Quickstart Guide to Develop on ZKSync : Explore Basic Paymaster (Chapter 3)
 Ridho Izzulhaq
Ridho IzzulhaqIn the previous chapter, we discussed the idea atlas and dApps on ZKsync. In this chapter, we will explore account abstraction and paymasters on ZKsync.
Note : in this chapter we use ATLAS IDE, for further guide about ATLAS IDE, let's check the previous chapter
Account Abstraction
Account abstraction refers to the concept of making Ethereum accounts more flexible by allowing them to function like smart contracts. This means accounts can have custom logic for handling transactions, security, and fee payment mechanisms, providing a higher level of programmability and security customization than the traditional model.
Account abstraction emerged in response to several limitations in how users interact with Ethereum through externally owned accounts (EOAs). In the traditional Ethereum model, only EOAs can initiate transactions or execute smart contracts. This restricts users' flexibility in interacting with Ethereum, such as making it difficult to batch transactions and requiring users to always maintain an ETH balance to cover gas fees.
One of the common applications of account abstraction is the use of paymasters. Paymasters are specialized smart contracts that manage the payment of transaction fees on behalf of users. They play a crucial role in making Ethereum more user-friendly and flexible by allowing users to interact with the blockchain without needing to hold ETH for gas fees. Here’s how they work and why they’re important:
Fee Sponsorship: Paymasters can cover gas fees for users, enabling transactions to be executed without the sender needing ETH. This can be particularly useful for onboarding new users who may not yet have ETH but want to interact with decentralized applications (DApps).
Custom Payment Methods: With paymasters, users can pay for gas fees using tokens other than ETH, such as ERC20 tokens. This broadens the accessibility and usability of Ethereum-based applications, as users can choose their preferred token for transaction fees.
Thanks to ZKSync for Native AA and Paymaster :
Thanks to ZKsync, native paymasters in their ecosystem bring a revolutionary way of managing transaction fees, making blockchain interactions smoother and more accessible.
Every paymaster has the following two functions:
validateAndPayForPaymasterTransaction: this function uses the transaction parameters (fields likefrom,amount,to) to execute the required validations and pay for the transaction fee.postTransaction: this optional function runs after the transaction is executed
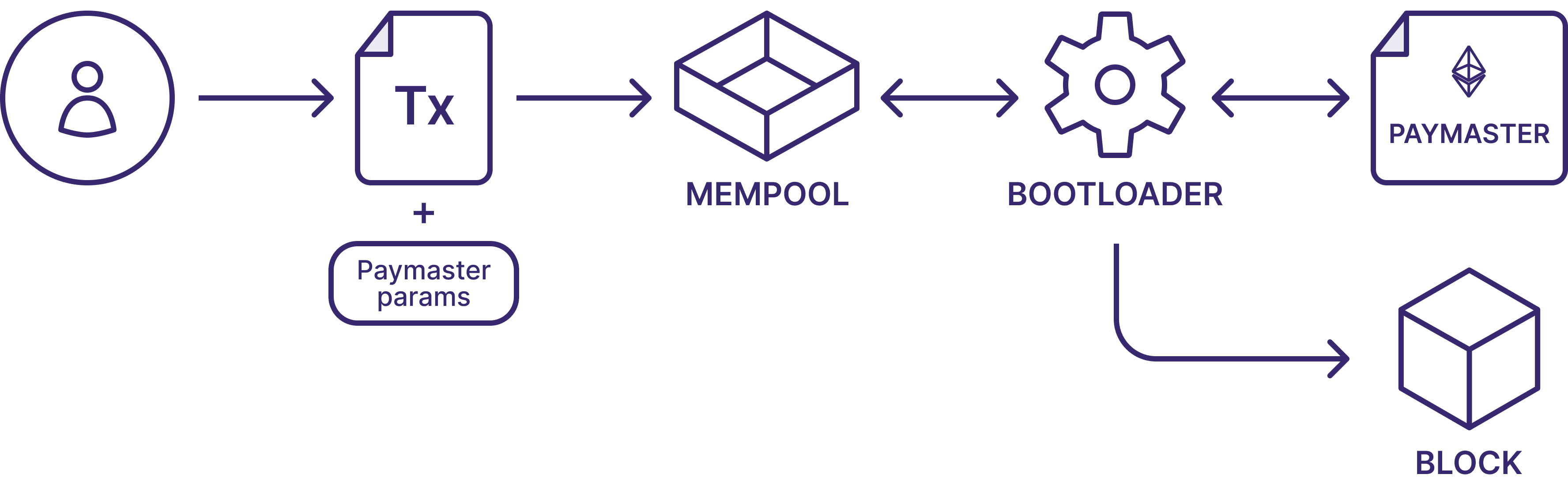
Example of paymaster information directly connected to the blockchain explorer :
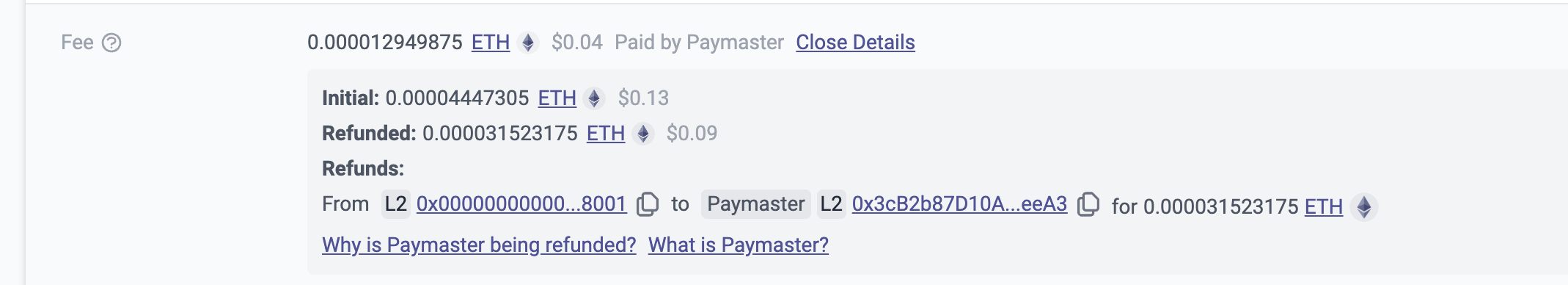
