check your proxy IP address and browser fingerprint in just a few seconds by visiting browserscan.net.
Moreover, tools like BrowserScan can help check if your real browser fingerprint is properly hidden, boosting your security measures.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from BrowserScan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

BrowserScan
BrowserScan
Am I 100% anonymous? Check your browser fingerprints and IP address to find how your online identity looks👉www.browserscan.net