Market quotes collector upgrade again
 FMZ Quant
FMZ Quant
Supporting CSV format file import to provide custom data source
Recently, a trader needs to use his own CSV format file as a data source for FMZ platform backtest system. our platform's backtest system has many functions and is simple and efficient to use, so that as long as users have their own data, they can perform backtesting according to these data, which is no longer limited to the exchanges and varieties supported by our platform data center.
Design ideas
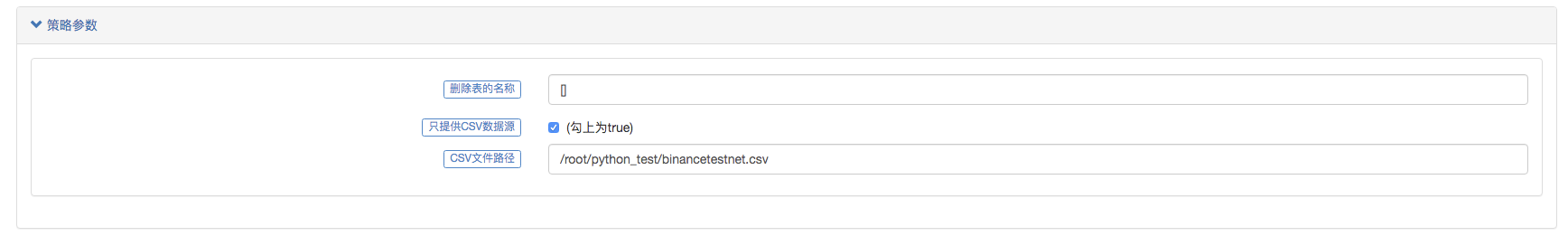
The design idea is actually very simple. We only need to change it slightly based on the previous market collector. We add a parameter isOnlySupportCSV to the market collector to control whether only the CSV file is used as the data source for the backtest system. The parameter filePathForCSV is used to set the path of the CSV data file placed on the server where the market collector robot runs. At last, it is based on whether the isOnlySupportCSV parameter is set to True to decide which data source to use (collected by yourself or the data in the CSV file), this change is mainly in the do_GET function of the Provider class.
What is a CSV file?
Comma-separated values, also known as CSV, sometimes referred to as character-separated values, because the separator character can also not be a comma. Its file stores the table data (numbers and text) in plain text. Plain text means that the file is a sequence of characters and contains no data that must be interpreted like a binary number. The CSV file consists of any number of records, separated by some newline character; each record is composed of fields, and the separators between fields are other characters or strings, and the most common are commas or tabs. Generally, all records have the exact same sequence of fields. They are usually plain text files. It is recommended to use WORDPAD or Excel to open.
The general standard of the CSV file format does not exist, but there are certain rules, generally one record per line, and the first line is the header. The data in each row is separated by commas.
For example, the CSV file we used for testing is opened with Notepad like this:
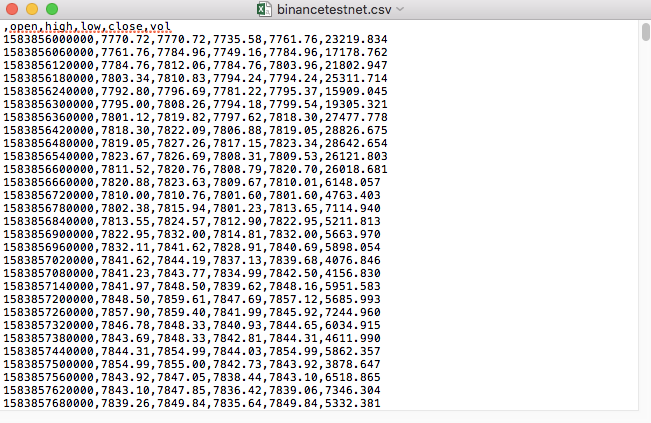
Observed that the first line of the CSV file is the table header.
,open,high,low,close,vol
We just need to parse and sort out these data, and then construct it into the format required by the custom data source of the backtest system. This code in our previous article has already been processed, and only needs to be modified slightly.