Let's Try to Develop Our First Paymester
Similarly to previous chapter, we will use the ATLAS IDE. In this stage, we will continue using the ATLAS IDE, specifically the ZKsync paymaster template provided by ZKsync. click for the template!
There are 2 contracts here:
TestToken.sol for creating a new token and ZeekMessages.sol, which is the contract used to test the Paymaster by allows users to send and store messages. It also provides functionalities to retrieve the total number of messages and the last message sent. Here is a detailed explanation of the contract's components and usage
import * as zk from "zksync-ethers";
import { default as hre, ethers } from "hardhat";
import { getDeployer } from "@atlas-labs-inc/hardhat-atlas-zksync-deploy";
// Address of the ZeekMessages contract
const ZEEK_MESSAGES_CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "0x26C6e7b1896c3807D6b8df9Bdd407755F9eB17dd";
// Address of the ERC20 token contract
const TOKEN_CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "0xfe92f30411F2871653Acbb16f613B3b2379e304F";
// Message to be sent to the contract
const NEW_MESSAGE = "This tx cost me no ETH!";
async function main() {
// connects to the wallet connected in the network tab -->
const { provider, signer } = await getDeployer(hre);
const zkProvider = new zk.Provider("https://sepolia.era.zksync.dev");
const signerAddress = await signer.getAddress();
console.log("Sending a transaction via the testnet paymaster");
// initialise messages and token contracts with address, abi and signer
const messagesContract = new zk.Contract(
ZEEK_MESSAGES_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
(await ethers.getContractFactory("ZeekMessages")).interface,
signer
);
const tokenContract = new zk.Contract(
TOKEN_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
(await ethers.getContractFactory("TestToken")).interface,
signer
);
// retrieve and print the current balance of the wallet
let ethBalance = await provider.getBalance(signerAddress);
let tokenBalance = await tokenContract.balanceOf(signerAddress);
console.log(
`Account ${signerAddress} has ${ethers.formatEther(ethBalance)} ETH`,
);
console.log(
`Account ${signerAddress} has ${ethers.formatUnits(
tokenBalance,
18,
)} tokens`,
);
// retrieve the testnet paymaster address
const testnetPaymasterAddress = await zkProvider.getTestnetPaymasterAddress();
console.log(`Testnet paymaster address is ${testnetPaymasterAddress}`);
const gasPrice = await zkProvider.getGasPrice();
// define paymaster parameters for gas estimation
const paramsForFeeEstimation = zk.utils.getPaymasterParams(
testnetPaymasterAddress,
{
type: "ApprovalBased",
token: TOKEN_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
// set minimalAllowance to 1 for estimation
