Let's get this party started
 Thomas Burkhart
Thomas Burkhart
If you haven't used GetIt before you might read this article first: One to find them all. If you are using GetIt for some time make sure to revisit the ReadMe in the API docs because a lot more was added in the last weeks. Like async factories and factories with parameters.
To use the features described in this post you need to use get_it V4.0.0 or higher. Please don't be angry with me, it also brings minor breaking changes that improved the API.
All too often your app has to do a lot of initialization work before it really can get to its actual purpose. And often this includes several asynchronous function calls like:
Reading from shared_preferences
opening a database or file
Calling some REST API to get the latest data updates
To make things more complicated one or more objects may depend on others to be initialized before they can be initialized like
Read API token from shared_preferences
before you can make your first REST call
before you can update your database.
You can orchestrate this sequence manually but it's a tedious process. To make your life easier I included some functions in GetIt that do that job for you and integrates nicely in a Flutter project.
Why in GetIt and not a separate package you might ask? The reason is that the objects that you register in GetIt are most often the objects that need to get initialized. So it makes sense to combine these processes.
There are two ways you can orchestrate your start-up, one that is almost completely automatic and another one that allows you complete control over the moment when an object signals that it's ready to be used.
So how does it work
GetIt offers a function allReady() that completes when all in GetIt registered objects have signaled that they are ready to use.
Future allReady(Timeout timeout)
The returned Future is ideally used as the source of a FutureBuilder like:
return FutureBuilder(
future: getIt.allReady(),
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot snapshot) {
if (snapshot.hasData) {
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Text('The first real Page of your App'),
),
);
} else {
return CircularProgressIndicator();
}
}
);
Your app can show some start-up page with an animation and switch the content as soon as allReady() completes.
If you want to switch-out the full page, instead of using a FutureBuilder you can do this in the initState() function of your StatefullWidget:
class _StartupPageState extends State {
@override
void initState() {
GetIt.I.allReady().then((_) => Navigator.pushReplacement(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => MainPage())
));
super.initState();
}
}
Orchestrating the start-up dance
Automatic
The easiest way to initialize a Singleton asynchronously is by using the new registerSingletonAsync function, which expects an async factory function. When that function has been completed it notifies GetIt that this object is ready. As an example let\'s take this class here:
class RestService {
Future init() async {
// do your async initialisation...
// simulating it with a Delay here
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2));
return this;
}
}
All you have to do to make it signal its ready state is to use registerSingletonAsync:
final getIt = GetIt.instance;
getIt.registerSingletonAsync<RestService>(() async {
final restService = RestService();
await restService.init();
return restService;
});
If your init function returns its instance like the RestService in the example above you can even write this shorter:
getIt.registerSingletonAsync(() async => RestService().init());
As soon as the last Singleton has finished its factory function the Future from allReady() will complete and trigger your UI to change.
Manual
You might encounter cases where you need to separate the initialization from the factory function of a Singleton. Or maybe you want to start the initialization as a fire end forget function from the constructor. To still synchronize it with other Singletons you can manually signal that your object is ready by using the signalReady() function. This requires informing GetIt that this object will signal ready later so that GetIt knows it has to wait for that before completing the allReady() Future. To do this you have two possibilities depending on your preferences:
Pass the optional
signalsReadyparameter to the registration functionsMake the type that you register to implement the empty abstract class
WillSignalReady. This has the advantage that the one registering the Singleton does not need to know how it will signal its ready state.
Here is an example of the separation of creation and registration:
class ConfigService implements WillSignalReady {
Future init() async {
// do your async initialization...
GetIt.instance.signalReady(this);
}
}
/// registering
getIt.registerSingleton(ConfigService());
/// initializing as a fire and forget async call
getIt<ConfigService>().init();
As you can see we used the non-async registration function in that case because we don't need to. If your factory function needs to be async too, you can use registerSingletonAsync again.
A nice way to hide the whole initialization is to start it as a fire-and-forget-call from the constructor:
class ConfigService {
ConfigService() {
_init();
}
Future _init() async {
// do your async initialisation...
