A Framework for Building Blockchain-Based Secured E-voting
 Abhishek Kandel
Abhishek Kandel
In an age where digital transformation is revolutionizing various sectors, the importance of secure and transparent voting systems in democratic societies is paramount.. Traditional voting methods face challenges such as tampering, errors, and logistical issues. Our research presents a novel approach to e-voting using blockchain technology, promising enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency.
Introduction
As the world continues to embrace digital transformation, the importance of secure and transparent voting systems in democratic societies cannot be overstated. Traditional voting methods are susceptible to tampering, errors, and significant logistical challenges. In a large democratic country like India, with a population exceeding a billion, ensuring a secure, tamper-free, and fraud-resistant voting system is crucial. Our research proposes a novel approach to electronic voting using blockchain technology, offering a decentralized and distributed ledger system to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency.
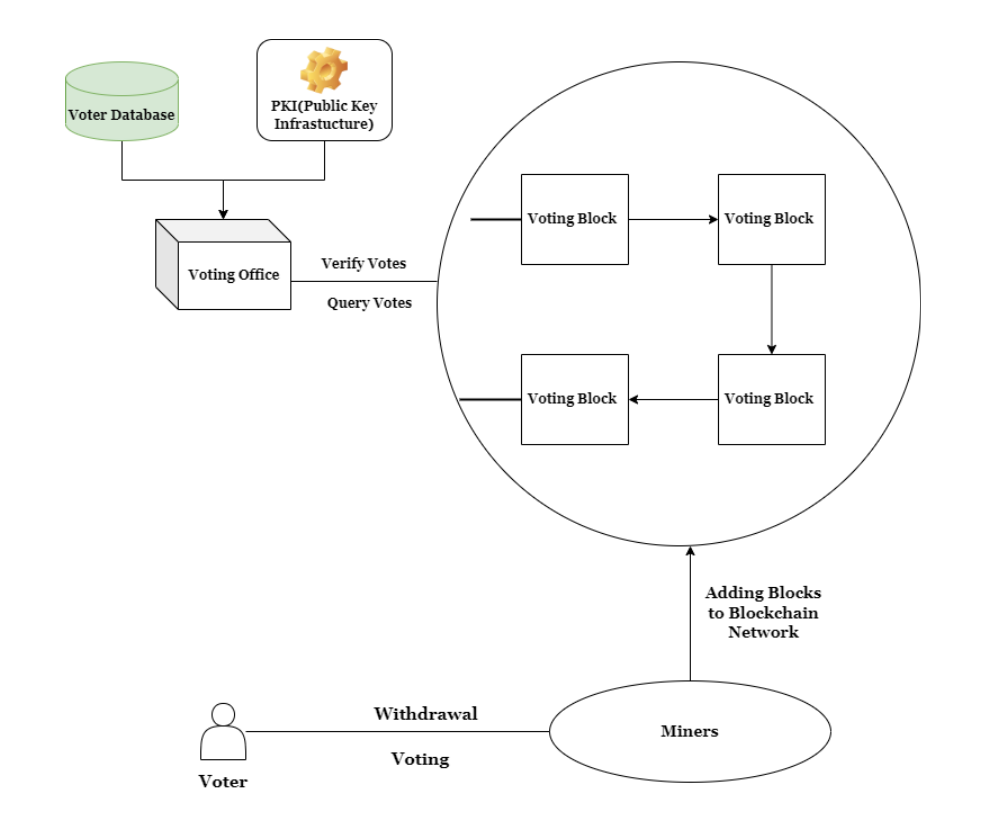
Blockchain Technology and E-voting
Blockchain technology, known for its decentralized and distributed nature, incorporates robust cryptographic principles to create effective security mechanisms. Each block in the blockchain is secured using a unique cryptographic hash, which acts as a fingerprint for each block. Any tampering with the data within a block changes its hash value, thereby preventing malicious activities and ensuring data integrity.
Our research highlights the successful adoption of blockchain-based e-voting systems in countries like Switzerland, Norway, and Estonia. These systems leverage blockchain’s core features:
Immutability: A cryptographic hash value assigned to each new block creates a secure and unchangeable chain, keeping all entries tamper-free.
Decentralization: The distributed network of blocks requires consensus before adding new blocks, enhancing security and reducing the risk of single-point failures.
Verifiability: The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures high accessibility, allowing all nodes to maintain the consensus version of the network.
Proposed E-voting Model
Our proposed e-voting model aims to address critical challenges such as voter privacy, vote secrecy, and end-to-end verification. By utilizing blockchain technology, our model ensures:
User Authenticity: Each voting transaction is safeguarded using a strong cryptographic hash, ensuring the confidentiality and authenticity of each vote. Eligible voters receive this hash value over secure communication channels.
Transparency and Security: The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain provides a transparent and secure platform for e-voting, reducing the risk of tampering and fraud.
Literature Review
Several research works have explored the integration of blockchain technology into e-voting systems, each offering unique approaches and methodologies:
Garg et al. implemented a smart contract-based Boardroom Voting system, ensuring voter anonymity using the Open Vote Network.
Abuidris et al. developed an end-to-end indisputable model using a token-based voting system, designed for governments and institutions.
Alam et al. researched digital voting integrated with blockchain, allowing eligible voters to issue votes through web browsers or voting districts.
Curran et al. proposed decentralized apps and Ethereum blockchain for e-voting, incorporating biometric readers for voter authentication.
Hsiao et al. designed a blockchain-based e-voting model using SHA-256 to secure the blockchain and manage user authentication.
Conclusion and Future Scope
Our research presents a secure and functional electronic voting system utilizing blockchain technology. This system addresses significant issues in the traditional voting process, providing a robust solution for large democratic countries like India. By ensuring user authenticity, vote secrecy, and end-to-end verification, our proposed model paves the way for a more secure and transparent voting process.
As we continue to refine our model, future improvements could focus on enhancing the scalability of the blockchain network, integrating advanced cryptographic techniques, and conducting extensive real-world testing to ensure the system’s robustness and reliability.
For the full paper and detailed analysis, you can read our publication on IEEE Xplore
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Abhishek Kandel directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Abhishek Kandel
Abhishek Kandel
Self-driven, quick starter, passionate programmer with a curious mind who enjoys solving a complex and challenging real-world problems.