minimalAllowance: ethers.toBigInt(1),
// empty bytes as testnet paymaster does not use innerInput
innerInput: new Uint8Array(0),
},
);
// estimate gasLimit via paymaster
const gasLimit = await messagesContract.sendMessage.estimateGas(NEW_MESSAGE, {
customData: {
gasPerPubdata: zk.utils.DEFAULT_GAS_PER_PUBDATA_LIMIT,
paymasterParams: paramsForFeeEstimation,
},
});
// fee calculated in ETH will be the same in
// ERC20 token using the testnet paymaster
const fee = gasPrice * gasLimit;
// new paymaster params with fee as minimalAllowance
const paymasterParams = zk.utils.getPaymasterParams(testnetPaymasterAddress, {
type: "ApprovalBased",
token: TOKEN_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
// provide estimated fee as allowance
minimalAllowance: fee,
// empty bytes as testnet paymaster does not use innerInput
innerInput: new Uint8Array(0),
});
// full overrides object including maxFeePerGas and maxPriorityFeePerGas
const txOverrides = {
maxFeePerGas: gasPrice,
maxPriorityFeePerGas: "1",
gasLimit,
customData: {
gasPerPubdata: zk.utils.DEFAULT_GAS_PER_PUBDATA_LIMIT,
paymasterParams,
},
};
console.log(`Sign the transaction in your wallet`);
// send transaction with additional paymaster params as overrides
const txHandle = await messagesContract.sendMessage(NEW_MESSAGE, txOverrides);
console.log(
`Transaction ${txHandle.hash} with fee ${ethers.formatUnits(
fee,
18,
)} ERC20 tokens, sent via paymaster ${testnetPaymasterAddress}`,
);
await txHandle.wait();
console.log(`Transaction processed`);
ethBalance = await provider.getBalance(signerAddress);
tokenBalance = await tokenContract.balanceOf(signerAddress);
console.log(
`Account ${signerAddress} now has ${ethers.formatEther(ethBalance)} ETH`,
);
console.log(
`Account ${signerAddress} now has ${ethers.formatUnits(
tokenBalance,
18,
)} tokens`,
);
console.log(`Done!`);
}
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract ZeekMessages {
string[] private messages;
// Event to acknowledge a new message
event MessageReceived(string);
constructor() {
// Zeek initializes the contract with a welcome message
emit MessageReceived("Zeek welcomes you to zkSync!");
}
function sendMessage(string memory _message) public {
messages.push(_message);
// Acknowledge the message receipt with Zeek's reply
emit MessageReceived("ZK is the endgame - Message received!");
}
// Function to count the total messages sent to Zeek
function getTotalMessages() public view returns (uint256) {
return messages.length;
}
// Function to return the last message sent to Zeek
function getLastMessage() public view returns (string memory) {
require(messages.length > 0, "No messages sent to Zeek yet!");
return messages[messages.length - 1];
}
}
In short, you just need to deploy both of them!
