3/09 - TVET STEPS and The Asian Nations
 Nana Azhar
Nana Azhar
Summary
This table provides a generalized view across the typical Asian nations' TVET strategies. The ratings reflect an overall "Medium" level due to the diversity in economic development, resources, and governmental support which results in varied effectiveness and implementation of TVET strategies across the continent.

To have a better look at how some nations fare within these region, let view several cases form this region.
CASE #1

Japan: TVET strategy across the TVET STEPS

Explanation:
SkillsFirst: Japan's vocational training is notable for its rigor and alignment with technological advancements and industry requirements, meriting a "Very Strong" rating.
SkillsFusion: The integration of theory and practice is deeply embedded in Japan's educational philosophy, particularly through the system of "Kosen" (Colleges of Technology), which combines high-level engineering education with practical skills training.
SkillsForward: Innovation is central to Japan's approach to TVET, particularly in fields like robotics, automotive engineering, and electronics, making it a leader in incorporating cutting-edge technology into vocational training.
SkillsAdapt: While Japan has robust programs for lifelong learning and skills development, there are opportunities to increase engagement and participation across a broader segment of the population.
Overall, Japan's TVET system is one of the most advanced and well-integrated globally, reflecting the country's commitment to maintaining a highly skilled workforce. The slight caveat in the "SkillsAdapt" area points to the potential for even greater emphasis on encouraging broader participation in ongoing education and training programs.
CASE #2

South Korea's TVET strategy across the TVET STEPS

Explanation:
SkillsFirst: South Korea's vocational training is notably advanced, with substantial government and corporate investment ensuring that training programs are closely aligned with industry needs and technological advancements, earning a "Very Strong" rating.
SkillsFusion: The country’s educational policies successfully blend theoretical knowledge with practical skills, supported by world-class training facilities and a curriculum that meets the high demands of its industrial sectors.
SkillsForward: Innovation is a hallmark of the South Korean approach to TVET, with ongoing efforts to integrate cutting-edge technology and foster a culture of continuous improvement in vocational education.
SkillsAdapt: While South Korea has a solid framework for promoting lifelong learning and professional development, enhancing the reach and engagement of these programs could further improve their effectiveness.
Overall, South Korea's TVET system ranks among the best globally, reflecting the country's commitment to maintaining a competitive edge by investing in a highly skilled workforce. The system's slight limitations in "SkillsAdapt" highlight areas where there could be more focus on ensuring that lifelong learning opportunities are accessible and appealing to all segments of the population.
CASE #3

Singapore's TVET strategy across the TVET STEPS

Singapore's TVET strategy is exemplary, characterized by a comprehensive and forward-thinking approach that not only prepares students for immediate employment but also ensures continual growth and adaptability in a rapidly changing global job market. The nation's investment in both foundational and advanced training, coupled with strong government support for lifelong learning, sets a high standard for TVET systems worldwide.
CASE #4

China's TVET strategy across the TVET STEPS
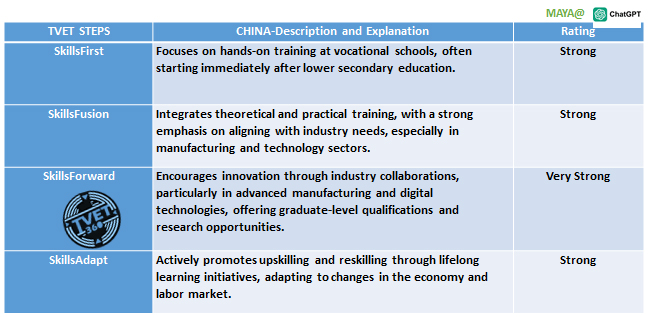
China's approach to TVET is robust, with a comprehensive strategy that effectively addresses each stage from foundational skills to advanced innovation and lifelong learning. The strong alignment with industry needs and the emphasis on continual learning are particularly noteworthy, ensuring that the workforce remains adaptable and competitive.
CASE #5

Malaysia's TVET strategy across the TVET STEPS

Explanation:
SkillsFirst: Malaysia excels in providing comprehensive hands-on training that aligns well with industry requirements, which is indicative of a strong implementation under the TVETSTEPS Rubrics criteria.
SkillsFusion: The integration of theoretical knowledge with practical training is effective, ensuring good industry relevance and preparing students for real-world applications, meeting the criteria for a strong rating.
SkillsForward: Malaysia's focus on innovation is present but still developing. The existence of some industry PhD programs and collaborations indicates progress, but it's not as extensive or mature as in countries with very strong innovation ecosystems, thus earning a medium rating.
SkillsAdapt: Efforts in lifelong learning are in place, but the reach and effectiveness of these programs are not as comprehensive as they could be, warranting a medium rating.
Disclaimer
All evaluations conducted by TVET360 are for educational purposes only. Although these evaluations are valid and based on reliable sources, they are not intended to degrade, belittle, or criticize any country. We respect the unique strengths, cultures, and challenges of each nation. For the most accurate and personalized information, individuals should consult local experts, official sources, and consider the specific context of their situation.
Thank you for your time ❤️
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nana Azhar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
