Understanding SQL Injection: A Beginner's Guide
 Dhananjay kulkarni
Dhananjay kulkarni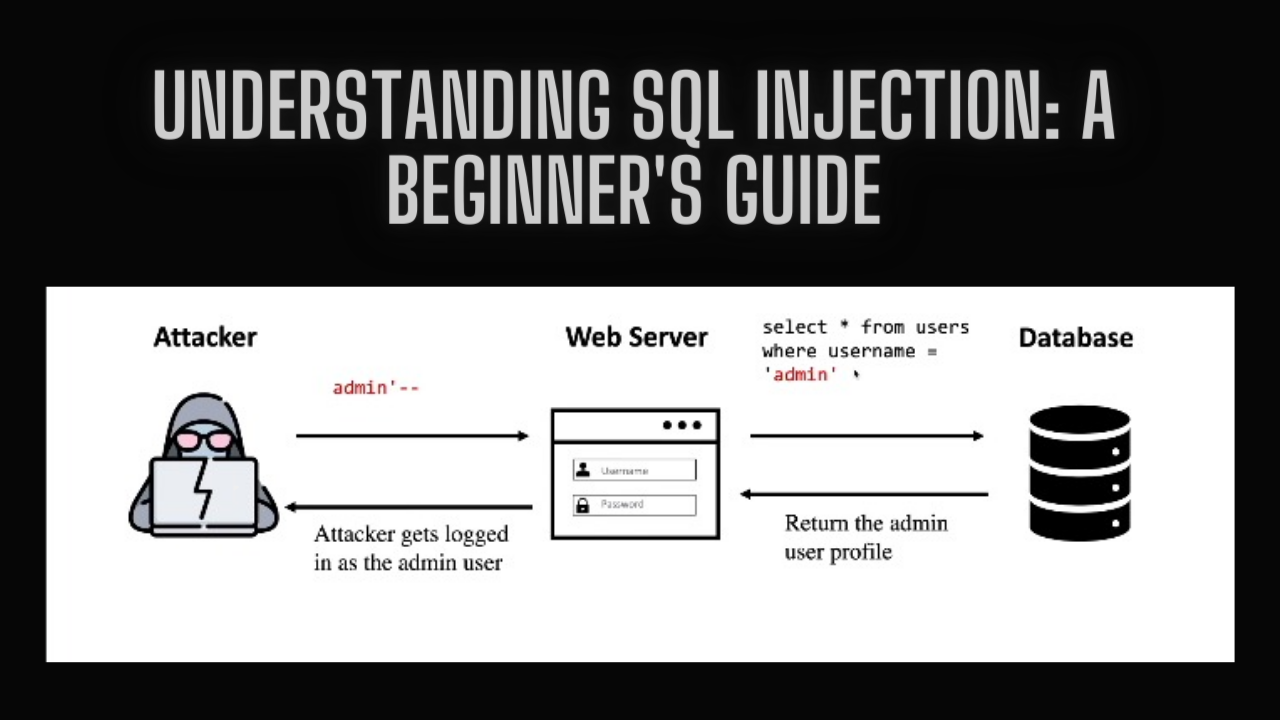
What is SQL Injection?
SQL Injection is a type of attack where an attacker can manipulate the SQL query sent to the database by adding SQL code into an input field of an application. This manipulation can allow the attacker to interact with and change the SQL query, potentially gaining unauthorized access to the database.
How Does SQL Injection Work?
Let's break down a typical example to understand how SQL injection works.
Scenario Setup:
Imagine you have an attacker, a web server, and a database.
The web server hosts an application with a login functionality where users enter their username and password to access their accounts.
Normal Process:
A legitimate user inputs their username and password.
The application sends a query to the database to verify these credentials.
If the username and password match an entry in the database, the user is granted access. If not, an error message is displayed.
Potential Vulnerability:
- The username and password fields are points where input is received from the user. These are known as input vectors and need to be tested to ensure they are not vulnerable to SQL injection.
Example of an SQL Injection Attack
Here's a step-by-step example of how an attacker can exploit an SQL injection vulnerability:
Attacker's Manipulation:
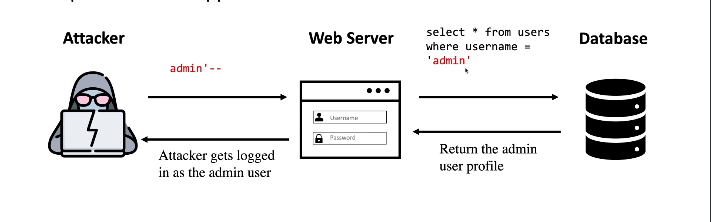
Instead of entering a regular username, the attacker inputs something like
admin'--'into the username field.The
adminpart is the username the attacker wants to access.The
--part is a SQL comment symbol that tells the database to ignore the rest of the query.
How the Query Changes:
Normally, the application's query to check credentials might look like this:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username='user_input' AND password='password_input';This query checks if both the username and password match an entry in the users table of the database.
With the attacker's input (
admin'--), the query becomes:SELECT * FROM users WHERE username='admin'--' AND password='';The
--comments out the rest of the query, changing it to only check if the username isadminand ignoring the password condition.
Result of the Attack:
If there is a user with the username
adminin the database, the modified query will return the admin's profile.This allows the attacker to log in as the admin without knowing the admin's password.
Why is This a Problem?
Bypassing Authentication: The attacker can gain unauthorized access to user accounts, including potentially privileged accounts like
admin.Data Theft or Manipulation: Once logged in, the attacker could steal, modify, or delete sensitive data.
How to Prevent SQL Injection
Parameterized Queries: Use parameterized queries or prepared statements that ensure user inputs are treated as data, not executable code.
For example, in many programming languages, you can use prepared statements that safely handle user inputs:
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM users WHERE username=%s AND password=%s", (username_input, password_input))
Input Validation and Sanitization: Always validate and sanitize user inputs to remove any potentially harmful characters.
- For instance, strip out or escape characters like
',",--,;, etc., which can be used in SQL injection attacks.
- For instance, strip out or escape characters like
Use ORM: Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) frameworks help prevent SQL injection by abstracting SQL queries and providing safe ways to interact with the database.
Least Privilege Principle: Ensure that the database user used by the application has the least privileges necessary, limiting the potential damage from an SQL injection attack.
Conclusion
SQL Injection is a powerful technique that attackers can use to manipulate SQL queries and gain unauthorized access to a database. By understanding how it works and implementing best practices like parameterized queries and input validation, you can protect your applications from such vulnerabilities. Always prioritize security in your development process to safeguard sensitive data and maintain the integrity of your applications.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Dhananjay kulkarni directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Dhananjay kulkarni
Dhananjay kulkarni
.