AWS Solution Architect Associate In-Depth | Session 5
 Muhammad Irfan
Muhammad Irfan
1. Overview of Session
This begins with an icebreaker activity discussing travel bucket lists, then transitions into a detailed explanation of setting up and securing a network on AWS. The instructor explains the creation of a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), subnets, route tables, and security measures like network access control lists (NACLs) and security groups. The session includes a demo on VPC creation, emphasizing the importance of customizing network configurations to suit specific needs.
2. Comprehensive Guide to AWS Networking
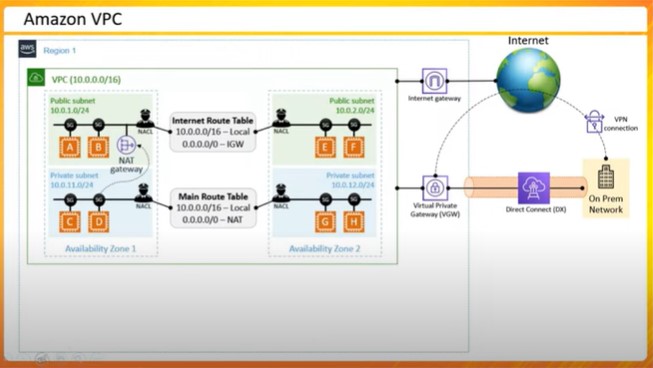
Understand the concept of Virtual Private Clouds (VPC) and Subnets.
Learn the crucial role of Route Tables and Internet Gateway in controlling network traffic.
Explore the distinction between public and private subnets and their respective uses.
3. Security Mechanisms in AWS
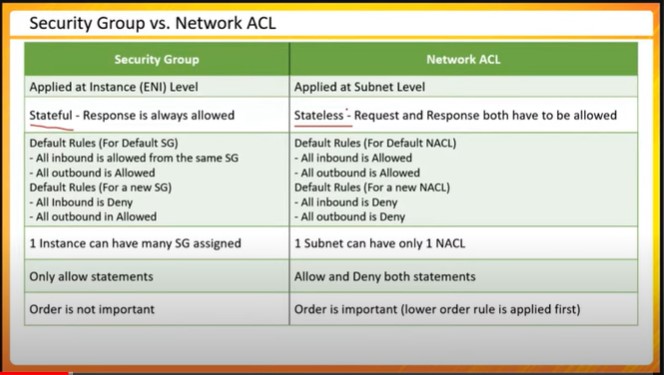
Understanding Network Access Control Lists (NACLs) and Security Groups:
The role of NACLs and security groups in controlling network traffic.
The differences between stateful and stateless firewalls and their implications for security.
Step-by-step guidance on creating and configuring a virtual private cloud (VPC) to implement network security measures.
4. AWS VPC
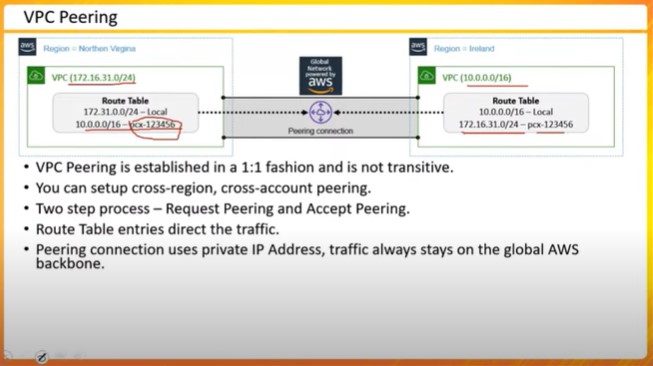
The complex world of designing highly available systems within Amazon Web Services (AWS). It focuses on the creation and management of Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), subnets, route tables, and internet gateways. This highlights the significance of availability zones for system resilience and discusses how to set up public and private subnets for controlled internet access. It also covers VPC peering, which allows communication between VPCs, emphasizing the requirement for non-overlapping CIDR blocks and one-to-one connectivity rules. Furthermore, the session explores options for connecting on-premises workloads to the AWS Cloud, comparing VPNs and AWS Direct Connect based on bandwidth requirements.
