How VPN works (step-by-step guide with diagrams)
 Vignesh Aithal
Vignesh Aithal
What is a VPN?
A VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It gives users a secure way to browse the internet by hiding their IP address and encrypting their data.
As the name says VPN is,
Virtual - Meaning no physical connection with the server.
Private - No one involved will know who you are.
Network - A group of servers interlinked.

Why do I need it?
You need a VPN because, the internet by default is not secure nor private.

Yes, you see the internet shares details such as your IP address, your browsing history, etc. to the ISP(Internet Service Provider) and the website you are visiting.
This was fine a few decades ago when, marketers were not so innovative.
But, now they want to show you personalised ads so, they want to track you as much as possible.
And also the ISP can track and block content based on your location. Like during elections they can block certain parties website for you.
Here is how the current internet works.
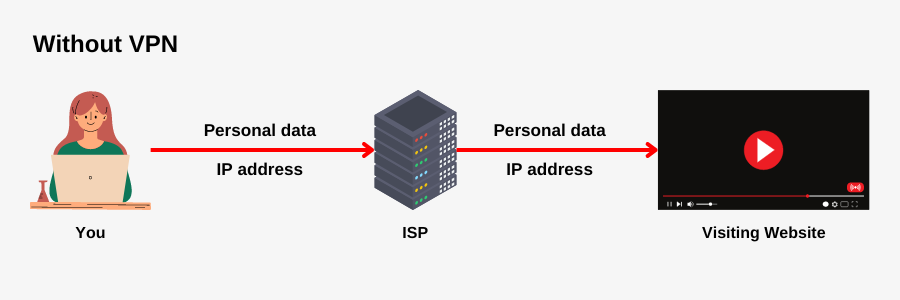
For example if you visit YouTube on your laptop, here is how the process looks like,
First you type YouTube.com.
Then the request is sent to your ISP which can see your IP address, your personal data such as browsing history, etc.
Then it passes that request along with your personal data to our desired website server i.e. in our case YouTube server. Which can also see our IP address, personal data.
And this process also continues for data returned from YouTube to you.
So, here we can see the internet is neither secure nor private. Both the parties involved can see what all you browse and can find your location by using your IP address.
What all data do they collect?
ISP and websites collect a wide range of data such as,
IP Address: IP address can be used to track your exact geographical location and be used to track your online activities.
Browsing history: Your ISP can log your browsing history with URL, timestamps, etc.
DNS Request: Whenever you visit a website you make a DNS request to that site, which converts the domain name such as google.com to an IP address such as 8.8.8.8. The ISP can also log these requests.
Referral URL: When you click on a link to visit a website, the referrer URL (the URL of the previous page you were on) is sent to the new website, helping websites understand how you arrived at their site.
Session Data: Websites can track what you do during a session, like which pages you visit, how long you stay on each page, what you click on, and how you interact with things like videos and ads.
Behavioural Data: Websites often use tracking scripts and analytics tools(like Microsoft Clarity, Hotjar) to watch what you do, including how you move through the site, scroll, move your mouse, and interact with different parts of the site.
Third Party Trackers: Many websites use third-party trackers (like Google Analytics and Facebook Pixel) to collect data about your visit and share it with other companies for ads and analytics.
So, without a VPN, your ISP and the websites can see a lot of information about your online activity. This can affect your privacy, security, and overall internet experience.
How does a VPN work?
So, VPN must use a different method right?
Yes, it does.
The VPN does these three things to solve the internets inherent problem,
Encrypt Data: It encrypts your personal data on-device before sending it to the ISP. So, that the ISP can't see your personal data.
Send request to VPN server : The ISP will pass your request to the VPN server instead of the actual website because, the VPN app routes all requests to the VPN server. So, this way the ISP can't know which website you are visiting. All requests are to the same server. Sorry ISP 🤣
Mask IP: It replaces your original IP with their custom ones which makes websites difficult to track you as your VPN server IP may be pooled i.e. many thousands, millions of that VPN users may have this same IP address.
Now lets see how this process works,
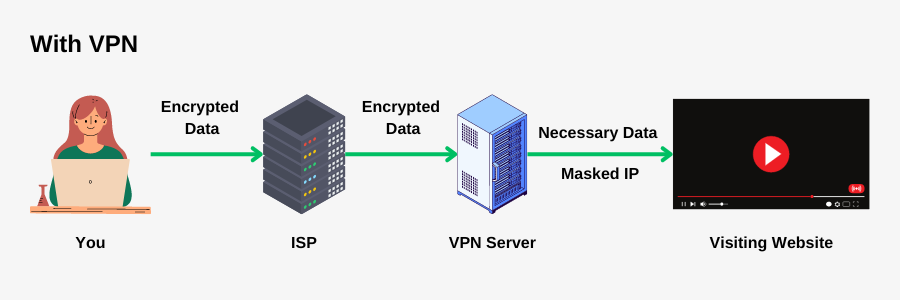
From above diagram you can see,
First the data is encrypted on-device before sending to the ISP.
Then the ISP sends it to the VPN server. It then decrypts to get website data.
Then it masks your IP and passes the necessary data required(such as login info, your preferences) to the website.
Then this processes continues for the return of data from the website to your device.
Common VPN protocols
| Protocol | Description | Use Case |
| OpenVPN | An open-source protocol known for balancing speed and security. It’s very customizable and widely used. | Best overall use |
| L2TP/IPsec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) | Combines the best features of two protocols. L2TP establishes the tunnel, while IPsec handles the encryption. It’s secure but can be slower due to double encapsulation. | Best option for basic setup |
| IKEv2 / IPSec (Internet Key Exchange version 2) | IKEv2 is a protocol often used with IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) for great security and speed. IKEv2/IPSec is excellent because it keeps your connection stable even when your internet is unstable or you’re switching between cellular data and Wi-Fi. This makes it the best choice for mobile VPNs. | Best option for mobile browsing |
| WireGuard | WireGuard is a new and popular protocol in the VPN world. It has a smaller codebase, modern encryption, and works well on mobile devices. Like OpenVPN, it is also open-source. | Best option for early adopters |
Pros and Cons of Using a VPN