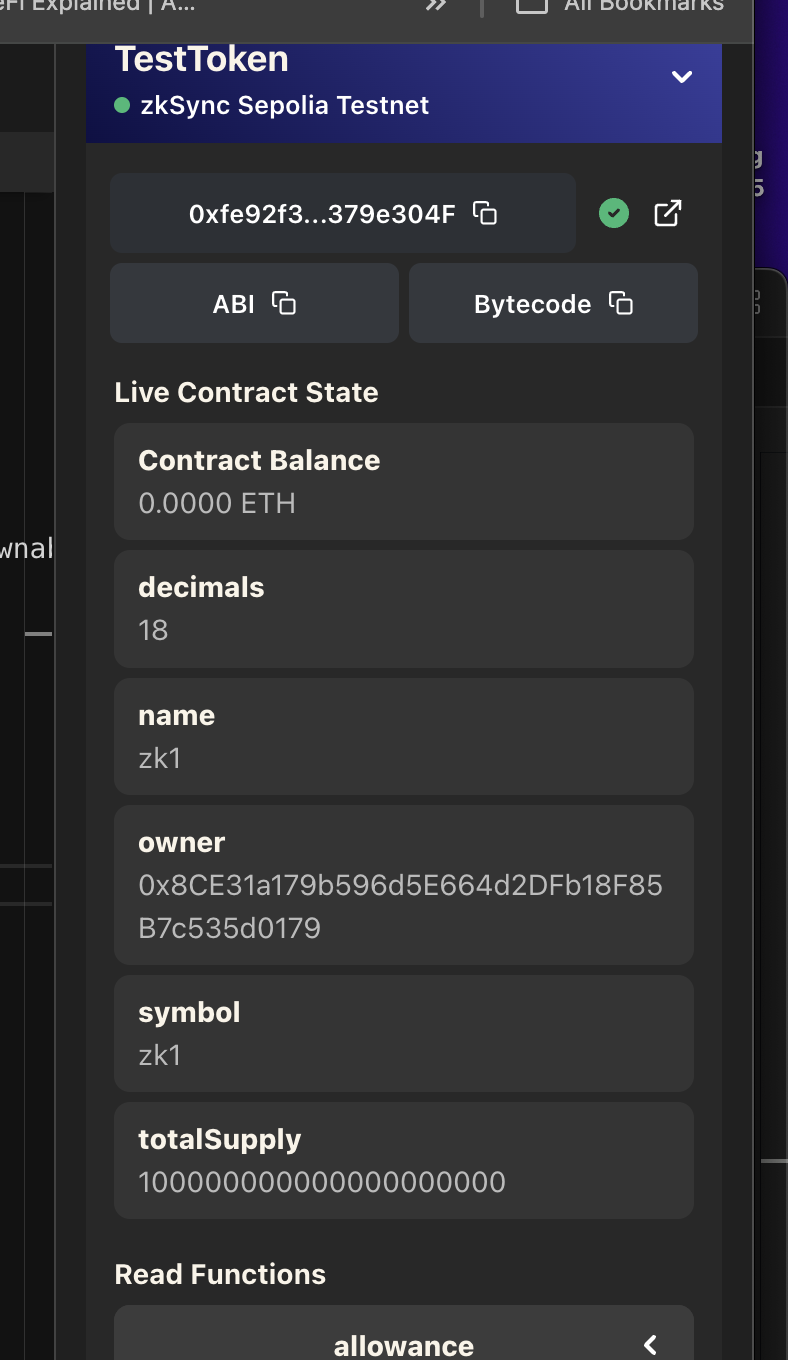
Run the Typescript Paymaster
Configuration of the addresses and input of your first message at paymaster-transaction.ts
// Address of the ZeekMessages contract
const ZEEK_MESSAGES_CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "0x26C6e7b1896c3807D6b8df9Bdd407755F9eB17dd";
// Address of the ERC20 token contract
const TOKEN_CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "0xfe92f30411F2871653Acbb16f613B3b2379e304F";
