Mastering Web Development: Integrate MongoDB with Node.js and Express
 Rohan Shrivastava
Rohan Shrivastava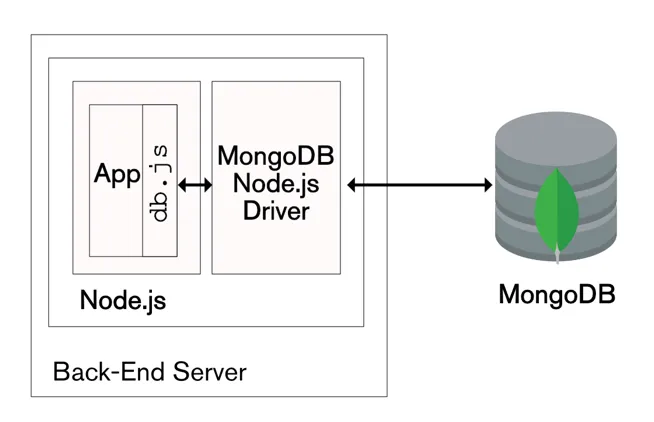
Introduction
In this tutorial, we'll explore how to connect a MongoDB database to a Node.js application using the Express server framework. MongoDB, Node.js, and Express.js are popular choices for building scalable and efficient web applications. By the end of this tutorial, you'll have a clear understanding of how to set up and connect these technologies to build a robust web application.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure you have the following installed:
Node.js: Download Node.js
MongoDB: Download MongoDB
MongoDB Compass (Optional): A GUI for MongoDB. Download MongoDB Compass
Step 1: Setting Up the Project
Initialize a Node.js Project
Open your terminal and create a new directory for your project. Navigate into this directory and initialize a new Node.js project:
bashCopy codemkdir mongo-express-app cd mongo-express-app npm init -yInstall Dependencies
We'll need
express,mongoose(an ODM for MongoDB and Node.js), anddotenvto manage environment variables:bashCopy codenpm install express mongoose dotenv
Step 2: Creating the Express Server
Create Server Files
In your project directory, create a new file named
server.js:javascriptCopy codeconst express = require('express'); const mongoose = require('mongoose'); const dotenv = require('dotenv'); dotenv.config(); const app = express(); const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000; // Middleware app.use(express.json()); // Routes app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send('Hello, world!'); }); // Connect to MongoDB mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true, }) .then(() => { console.log('Connected to MongoDB'); app.listen(PORT, () => { console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`); }); }) .catch((err) => console.error('Failed to connect to MongoDB', err));Environment Variables
Create a
.envfile in the root of your project directory to store your MongoDB URI:makefileCopy codeMONGO_URI=your_mongodb_connection_string
Step 3: Defining a Mongoose Schema
Create a new directory called models and within it, create a file named User.js:
javascriptCopy codeconst mongoose = require('mongoose');
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
email: {
type: String,
required: true,
unique: true,
},
password: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
});
const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema);
module.exports = User;
Step 4: Creating Routes
User Routes
Create a new directory called
routesand within it, create a file nameduserRoutes.js:javascriptCopy codeconst express = require('express'); const User = require('../models/User'); const router = express.Router(); // Create a new user router.post('/users', async (req, res) => { try { const user = new User(req.body); await user.save(); res.status(201).send(user); } catch (err) { res.status(400).send(err); } }); // Get all users router.get('/users', async (req, res) => { try { const users = await User.find(); res.status(200).send(users); } catch (err) { res.status(500).send(err); } }); module.exports = router;Integrate Routes in
server.jsUpdate your
server.jsto use the user routes:javascriptCopy codeconst express = require('express'); const mongoose = require('mongoose'); const dotenv = require('dotenv'); const userRoutes = require('./routes/userRoutes'); dotenv.config(); const app = express(); const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000; // Middleware app.use(express.json()); // Routes app.use('/api', userRoutes); // Connect to MongoDB mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true, }) .then(() => { console.log('Connected to MongoDB'); app.listen(PORT, () => { console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`); }); }) .catch((err) => console.error('Failed to connect to MongoDB', err));
Advantages and Disadvantages
MongoDB
Advantages:
Scalability: MongoDB is designed to scale out by distributing data across multiple servers.
Flexibility: It stores data in a flexible, JSON-like format.
Performance: Suitable for handling large volumes of data and high-throughput applications.
Disadvantages:
Complexity: Schema design can become complex for certain use cases.
Transactions: While supported, transactions can be more complex than in relational databases.
Node.js
Advantages:
Asynchronous and Event-Driven: Non-blocking I/O operations lead to high performance.
JavaScript: Uses the same language on the server and client side, simplifying development.
Large Ecosystem: Extensive libraries and frameworks available via npm.
Disadvantages:
Single-Threaded: Heavy computation can block the event loop, leading to performance issues.
Callback Hell: Managing asynchronous code can become complex without proper patterns like Promises or async/await.
Express.js
Advantages:
Minimalistic: Provides a thin layer of fundamental web application features, leaving more control to the developer.
Middleware: Flexible and modular middleware to handle various web application tasks.
Community Support: Large, active community with plenty of resources and third-party packages.
Disadvantages:
Minimal Structure: Provides less structure compared to some other frameworks, which can lead to inconsistent coding practices.
Middleware Overhead: Can introduce overhead if not managed properly.
Unique Features and Uses for Developers
MongoDB: Ideal for applications requiring flexible schema design, high performance, and scalability, such as real-time analytics, content management, and IoT.
Node.js: Suitable for building fast and scalable network applications, like web servers, real-time applications (e.g., chat applications), and APIs.
Express.js: Perfect for developers needing a lightweight framework to build robust APIs and web applications quickly and efficiently.
Conclusion
Connecting MongoDB with Node.js using Express.js provides a powerful stack for building scalable and efficient web applications.
By following the steps outlined in this tutorial, you can set up and connect these technologies seamlessly.
Understanding their advantages, disadvantages, and unique features helps developers make informed decisions when building their applications.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rohan Shrivastava directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Rohan Shrivastava
Rohan Shrivastava
Hi, I'm Rohan, a B.Tech graduate in Computer Science (Batch 2022) with expertise in web development (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Bootstrap, PHP, XAMPP). My journey expanded with certifications and intensive training at Infosys, covering DBMS, Java, SQL, Ansible, and networking. I've successfully delivered projects, including a dynamic e-commerce site and an Inventory Management System using Java. My proactive approach is reflected in certifications and contributions to open-source projects on GitHub. Recognized for excellence at Infosys, I bring a blend of technical proficiency and adaptability. Eager to leverage my skills and contribute to innovative projects, I'm excited about exploring new opportunities for hands-on experiences. Let's connect and explore how my skills align with your organization's goals.