Modified code
import _thread
import pymongo
import json
import math
import csv
from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler
from urllib.parse import parse_qs, urlparse
def url2Dict(url):
query = urlparse(url).query
params = parse_qs(query)
result = {key: params[key][0] for key in params}
return result
class Provider(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_GET(self):
global isOnlySupportCSV, filePathForCSV
try:
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header("Content-type", "application/json")
self.end_headers()
dictParam = url2Dict(self.path)
Log("The custom data source service receives the request,self.path:", self.path, "query parameter:", dictParam)
# At present, the backtest system can only select the exchange name from the list. When adding a custom data source, set it to Binance, that is: Binance
exName = exchange.GetName()
# Note that period is the bottom K-line period
tabName = "%s_%s" % ("records", int(int(dictParam["period"]) / 1000))
priceRatio = math.pow(10, int(dictParam["round"]))
amountRatio = math.pow(10, int(dictParam["vround"]))
fromTS = int(dictParam["from"]) * int(1000)
toTS = int(dictParam["to"]) * int(1000)
# Request data
data = {
"schema" : ["time", "open", "high", "low", "close", "vol"],
"data" : []
}
if isOnlySupportCSV:
# Handle CSV reading, filePathForCSV path
listDataSequence = []
with open(filePathForCSV, "r") as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
# Get table header
header = next(reader)
headerIsNoneCount = 0
if len(header) != len(data["schema"]):
Log("The CSV file format is wrong, the number of columns is different, please check!", "#FF0000")
return
for ele in header:
for i in range(len(data["schema"])):
if data["schema"][i] == ele or ele == "":
if ele == "":
headerIsNoneCount += 1
if headerIsNoneCount > 1:
Log("The CSV file format is incorrect, please check!", "#FF0000")
return
listDataSequence.append(i)
break
# Read content
while True:
record = next(reader, -1)
if record == -1:
break
index = 0
arr = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
for ele in record:
arr[listDataSequence[index]] = int(ele) if listDataSequence[index] == 0 else (int(float(ele) * amountRatio) if listDataSequence[index] == 5 else int(float(ele) * priceRatio))
index += 1
data["data"].append(arr)
Log("data: ", data, "Respond to backtest system requests.")
self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode())
return
# Connect to the database
Log("Connect to the database service to obtain data, the database: ", exName, "table: ", tabName)
myDBClient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017")
ex_DB = myDBClient[exName]
exRecords = ex_DB[tabName]
# Construct query conditions: greater than a certain value {'age': {'$ gt': 20}} less than a certain value {'age': {'$lt': 20}}
dbQuery = {"$and":[{'Time': {'$gt': fromTS}}, {'Time': {'$lt': toTS}}]}
Log("Query conditions: ", dbQuery, "Number of inquiries: ", exRecords.find(dbQuery).count(), "Total number of databases: ", exRecords.find().count())
for x in exRecords.find(dbQuery).sort("Time"):
# Need to process data accuracy according to request parameters round and vround
bar = [x["Time"], int(x["Open"] * priceRatio), int(x["High"] * priceRatio), int(x["Low"] * priceRatio), int(x["Close"] * priceRatio), int(x["Volume"] * amountRatio)]
data["data"].append(bar)
Log("data: ", data, "Respond to backtest system requests.")
# Write data response
self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode())
except BaseException as e:
Log("Provider do_GET error, e:", e)
def createServer(host):
try:
server = HTTPServer(host, Provider)
Log("Starting server, listen at: %s:%s" % host)
server.serve_forever()
except BaseException as e:
Log("createServer error, e:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
def main():
LogReset(1)
if (isOnlySupportCSV):
try:
# _thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("localhost", 9090), )) # local test
_thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("0.0.0.0", 9090), )) # Test on VPS server
Log("Start the custom data source service thread, and the data is provided by the CSV file. ", "#FF0000")
except BaseException as e:
Log("Failed to start the custom data source service!")
Log("Error message: ", e)
raise Exception("stop")
while True:
LogStatus(_D(), "Only start the custom data source service, do not collect data!")
Sleep(2000)
exName = exchange.GetName()
period = exchange.GetPeriod()
Log("collect", exName, "Exchange K-line data,", "K line cycle:", period, "Second")
# Connect to the database service, service address mongodb: //127.0.0.1: 27017 See the settings of mongodb installed on the server
Log("Connect to the mongodb service of the hosting device, mongodb://localhost:27017")
myDBClient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017")
# Create a database
ex_DB = myDBClient[exName]
# Print the current database table
collist = ex_DB.list_collection_names()
Log("mongodb", exName, "collist:", collist)
# Check if the table is deleted
arrDropNames = json.loads(dropNames)
if isinstance(arrDropNames, list):
for i in range(len(arrDropNames)):
dropName = arrDropNames[i]
if isinstance(dropName, str):
if not dropName in collist:
continue
tab = ex_DB[dropName]
Log("dropName:", dropName, "delete:", dropName)
ret = tab.drop()
collist = ex_DB.list_collection_names()
if dropName in collist:
Log(dropName, "failed to delete")
else :
Log(dropName, "successfully deleted")
# Start a thread to provide a custom data source service
try:
# _thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("localhost", 9090), )) # local test
_thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("0.0.0.0", 9090), )) # Test on VPS server
Log("Open the custom data source service thread", "#FF0000")
except BaseException as e:
Log("Failed to start the custom data source service!")