// Message to be sent to the contract
const NEW_MESSAGE = "This tx cost me no ETH!";
And run your fist paymaster program
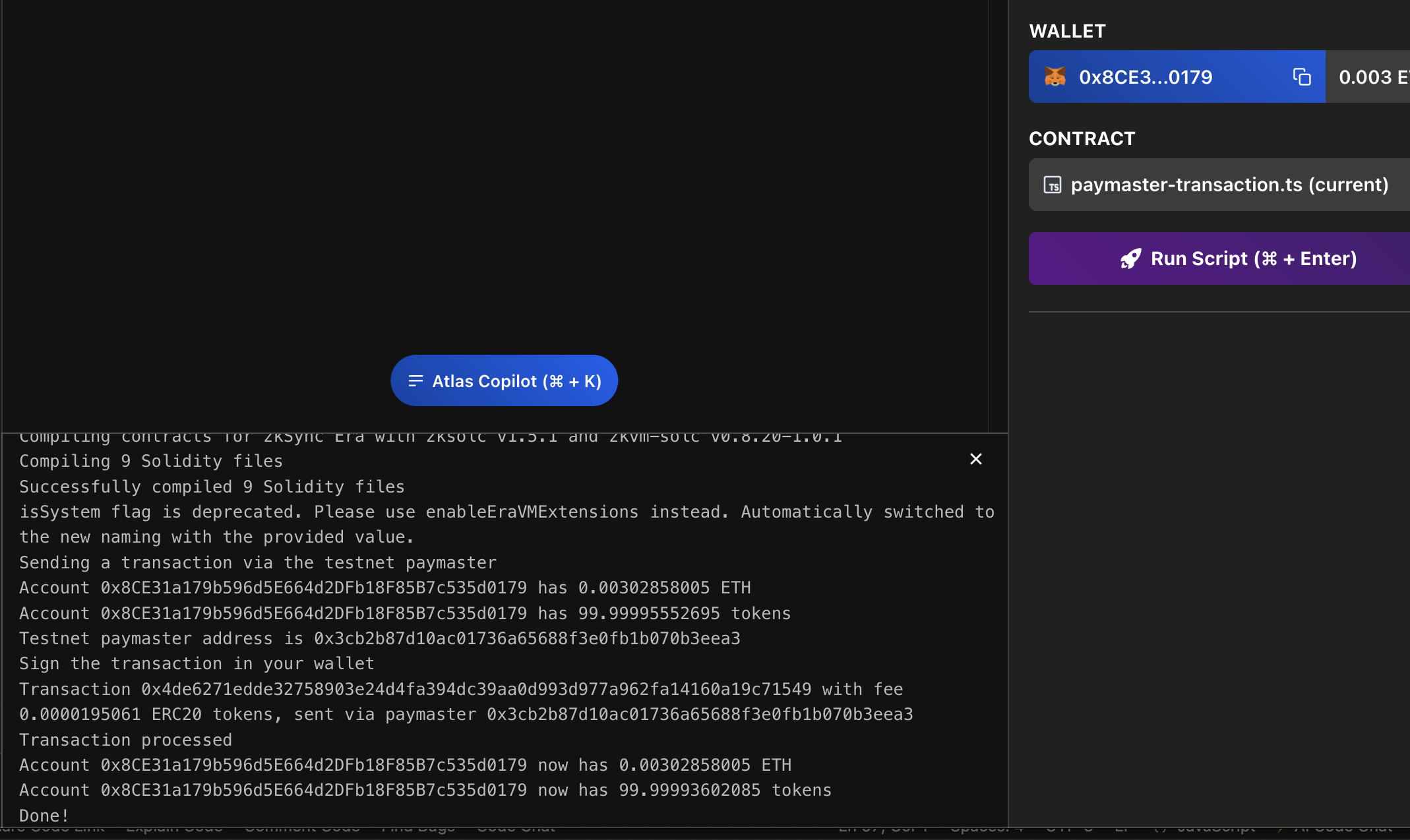
We can view the transaction hash programmatically on ZKsync's explorer and observe how the paymaster natively functions by charging transaction fees in the ERC-20 token we create and performing ETH refunds.
