Core Components in Network Systems
 Aman Singh
Aman SinghTable of contents
- What is Network?
- What is the internet?
- What is SWITCH?
- Difference between Switch and Hub
- Hold on, if you're not familiar with the OSI Model, don't worry! We'll cover it in the next article.
- Key Differences between Switch and Hub
- What is a Router?
- Key Points:
- Thanks to everyone who read this! I hope you enjoyed it. If you found it helpful, please drop a comment, give it a like, and share it with your friends.
- Resources
What is Network?
Think of a network like a group of friends who are all connected and can talk to each other. In tech, it's a bunch of computers and devices linked together to share information and resources.
Before a network, it was like everyone had to pass notes by hand to share information. After a network, it's like having a group chat where everyone can instantly share and access information.
What is the internet?
The internet is like a massive global group chat where millions of computers and devices are connected. They can share information, talk to each other, and access tons of resources instantly.
Choosing a WAP (Wireless Access Point) at home is like having Wi-Fi that lets everyone in the house connect to the internet without needing cables. It's convenient because you can move around freely with your devices.
On the other hand, Choosing a wired internet connection is like having a direct line to the internet. It's usually faster and more reliable, which is great for a company where you need a stable connection for important tasks.
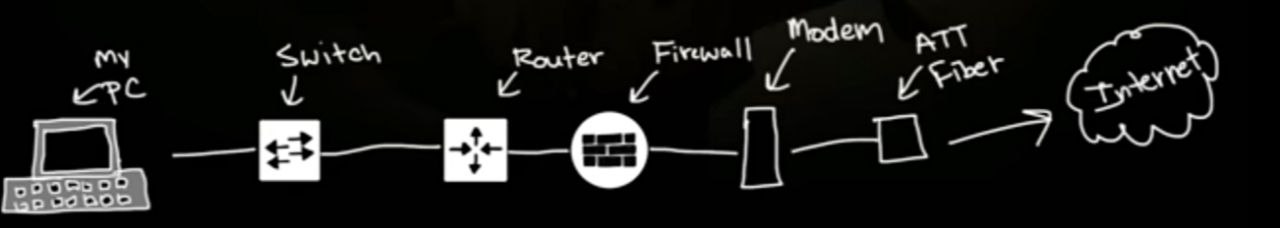
My PC connects to the Router, then to the Firewall, then to the Modem, then to the Fiber, and Finally to the Internet.
Ethernet: it is like using a wired connection to get online. It's fast and stable, perfect for when you need a reliable internet connection.
Switches: Think of switches like the organizers at a party. They connect different devices in your network and make sure data gets sent to the right place.
Router: A router is like the traffic cop or police of your network. It directs data between your home network and the internet, making sure everything goes where it needs to.
Firewall: A firewall is like a security guard. It monitors incoming and outgoing traffic and blocks anything suspicious to keep your network safe.
Modem: A modem is the translator. It converts the data from your internet service provider into a format your devices can understand and vice versa.
Fiber: Fiber is like a super-fast highway. It's a type of internet connection that uses light to transmit data, making it incredibly fast and reliable.
Internet: The internet is the giant global network that connects millions of computers and devices, allowing them to share information and resources.

What is SWITCH?
Switch is like the organizer at a party. It connects different devices (like computers and printers) and ensures data gets sent to the right device. If your computer wants to send a file to the printer, the switch makes sure it goes directly to the printer. It keeps communication within your network smooth and efficient.
Difference between Switch and Hub
A switch and a hub both connect multiple computers and devices within a network, but they work differently and have unique functions.
Hub
A hub is a basic networking device that connects multiple devices in a network. It operates at the physical layer (Layer 1) of the OSI model. When a hub receives data from one device, it broadcasts the data to all connected devices, regardless of the intended recipient. This can cause network inefficiencies and collisions, slowing down the network.
Switch
Switch is a more advanced device that operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model. Unlike a hub, a switch is intelligent and can identify connected devices. When it receives data, it examines the destination address and forwards it only to the intended device. This reduces unnecessary traffic and collisions, making the network more efficient and faster.

Hold on, if you're not familiar with the OSI Model, don't worry! We'll cover it in the next article.
Key Differences between Switch and Hub
Data Transmission:
Hub: Broadcasts data to all devices.
Switch: Sends data only to the recipient.
Network Efficiency:
Hub: Less efficient due to broadcasting and collisions.
Switch: More efficient with reduced traffic and fewer collisions.
Layer of Operation:
Hub: Operates at Layer 1.
Switch: Operates at Layer 2.
Intelligence:
Hub: Does not differentiate devices.
Switch: Identifies and communicates with specific devices.
Overall, while both hubs and switches connect multiple devices in a network, switches manage data traffic more efficiently and intelligently, making them a better choice for most modern networks.
What is a Router?
A router is like a smart traffic director for your network. It works at Layer 3 of the OSI model (Network layer). When data comes in, the router looks at the destination address and decides the best way to send it there. It connects different networks together and can even link up to the internet.
Key Points:
Data Handling: Routes data between different networks.
Network Layer: Operates at Layer 3.
Decision Making: Chooses the best path for data.
Internet Connection: Can connect your local network to the internet.

Thanks to everyone who read this! I hope you enjoyed it. If you found it helpful, please drop a comment, give it a like, and share it with your friends.
Resources
If you prefer learning through videos, check out these lectures. I promise you'll definitely learn a lot!
For Hindi listeners:
For English Listener:
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aman Singh directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aman Singh
Aman Singh
Hey folks! I’m Aman. I'm currently in my second year of BCA in Information Technology and learning frontend development with the help of various communities. I'm doing LearnInPublic and BuildInPublic, so I’ll be sharing my learning on my social media. I'll also create content by documenting my journey.