Log("Error message:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
# Create the records table
ex_DB_Records = ex_DB["%s_%d" % ("records", period)]
Log("Start collecting", exName, "K-line data", "cycle:", period, "Open (create) the database table:", "%s_%d" % ("records", period), "#FF0000")
preBarTime = 0
index = 1
while True:
r = _C(exchange.GetRecords)
if len(r) < 2:
Sleep(1000)
continue
if preBarTime == 0:
# Write all BAR data for the first time
for i in range(len(r) - 1):
bar = r[i]
# Write root by root, you need to determine whether the data already exists in the current database table, based on timestamp detection, if there is the data, then skip, if not write
retQuery = ex_DB_Records.find({"Time": bar["Time"]})
if retQuery.count() > 0:
continue
# Write bar to the database table
ex_DB_Records.insert_one({"High": bar["High"], "Low": bar["Low"], "Open": bar["Open"], "Close": bar["Close"], "Time": bar["Time"], "Volume": bar["Volume"]})
index += 1
preBarTime = r[-1]["Time"]
elif preBarTime != r[-1]["Time"]:
bar = r[-2]
# Check before writing data, whether the data already exists, based on time stamp detection
retQuery = ex_DB_Records.find({"Time": bar["Time"]})
if retQuery.count() > 0:
continue
ex_DB_Records.insert_one({"High": bar["High"], "Low": bar["Low"], "Open": bar["Open"], "Close": bar["Close"], "Time": bar["Time"], "Volume": bar["Volume"]})
index += 1
preBarTime = r[-1]["Time"]
LogStatus(_D(), "preBarTime:", preBarTime, "_D(preBarTime):", _D(preBarTime/1000), "index:", index)
# Increase drawing display
ext.PlotRecords(r, "%s_%d" % ("records", period))
Sleep(10000)
Run test
First, we start the market collector robot. We add an exchange to the robot and let the robot run.
Parameter configuration:
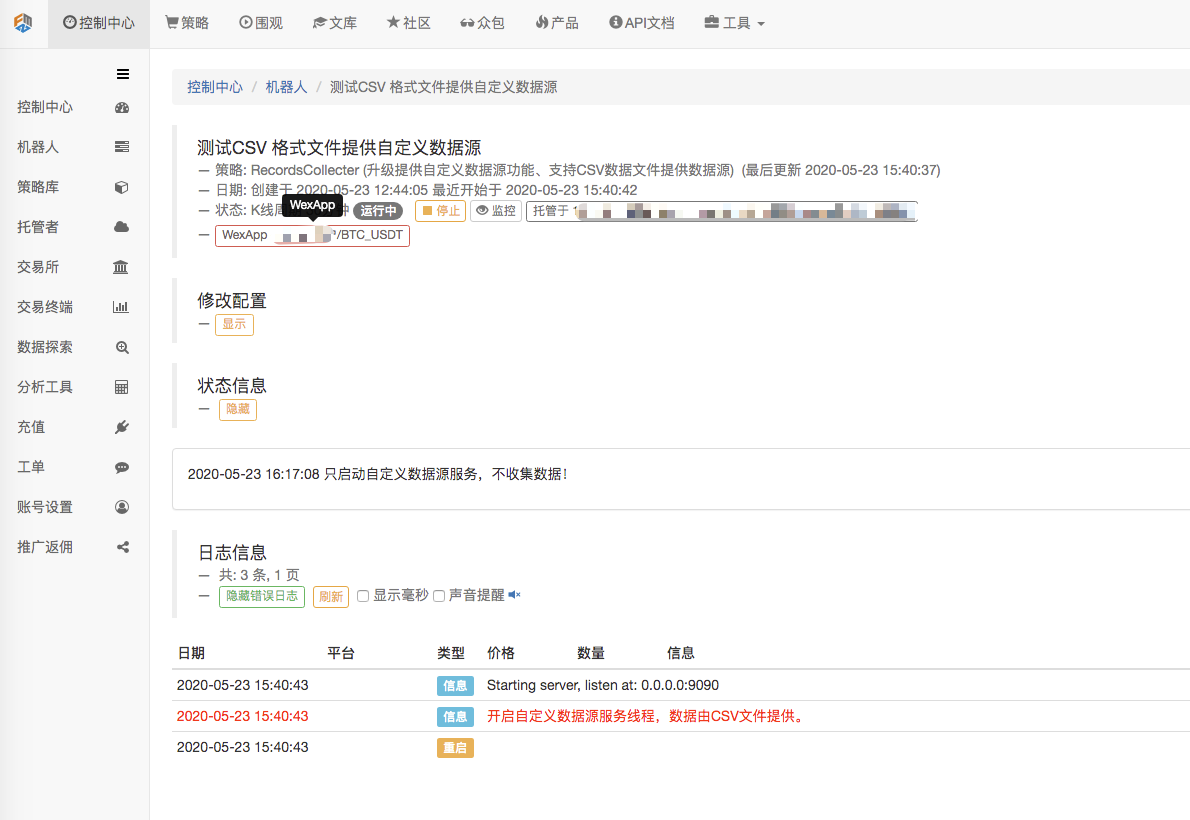
Then we create a test strategy:
function main() {
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
}
The strategy is very simple, only obtain and print K-line data three times.