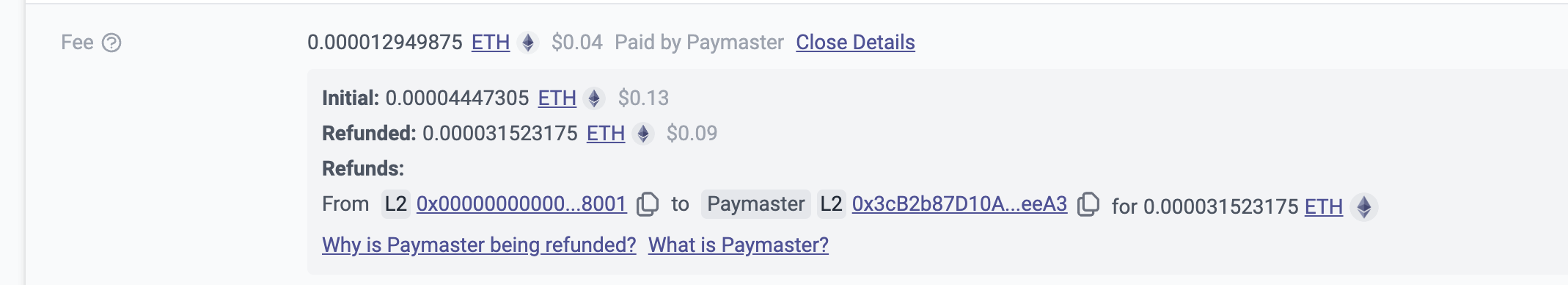
Build Paymaster for Voting Smart Contract (Chapter 2 Code)
In Chapter 2, we discussed a voting DAPP and deployed a smart contract related to it on ZKSync. Now, let's implement a paymaster to vote for candidate 1 on that contract.
Vote.sol :
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.9;
contract Voting {
struct Candidate {
uint id;
string name;
uint voteCount;
}
mapping(uint => Candidate) public candidates;
mapping(address => bool) public voters;
uint public candidatesCount;
constructor(string[] memory _candidateNames) {
for (uint i = 0; i < _candidateNames.length; i++) {
addCandidate(_candidateNames[i]);
}
}
function addCandidate(string memory _name) private {
candidatesCount++;
candidates[candidatesCount] = Candidate(candidatesCount, _name, 0);
}
function vote(uint _candidateId) public {
require(!voters[msg.sender], "You have already voted.");
require(_candidateId > 0 && _candidateId <= candidatesCount, "Invalid candidate ID.");
voters[msg.sender] = true;
candidates[_candidateId].voteCount++;
}
function getVotes(uint _candidateId) public view returns (uint) {
require(_candidateId > 0 && _candidateId <= candidatesCount, "Invalid candidate ID.");
return candidates[_candidateId].voteCount;
}
}
Note : For more smart contract explain, visit chapter 2
Build paymaster-vote.ts
import * as zk from "zksync-ethers";
import { default as hre, ethers } from "hardhat";
import { getDeployer } from "@atlas-labs-inc/hardhat-atlas-zksync-deploy";
// Address of the Voting contract
const VOTING_CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "";
// Address of the ERC20 token contract
const TOKEN_CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "";
// Candidate ID to vote for
const CANDIDATE_ID = 2;
async function main() {
// Connects to the wallet connected in the network tab
const { provider, signer } = await getDeployer(hre);
const zkProvider = new zk.Provider("https://sepolia.era.zksync.dev");
const signerAddress = await signer.getAddress();
console.log("Sending a transaction via the testnet paymaster");
// Initialize the Voting and token contracts with address, ABI, and signer
const votingContract = new zk.Contract(
VOTING_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
(await ethers.getContractFactory("Vote")).interface,
signer
);
const tokenContract = new zk.Contract(
TOKEN_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
(await ethers.getContractFactory("TestToken")).interface,
signer
);
// Debug: Log contract addresses and signer address
console.log(Voting Contract Address: ${VOTING_CONTRACT_ADDRESS});
console.log(Token Contract Address: ${TOKEN_CONTRACT_ADDRESS});
console.log(Signer Address: ${signerAddress});
// Retrieve and print the current balance of the wallet
try {
let ethBalance = await provider.getBalance(signerAddress);
let tokenBalance = await tokenContract.balanceOf(signerAddress);
console.log(Account ${signerAddress} has ${ethers.formatEther(ethBalance)} ETH);
console.log(Account ${signerAddress} has ${ethers.formatUnits(tokenBalance, 18)} tokens);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error retrieving balances:", error);
}
// Retrieve the testnet paymaster address
const testnetPaymasterAddress = await zkProvider.getTestnetPaymasterAddress();
console.log(Testnet paymaster address is ${testnetPaymasterAddress});
const gasPrice = await zkProvider.getGasPrice();