GetIt.instance.signalReady(this);
}
}
Dealing with dependencies
Automatic synchronisation
If the singletons that require an async initialization depend on each other we can use the optional parameter dependsOn of registerSingletonAsync and registerSingletonWithDependencies. The latter one is used if you have a Singleton that doesn't need any async initialization but that's constructor depends on other singletons being ready.
Imaging this set of services:
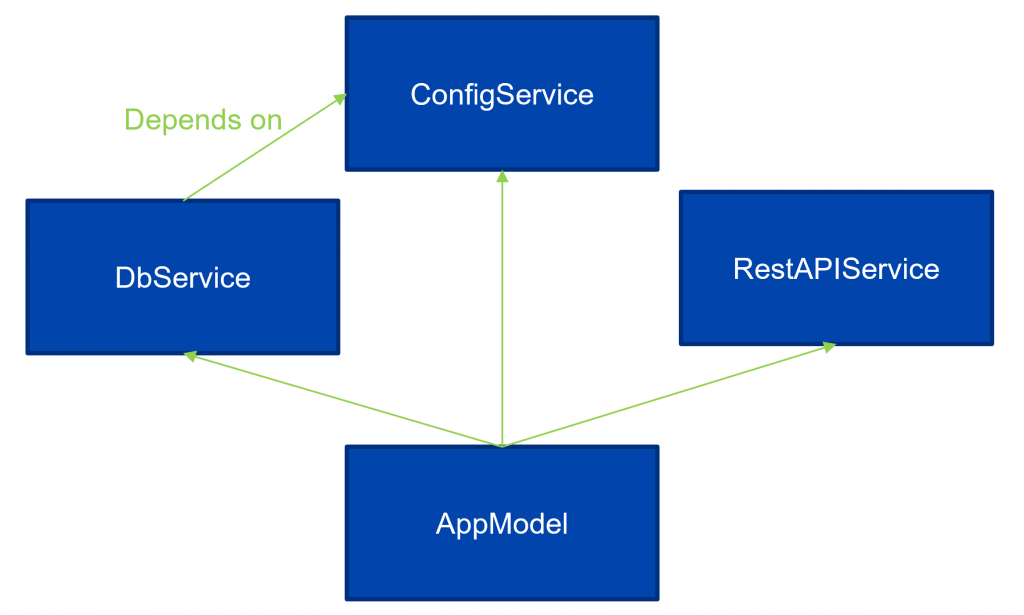
In code, this could look like this:
getIt.registerSingletonAsync(() async {
final configService = ConfigService();
await configService.init();
return configService;
});
getIt.registerSingletonAsync(() async => RestService().init());
/// this example uses an async factory function
getIt.registerSingletonAsync(createDbServiceAsync, dependsOn: [ConfigService]);
getIt.registerSingletonWithDependencies(
() => AppModelImplementation(),
dependsOn: [ConfigService, DbService, RestService]
);
This will ensure that dependent singletons will wait with their construction until the ones they depend on have signaled their ready state
Be careful not to create circular dependencies. If you have some deadlocks between the different initialization functions allReady or isReady with throw a WaitingTimeOutException which contains detailed information on who is waiting for whom at that moment.
Manual synchronization
If somehow the automatic synchronization does not fit your need, you can manually wait for another Singleton to signal ready by using the isReadyFunction:
/// Returns a Future that completes if the instance of a Singleton, defined by Type [T] or
/// by name [instanceName] or by passing an existing [instance], is ready.
/// If you pass a [timeout], a [WaitingTimeOutException] will be thrown if the instance
/// is not ready in the given time. The Exception contains details on which Singletons are
/// not ready at that time.
/// [callee] optional parameter which makes debugging easier. Pass `this` in here.
Future isReady({
Object instance,
String instanceName,
Duration timeout,
Object callee,
});
I hope you like the latest addition to GetIt and that it will make your app start-up easier than ever.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Thomas Burkhart directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