Pros
Enhanced Security: VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, making it hard for hackers and other malicious entities to intercept and access your data. This is especially important when using public Wi-Fi networks, which are often insecure
Privacy Protection: A VPN hides your IP address, making your online activities almost untraceable. This helps protect your privacy from ISPs, advertisers, and government surveillance.
Access to Geo-Restricted Content: VPNs allow you to bypass geographic restrictions on content by connecting to servers in different countries. This means you can access streaming services, websites, and other online content that may be unavailable in your region.
Avoiding Censorship: In countries with strict internet censorship, a VPN can help you access blocked websites and services, providing a freer and more open internet experience.
Secure Remote Work: VPNs are widely used in business environments to enable secure remote access to company networks. This ensures that employees can safely access company resources from anywhere without compromising security.
Avoiding ISP Throttling: Some ISPs throttle (slow down) your internet speed based on your online activities, such as streaming or downloading large files. A VPN hides your activities from your ISP, helping to prevent throttling and maintain consistent speeds.
Safe Online Shopping: When shopping online, especially on unfamiliar or unsecured websites, a VPN provides an extra layer of security by encrypting your payment information and personal details.
Anonymity: By masking your IP address and routing your traffic through a VPN server, a VPN helps maintain your anonymity online. This can be particularly useful for activists, journalists, and anyone concerned about their online privacy.
Cons
Reduced Internet Speed: VPNs can slow down your internet connection because your data is being routed through additional servers. This can affect activities that require high bandwidth, like streaming or online gaming.
Expensive: Premium VPN services often come with a subscription fee. While free VPNs exist, they may come with limitations or security concerns. The cost of a reliable VPN can add up over time.
Complex Configuration: Setting up a VPN can sometimes be complicated, especially for those who are not tech-savvy. Incorrect configuration can lead to security vulnerabilities.
Service Restrictions: Some websites and online services can detect and block VPN traffic, limiting your access even when using a VPN. This can be frustrating if you’re trying to access region-specific content.
Trust and Privacy Concerns: When using a VPN, you are entrusting the provider with your data. If the provider logs your activities or has poor security practices, your privacy could be at risk. It’s essential to choose a reputable VPN provider.
Battery Drain: Running a VPN can consume more battery and processing power on your devices, which may lead to reduced performance and shorter battery life, especially on mobile devices.
Legal Issues: In some countries, the use of VPNs is restricted or even illegal. It’s important to be aware of the laws and regulations regarding VPN use in your location to avoid potential legal issues.
Who should use a VPN?