On backtest page, set the data source of the backtest system as a custom data source, and fill in the address of the server where the market collector robot runs. Since the data in our CSV file is a 1-minute K line. So when backtest, we set the K-line period to 1 minute.
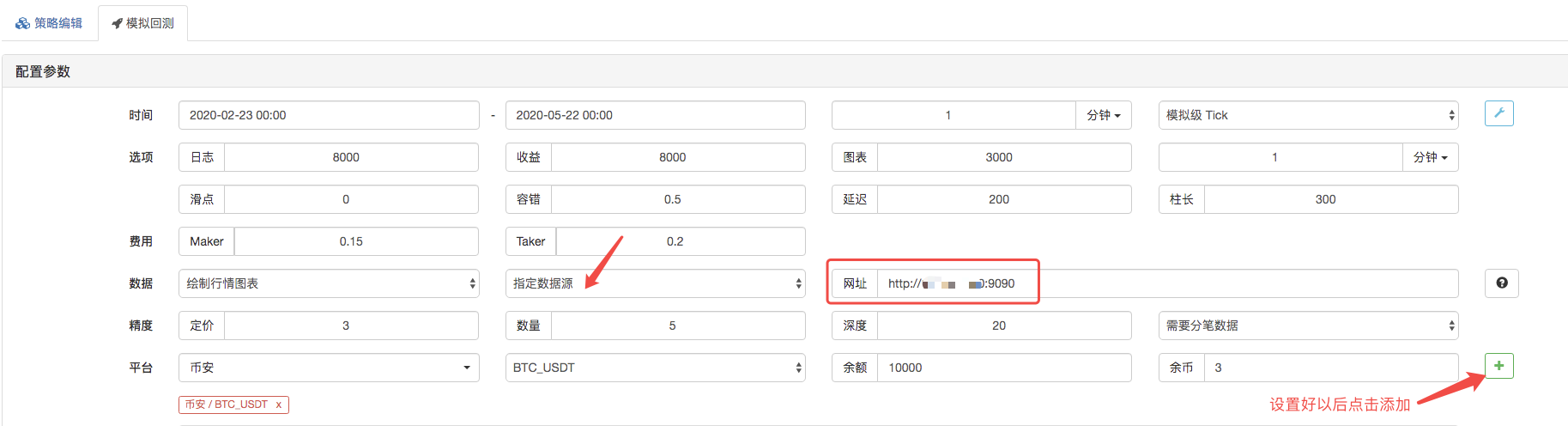
Click to start the backtest, and the market collector robot receives the data request:
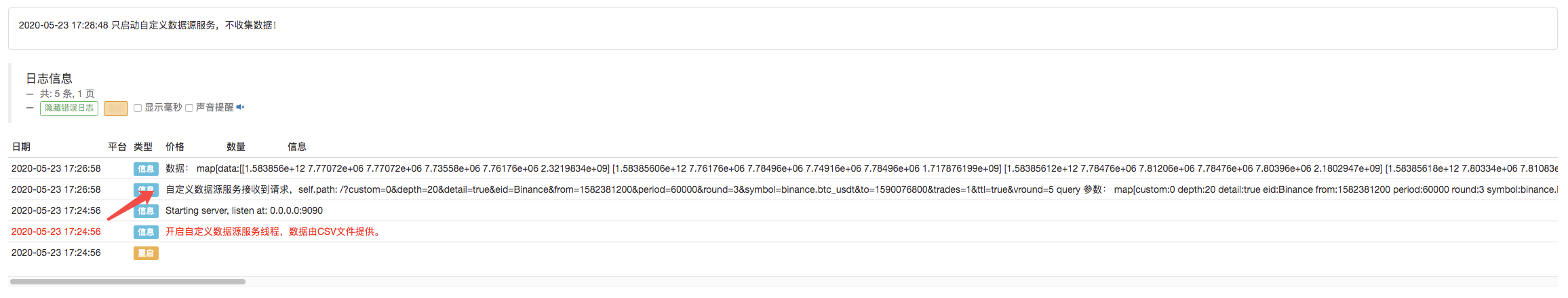
