Navigating the Cloud
 shiva kumar
shiva kumar
Introduction
Cloud computing is a technology that allows users to access and use computing resources over the internet, rather than relying on local servers or personal computers. It provides on-demand delivery of IT resources such as storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence.
Imagine you have a powerful computer you can access from anywhere, anytime, without having to own that computer. That's basically what cloud computing is. Instead of using your own computer’s hard drive or server, you use the internet (the cloud) to store and manage your data.
Cloud computing started small, just like any other technology. It began with companies offering simple online storage. Over time, it grew and evolved.
What does cloud technology offer?

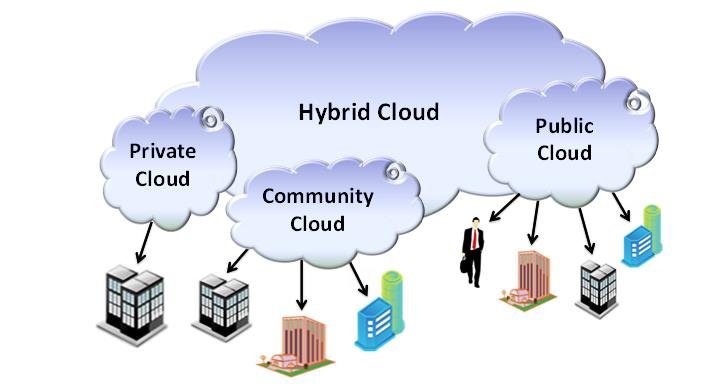
Cloud Deployment Models
Public Cloud
A public cloud is a type of cloud computing where services are delivered over the public internet and shared across multiple organizations or users. Public cloud services are provided by third-party vendors and are accessible to anyone who wants to use or purchase them.
Example: Think of it like renting a car that anyone can rent. Services are available to anyone over the internet.
Benefits: Cost Efficiency, Accessibility, Scalability, Reliability
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a type of cloud computing where the infrastructure is dedicated exclusively to a single organization. This setup can be managed internally or by a third party and can be hosted either on-premises or externally.
Example: This is like owning a car that only you and your family can use. Similarly the private cloud services are used by one organization.
Benefits: Security and Privacy, Control, Performance
Private clouds typically involve higher upfront costs and ongoing maintenance compared to public clouds, which offer a pay-as-you-go model.
Private clouds offer more control and potentially higher security, making them suitable for sensitive data and regulated industries.
Community Cloud
A community cloud is a type of cloud computing deployment model that is shared among several organizations with similar computing concerns and security requirements. In a community cloud, infrastructure and resources are accessible and used by a specific community of users from multiple organizations, rather than being open to the general public.
Example: Consider a shared car owned by a group of neighbors. Only the group can use it, and it's specifically shared among them based on the mutual agreement. This is similar to a community cloud, where the infrastructure is shared among organizations with common concerns
Benefits: Collaboration, Resource Optimization
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines on-premises private cloud and third-party public cloud services. You can use your private cloud for important stuff that needs extra security, like sensitive data or key applications. Then, for things that need to be really big or can change a lot, you use the public cloud. It's great for handling big bursts of activity without you needing to buy more equipment.
Example: Imagine you own a car but sometimes rent one when you need more capacity. This combines both public and private clouds.