Highly Available Architecture
Discusses the need for multiple availability zones
Explains route tables and traffic direction
Shows the creation of VPCs and subnets
VPC Peering and Connectivity
Introduces VPC peering for inter-VPC communication
Details the requirements and limitations of VPC peering
Describes alternative connectivity options
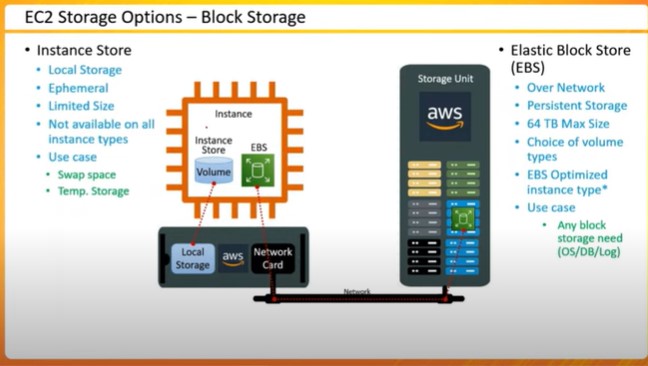
EC2 Instances and Storage Options
Differentiates between shared and dedicated instances
Explains EBS volumes and instance store differences
Suggests EBS for persistent data storage
S3 Storage and Data Protection
Advises on versioning in S3 for data recovery
Discusses object lock to prevent accidental deletion
Compares EBS and S3 for different storage needs
5. S3 Bucket Policies
There is an options for object lock protection, MFA deletion configuration using command line, and bucket policies for controlling access. It also explains how to protect publicly accessible S3 buckets used for static websites without compromising their public visibility. It leverages CloudFront and WAF for enhanced security and incorporates SSL certificate integration.
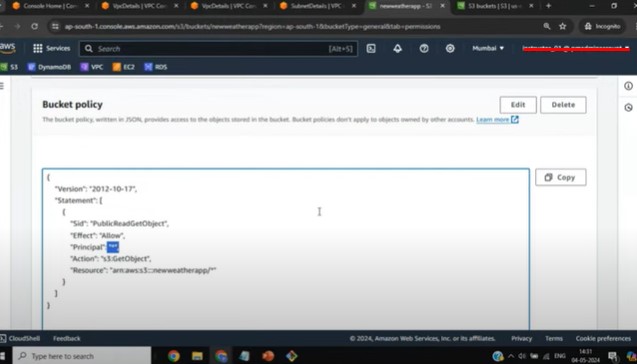
Object Lock and MFA Delete
Explains object lock for write-once-read-many (WORM) model
Details MFA delete setup from command line for added security
Discusses bucket policies and permissions for IAM users
Securing Public S3 Buckets
Describes how to host static websites with S3 without public access
Suggests using CloudFront with HTTPS requests for security
Recommends WAF for additional protection and SSL certificates
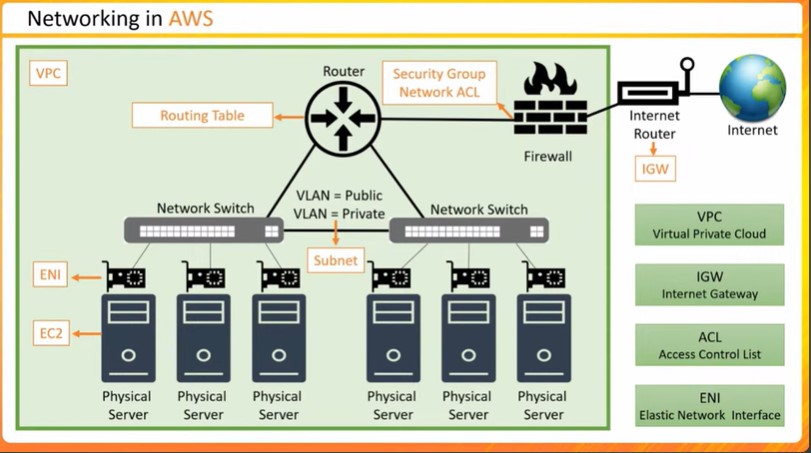
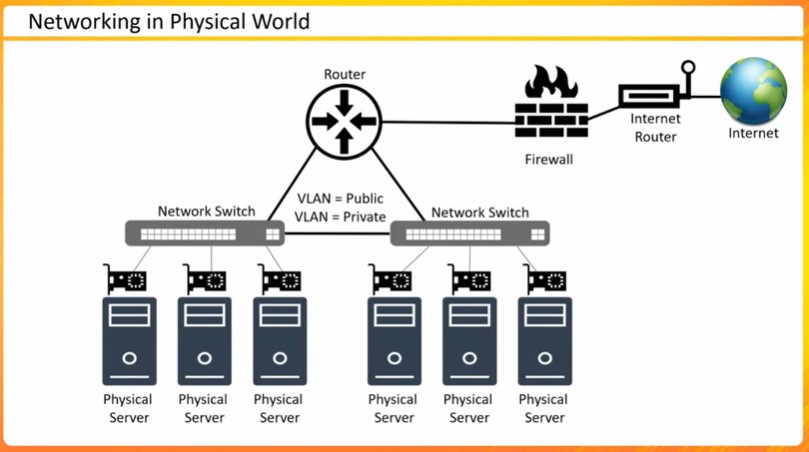
AWS Networking Analogies
Provides analogies to explain AWS networking concepts
Compares physical networking components with AWS services
Illustrates VPC peering and site-to-site VPN with real-world examples
Behavioral Skills for Solutions Architects
Emphasizes the importance of understanding the audience
Highlights the need for clear communication and problem understanding
Discusses the role of analogies and visuals in explaining complex topics
6. Skills For Solution Architect
Following key skills for Solution Architects:
Effective Communication
Clearly conveying technical concepts in accessible language
Using visual aids to explain ideas effectively.
Mastering the core principles of domain.
Effectively planning and prioritizing tasks.
The goal is to make complex ideas understandable to all participants.
Understanding the Basics