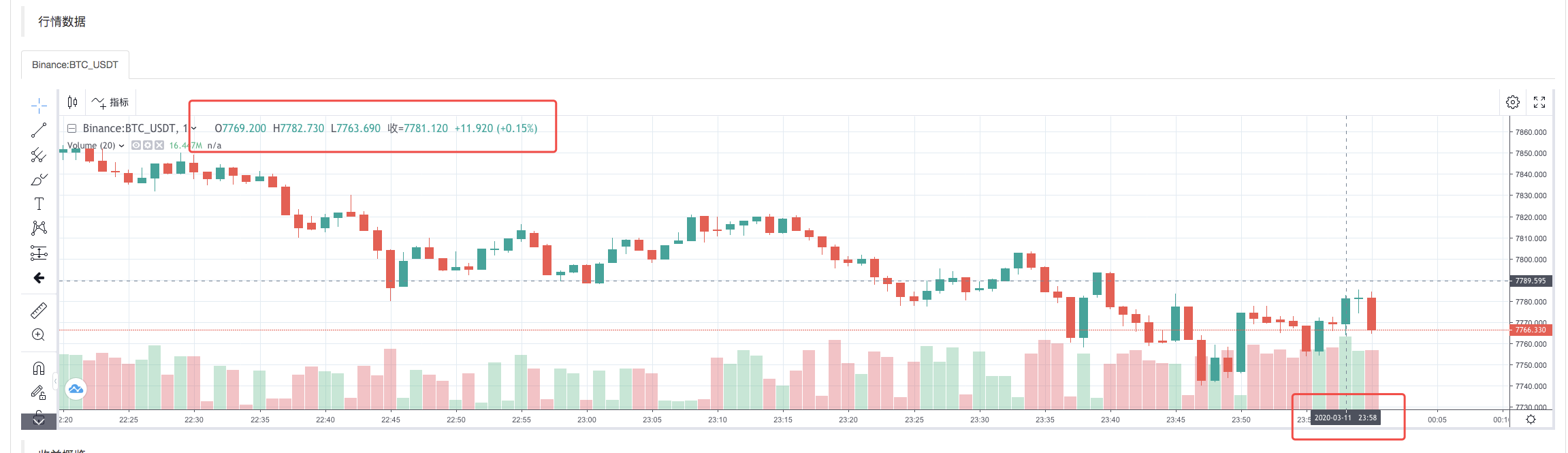
After the execution strategy of the backtest system is completed, a K-line chart is generated based on the K-line data in the data source.
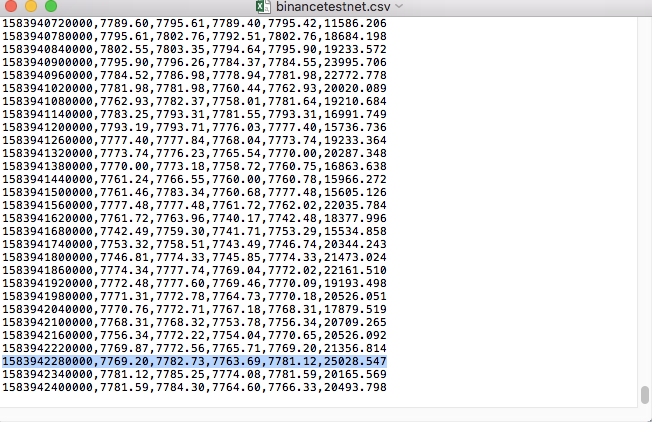
Compare the data in the file:

Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from FMZ Quant directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

FMZ Quant
FMZ Quant
Quantitative Trading For Everyone