Benefits: Improved Security and Compliance, Optimized Resource Utilization
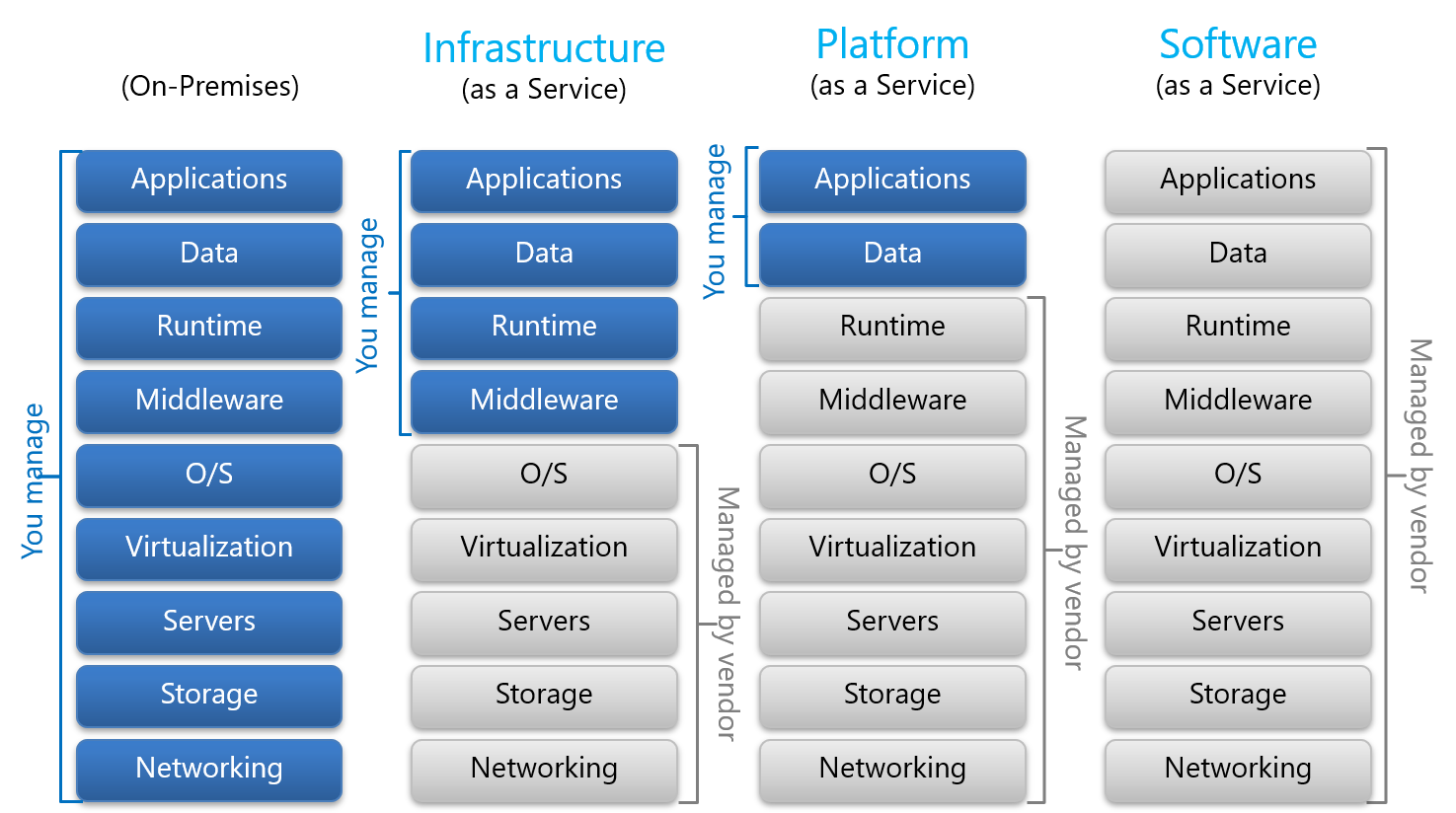
Cloud Service Models
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Instead of buying physical servers, storage, or networking equipment, you rent them from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis.
You manage the applications, data, runtime, middleware, and OS, while the cloud provider manages virtualization, servers, storage, and networking.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure. It typically includes development tools, databases, middleware, and more, all delivered over the internet.
You manage the applications and data, while the cloud provider manages everything including the runtime, middleware, OS, virtualization, servers, storage, and networking.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) provides software applications which are hosted and maintained by a third-party provider and made available to customers over the internet. In this model, users access the software via a web browser or API without needing to install or manage any software locally on their devices.
The cloud provider manages everything: applications, runtime, middleware, OS, virtualization, servers, storage, and networking. Users only need to use the software over the internet.
Major Players in Cloud Computing
Amazon Web Services
Microsoft Azure
Google Cloud Platform
IBM Cloud
While Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and IBM Cloud are some of the leading providers, there are many other companies also offering a variety of cloud computing services, catering to different needs and industries.

Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from shiva kumar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