Ever wondered who actually needs a VPN? Well, a VPN can be a game-changer for quite a few people:
Privacy Buffs: If you’re someone who values privacy and wants to keep your online activities away from prying eyes, a VPN is your best friend.
Frequent Travellers: For those who travel a lot and need to access websites or services that might be blocked in different countries, a VPN is super handy.
Remote Workers: If you work from home or a coffee shop and need a secure connection to your company’s network, a VPN keeps everything safe.
Public Wi-Fi Users: Anyone who regularly uses public Wi-Fi in places like cafes or airports should use a VPN to protect their data from hackers.
Streaming Fans: Love watching shows that aren’t available in your country? A VPN can help you access geo-restricted content on platforms like Netflix or BBC iPlayer.
Online Shoppers: Looking for better deals in different regions or wanting to avoid being tracked by advertisers? A VPN can help you out.
Journalists and Activists: If you need to keep your communications secure and maintain anonymity, especially in countries with strict internet censorship, a VPN is essential.
Gamers: Gamers who want to access servers not available in their region or reduce lag can benefit from using a VPN.
Torrent Users: If you download torrents and want to keep it on the down-low from your ISP to avoid throttling or legal issues, a VPN is the way to go.
Students: Studying abroad and need to access educational resources from back home? A VPN can make that happen.
Myths and Misconceptions about VPN

Myth 1: VPNs Are Only for Tech-Savvy People
While VPNs may seem complicated, modern VPN services are made to be easy to use, with simple installation and user-friendly interfaces for everyone.
Myth 2: VPNs Provide Complete Anonymity
While VPNs improve your privacy, they don't make you completely anonymous. Your VPN provider can still see your activity, so it's important to choose a trustworthy provider with a strict no-logs policy.
Myth 3: Free VPNs Are as Good as Paid Ones
Free VPNs often have limitations like slower speeds, fewer servers, and possible security risks. Paid VPNs usually provide better performance, security, and customer support.
Myth 4: VPNs Are Illegal
VPNs are legal in most countries like the US and those in Europe, but some places, like China and Russia, impose restrictions on their use. In North Korea and Iraq, VPNs are banned.
Myth 5: VPNs Are Only for Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
While accessing geo-restricted content is a popular use, VPNs also provide significant security and privacy benefits, making them valuable tools for everyday internet use.
Best VPNs on the Market

ExpressVPN is super reliable with great speed and a user-friendly interface, making it a top choice for streaming and browsing safely. It’s a bit pricier, but totally worth it for the performance and security.
NordVPN offers excellent security features and a huge network of servers, plus it’s quite affordable. Sometimes the app can be a bit clunky, but overall, it’s a solid choice for privacy and streaming.
SurfShark is budget-friendly without skimping on features, and it allows unlimited devices, which is awesome for families. It might not be as fast as the other two, but it’s still a fantastic option for its price.
ProtonVPN stands out with its strong privacy policies and free plan, though the free version is slower and has limited servers. The paid plans are a bit more expensive, but the focus on security and no-logs policy is top-notch.
There are many more options but, I have only tried these four. I will update this list as I try others.
Conclusion
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) enhances online privacy and security by encrypting your data and masking your IP address. It helps protect against data collection by ISPs, websites, and third-party trackers. VPNs are beneficial for privacy-conscious users, frequent travelers, remote workers, public Wi-Fi users, streamers, gamers, and more. Key VPN protocols include OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, IKEv2/IPSec, and WireGuard. While VPNs offer many advantages like enhanced security and access to geo-restricted content, they also come with downsides such as potential speed reduction and cost. Popular VPN options include ExpressVPN, NordVPN, SurfShark, and ProtonVPN.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Vignesh Aithal directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by