JavaScript Cookies
 Aditya Gadhave
Aditya Gadhave
A cookie is an amount of information that persists between a server-side and a client-side.
A web browser stores this information at the time of browsing.
A cookie contains the information as a string generally in the form of a name-value pair separated by semi-colons.
It maintains the state of a user and remembers the user's information among all the web pages.
How Cookies Works?
When a user sends a request to the server, then each of that request is treated as a new request sent by the different user.
So, to recognize the old user, we need to add the cookie with the response from the server.
browser at the client-side.
Now, whenever a user sends a request to the server, the cookie is added with that request automatically. Due to the cookie, the server recognizes the users.

How to create a Cookie in JavaScript?
- In JavaScript, we can create, read, update and delete a cookie by using document.cookie property.
The following syntax is used to create a cookie:
- document.cookie="name=value";
JavaScript Cookie Example
Let's see an example to set and get a cookie.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="setCookie" onclick="setCookie()">
<input type="button" value="getCookie" onclick="getCookie()">
<script>
function setCookie()
{
document.cookie="username=Duke Martin";
}
function getCookie()
{
if(document.cookie.length!=0)
{
alert(document.cookie);
}
else
{
alert("Cookie not available");
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Cookie Attributes :
JavaScript provides some optional attributes that enhance the functionality of cookies.
Here, is the list of some attributes with their description.
| Attributes | Description |
| expires | It maintains the state of a cookie up to the specified date and time. |
| max-age | It maintains the state of a cookie up to the specified time. Here, time is given in seconds. |
| path | It expands the scope of the cookie to all the pages of a website. |
| domain | It is used to specify the domain for which the cookie is valid. |
Cookie expires attribute:
The cookie expires attribute provides one of the ways to create a persistent cookie.
Here, a date and time are declared that represents the active period of a cookie.
Once the declared time is passed, a cookie is deleted automatically.
Let's see an example of cookie expires attribute.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="setCookie" onclick="setCookie()">
<input type="button" value="getCookie" onclick="getCookie()">
<script>
function setCookie()
{
document.cookie="username=Duke Martin;expires=Sun, 20 Aug 2030 12:00:00 UTC";
}
function getCookie()
{
if(document.cookie.length!=0)
{
var array=document.cookie.split("=");
alert("Name="+array[0]+" "+"Value="+array[1]);
}
else
{
alert("Cookie not available");
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Cookie path attribute :
If a cookie is created for a webpage, by default, it is valid only for the current directory and sub-directory.
JavaScript provides a path attribute to expand the scope of cookie up to all the pages of a website.
Cookie path attribute Example
Let's understand the path attribute with the help of an example.
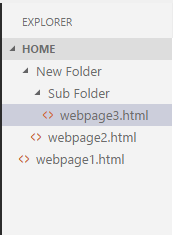
Here, if we create a cookie for webpage2.html, it is valid only for itself and its sub-directory (i.e., webpage3.html). It is not valid for webpage1.html file.
In this example, we use path attribute to enhance the visibility of cookies up to all the pages.
Here, you all just need to do is to maintain the above directory structure and put the below program in all three web pages.
Now, the cookie is valid for each web page.
Cookie domain attribute :
A JavaScript domain attribute specifies the domain for which the cookie is valid.
Let's suppose if we provide any domain name to the attribute such like:
domain=adityagadhave.com
Here, the cookie is valid for the given domain and all its sub-domains.
However, if we provide any sub-domain to the attribute such like:
omain=project.adityagadhave.com
- Here, the cookie is valid only for the given sub-domain. So, it's a better approach to provide domain name instead of sub-domain.
Cookie with multiple Name-Value pairs :
In JavaScript, a cookie can contain only a single name-value pair.
However, to store more than one name-value pair, we can use the following approach: -
Serialize the custom object in a JSON string, parse it and then store in a cookie.
For each name-value pair, use a separate cookie.
Examples to Store Name-Value pair in a Cookie:
Let's see an example to check whether a cookie contains more than one name-value pair
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
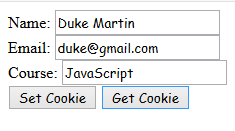
Name: <input type="text" id="name"><br>
Email: <input type="email" id="email"><br>
Course: <input type="text" id="course"><br>
<input type="button" value="Set Cookie" onclick="setCookie()">
<input type="button" value="Get Cookie" onclick="getCookie()">
<script>
function setCookie()
{
//Declaring 3 key-value pairs
var info="Name="+ document.getElementById("name").value+";Email="+document.getElementById("email").value+";Course="+document.getElementById("course").value;
//Providing all 3 key-value pairs to a single cookie
document.cookie=info;
}
function getCookie()
{
if(document.cookie.length!=0)
{
//Invoking key-value pair stored in a cookie
alert(document.cookie);
}
else
{
alert("Cookie not available")
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
On clicking Get Cookie button, the below dialog box appears.
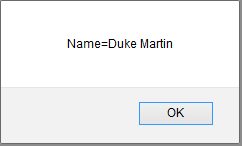
Here, we can see that only a single name-value is displayed.
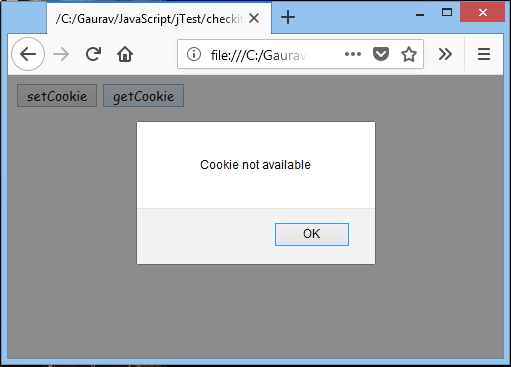
However, if you click, Get Cookie without filling the form, the below dialog box appears.
Deleting a Cookie in JavaScript :
In the previous section, we learned the different ways to set and update a cookie in JavaScript.
Apart from that, JavaScript also allows us to delete a cookie.
Here, we see all the possible ways to delete a cookie
Different ways to delete a Cookie :
These are the following ways to delete a cookie:
A cookie can be deleted by using expire attribute.
A cookie can also be deleted by using max-age attribute.
We can delete a cookie explicitly, by using a web browse
Examples to delete a Cookie :
In this example, we use expire attribute to delete a cookie by providing expiry date (i.e. any past date) to it.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="Set Cookie" onclick="setCookie()">
<input type="button" value="Get Cookie" onclick="getCookie()">
<script>
function setCookie()
{
document.cookie="name=Martin Roy; expires=Sun, 20 Aug 2000 12:00:00 UTC";
}
function getCookie()
{
if(document.cookie.length!=0)
{
alert(document.cookie);
}
else
{
alert("Cookie not avaliable");
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Whats Next?
JS Exception Handling
JavaScript try-catch
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aditya Gadhave directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aditya Gadhave
Aditya Gadhave
👋 Hello! I'm Aditya Gadhave, an enthusiastic Computer Engineering Undergraduate Student. My passion for technology has led me on an exciting journey where I'm honing my skills and making meaningful contributions.