Always consider the big picture when answering questions
Start with basic storage types before diving into specifics like EBS, SSD, or HDD
Relate cloud offerings to on-prem knowledge for better understanding
Full Spectrum Explanation
Explain all options available without overwhelming the customer
Use examples to clarify how cloud services translate from on-prem solutions
Focus on what the customer needs to monitor, not just the monitoring tools
Time Management
Manage time effectively during meetings and presentations
Be prepared to follow up with additional information if needed
Ensure the customer understands the discussion and has their questions answered
7. Learn with QnA
These questions focus on the main themes discussed in the session, such as cloud migration, VPC setup, storage options, and the importance of soft skills and consistency in the field of solution architecture.
Q1.How does moving to the cloud change to manage IT resources?
ANSWER: Migrating to the cloud revolutionizes IT resource management by replacing physical hardware with virtualized services. This approach facilitates scalable, adaptable, and economical solutions. Consider Amazon Web Services (AWS), where creating a network via Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) mimics an on-premises network within the cloud. VPCs can extend across multiple availability zones, ensuring high availability. Moreover, the cloud provides managed services, such as NAT Gateways and Direct Connect, which streamline operations and eliminate the need for internal maintenance. Cloud computing also empowers users with comprehensive monitoring and security capabilities. For instance, object-level management in S3 using versioning and utilizing CloudFront with S3 for secure content delivery. In summary, cloud computing offers greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness through its virtualization capabilities, managed services, and robust security measures, making it a compelling option for organizations seeking to transform their IT infrastructure.
Q2.What are the key components of setting up a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) in AWS?
ANSWER: In setting up a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) in AWS, the key components include:
VPC :A virtual network dedicated to your AWS account.
Subnets: Subdivisions of your VPC where you can launch AWS resources.
Route Tables: Define rules to determine where network traffic is directed.
Internet Gateway (IGW): Connects your VPC to the internet.