// Define paymaster parameters for gas estimation
const paramsForFeeEstimation = zk.utils.getPaymasterParams(testnetPaymasterAddress, {
type: "ApprovalBased",
token: TOKEN_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
minimalAllowance: ethers.toBigInt(1),
innerInput: new Uint8Array(0),
});
// Estimate gasLimit via paymaster
const gasLimit = await votingContract.vote.estimateGas(CANDIDATE_ID, {
customData: {
gasPerPubdata: zk.utils.DEFAULT_GAS_PER_PUBDATA_LIMIT,
paymasterParams: paramsForFeeEstimation,
},
});
// Fee calculated in ETH will be the same in ERC20 token using the testnet paymaster
const fee = gasPrice * gasLimit;
// New paymaster params with fee as minimalAllowance
const paymasterParams = zk.utils.getPaymasterParams(testnetPaymasterAddress, {
type: "ApprovalBased",
token: TOKEN_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
minimalAllowance: fee,
innerInput: new Uint8Array(0),
});
// Full overrides object including maxFeePerGas and maxPriorityFeePerGas
const txOverrides = {
maxFeePerGas: gasPrice,
maxPriorityFeePerGas: "1",
gasLimit,
customData: {
gasPerPubdata: zk.utils.DEFAULT_GAS_PER_PUBDATA_LIMIT,
paymasterParams,
},
};
console.log(Sign the transaction in your wallet);
// Send transaction with additional paymaster params as overrides
const txHandle = await votingContract.vote(CANDIDATE_ID, txOverrides);
console.log(Transaction ${txHandle.hash} with fee ${ethers.formatUnits(fee, 18)} ERC20 tokens, sent via paymaster ${testnetPaymasterAddress});
await txHandle.wait();
console.log(Transaction processed);
// Retrieve and print the updated balance of the wallet
ethBalance = await provider.getBalance(signerAddress);
tokenBalance = await tokenContract.balanceOf(signerAddress);
console.log(Account ${signerAddress} now has ${ethers.formatEther(ethBalance)} ETH);
console.log(Account ${signerAddress} now has ${ethers.formatUnits(tokenBalance, 18)} tokens);
console.log(Done!);
}
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
Please configure by including the deployed voting contract and token address, then enter the candidate ID you wish to vote for
const VOTING_CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "";
// Address of the ERC20 token contract
const TOKEN_CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "";
// Candidate ID to vote for
const CANDIDATE_ID = 2;
Code that execute the transaction :
const txHandle = await votingContract.vote(CANDIDATE_ID, txOverrides);
console.log(Transaction ${txHandle.hash} with fee ${ethers.formatUnits(fee, 18)} ERC20 tokens, sent via paymaster ${testnetPaymasterAddress});
await txHandle.wait();
console.log(Transaction processed);
ZyFi: Instant Paymaster with just one API shortcut
ZyFi is a Paymaster-as-a-Service platform built for flexibility and seamless integration, aimed at enhancing the adoption of paymasters within the zkSync ecosystem. It has already been successfully implemented with various blockchain DApps, including PancakeSwap. I recommend checking out the tutorial on ZyFi integration in docs and magic link tutorial to delve deeper into understanding ZyFi capabilities and integration possibilities.
Closing
Thank you for your support and interest in this series of articles, which is part of a grant program available at Wave Hacks on Akindo.
Structure :
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ridho Izzulhaq directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