NAT Gateways: Enable instances in a private subnet to connect to the internet.
Network Access Control Lists (NACLs): Act as a firewall for associated subnets, controlling inbound and outbound traffic.
Security Groups: Act as a virtual firewall for your instances to control inbound and outbound traffic.
For detailed configurations and security, AWS provides various options like VPC peering, VPN connections, and Direct Connect.
Q3.How do availability zones contribute to high availability in cloud architecture?
ANSWER: Availability zones (AZs) are distinct locations within a cloud region that are engineered to be isolated from failures in other AZs. They offer physical redundancy and network connectivity to support high availability. Here’s how they contribute:
Physical Isolation: Each AZ is a separate data center with its own power, cooling, and networking, reducing the risk of simultaneous failures.
Network Connectivity: AZs are interconnected with high-speed, low-latency networking, enabling quick failover and load balancing.
Resource Distribution: By deploying resources across multiple AZs, you can ensure that if one AZ experiences an issue, others can handle the load, minimizing downtime.
Q4.What are the differences between ephemeral and persistent storage in AWS?
ANSWER: Temporary storage, known as instance store, is directly connected to the host computer. It disappears when the instance ends. Permanent storage, like Amazon EBS, is an independent storage space that remains available even after the instance ends. It can be moved from one instance to another, offering more freedom and security. Ephemeral storage is for data that changes quickly and is only needed temporarily. Persistent storage is better for keeping data for a long time.
Q5.Why are behavioral skills important for a Solutions Architect during customer interactions?
ANSWER: Behavioral skills are essential for Solutions Architects (SAs), enabling them to effectively: Communicate and understand customer requirements Explain complex technical concepts clearly and concisely.
Build Rapport: Establish trust and a positive relationship with the customer.
Engage in active listening
Show empathy and understanding
Tailor communication to the customer’s technical level
Clarify Requirements: Ensure a clear understanding of the customer’s problems and goals.
Ask relevant questions
Seek additional context
Reiterate the problem to confirm understanding
Present Solutions: Explain technical solutions in a way that aligns with the customer’s business objectives.
Use analogies and examples
Discuss options and trade-offs
Highlight benefits in a non-technical language
Q6.How does consistency play a role in learning and applying cloud architecture principles?
ANSWER: Staying consistent is vital for learning and using cloud architecture principles. It helps to make steady progress and remember what have been learned. Consistency keeps focusing on goals, motivated, and helps to build on what is already covered. For cloud architecture, practicing consistently allows for better grasp complex ideas, solve problems more effectively, and apply principles skillfully in real-world situations.
Importance of Consistency
Emphasized as key to success in cloud architecture learning
Encouraged to be part of the 5% who consistently engage with content
Highlighted in the context of email engagement statistics
Consistency vs. Motivation
Compared to motivation, which can fluctuate
Consistency depicted as a straight line, indicating steady progress
Suggested as more reliable than sporadic bursts of enthusiasm
Consistent Efforts
Necessary for deepening understanding and skill development
Linked to better outcomes and rewards, like bonus sessions
Presented as a commitment to continuous learning and improvement
8. Summary
This article provides a comprehensive guide to setting up and securing networks in AWS, including Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), subnets, route tables, and security measures such as NACLs and security groups. It also covers AWS networking concepts, highly available architectures, VPC peering, connectivity options, and storage solutions like S3. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of behavioral skills and effective communication for Solution Architects. The document concludes with a Q&A section addressing key topics in cloud migration, VPC setup, storage options, and the significance of consistent learning in cloud architecture.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Muhammad Irfan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Muhammad Irfan
Muhammad Irfan
I am passionate about the transformative power of Linux, DevOps, and cloud technologies. With a background in system administration, I’m on a journey to master cloud infrastructure, automation, and containerization. On my GitHub, you’ll find projects where I explore automation, AWS, CI/CD, and scripting to solve real-world problems. 📚 Current Focus: Enhancing my expertise in Linux systems, AWS, and scripting. Here, I share insights and experiences from my hands-on projects to help and inspire fellow tech enthusiasts.