AWS Network & Security { Part - IV }
 N Chandra Prakash Reddy
N Chandra Prakash Reddy
What is a Key Pairs in AWS EC2
Definition : A set of security credentials required to authenticate access to EC2 instances is called a key pair in AWS EC2.
Components : It consists of a public key and a private key.
Purpose : The key pair makes sure that the EC2 instances can only be accessed by authorized users.
Key Features of Key Pairs
Secure Access : Gives access to EC2 instances in a secure manner.
Public-Private Key Encryption : Protects communication by using asymmetric encryption.
SSH Access : frequently used to access Linux instances using SSH (Secure Shell).
Integration : For increased security, it can be combined with other AWS services.
No Passwords : Eliminates the requirement for authentication with a password.
How Key Pairs Work
Generation Process :
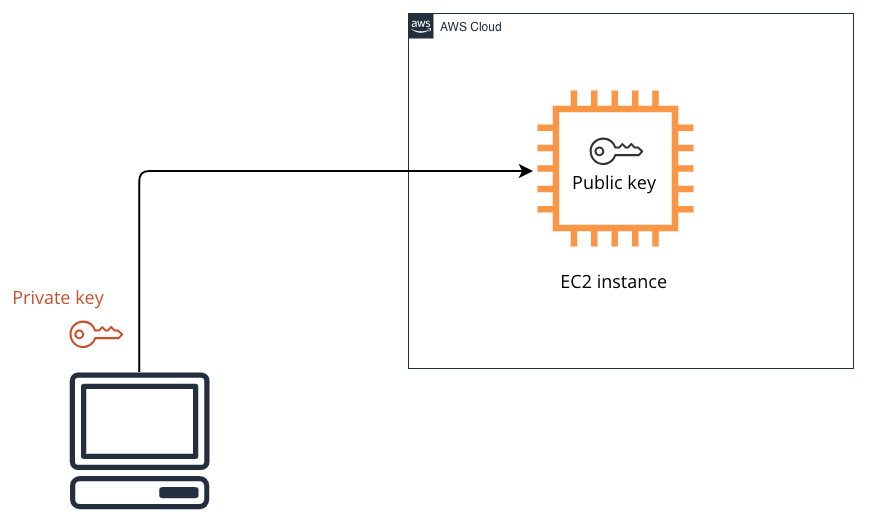
Public Key : The public key is generated by AWS and is kept on the EC2 instance.
Private Key : You can download the private key from AWS. Because AWS does not keep a copy, it is essential that you store it safely.
SSH Connection :
Client-Side : The SSH client (such as PuTTY or OpenSSH) is used to establish a connection with an EC2 instance.
Private Key Usage : An encryption request for a session initiation is made by the SSH client using the private key.
Public Key Verification : If the private key and the saved public key match, the EC2 instance establishes a secure connection.
Session Establishment :
- Symmetric Key Exchange : Following the first verification, the SSH protocol creates a session-specific symmetric encryption key to guarantee the security of any data transferred.
Encryption and Decryption :
Data Encryption : The public key is used to encrypt data that is transferred to the EC2 instance.
Data Decryption : This data can only be decrypted with the matching private key, guaranteeing that intercepted data cannot be viewed without the private key.
Login Process :
Authorized Keys File : On Linux instances, the public key is added to the
~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile of the specified user.Access Control : Only users with the private key that matches the public key in the
authorized_keysfile can log in.
Key Pair Storage :
AWS Storage : AWS stores only the public key.
User Responsibility : It is the user's responsibility to safely store and handle the private key.
No Passwords Needed :
- Key-Based Authentication : Eliminates the need for passwords, reducing the risk of password-related vulnerabilities.
Revocation and Rotation :
Key Revocation : If a private key is compromised, you can revoke access by removing the corresponding public key from the
authorized_keysfile.Key Rotation : Updating key pairs on a regular basis reduces the possibility of key compromise. The following blogs will provide us with important updates. How can we make a new key and attach it to the EC2 instance, for instance, if we delete the original key file by any chance?
Creating a Key Pair During Instance Launch
AWS Management Console :
Step 1 : Launch Instance :
Go to the EC2 dashboard.
Click on "Launch Instance".
Step 2 : Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) :
- Select an AMI that suits your needs (e.g., Amazon Linux 2, Ubuntu).
Step 3 : Choose an Instance Type:
- Select the instance type (e.g., t2.micro).
Step 4 : Configure Key Pair :
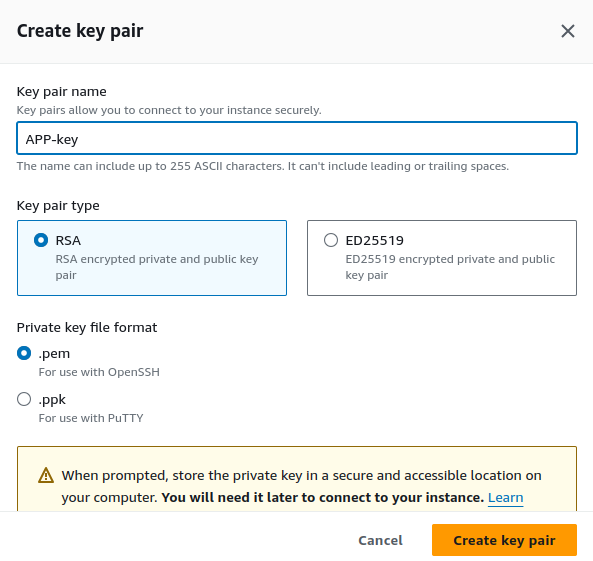
Create a New Key Pair:
select "Create new key pair".
Provide a name for your key pair.
Choose the key pair file format:
PEM (for SSH clients).
PPK (for PuTTY).
Click on "Create key pair".
Download the private key file (.pem or .ppk). Save it securely, as you won't be able to download it again.
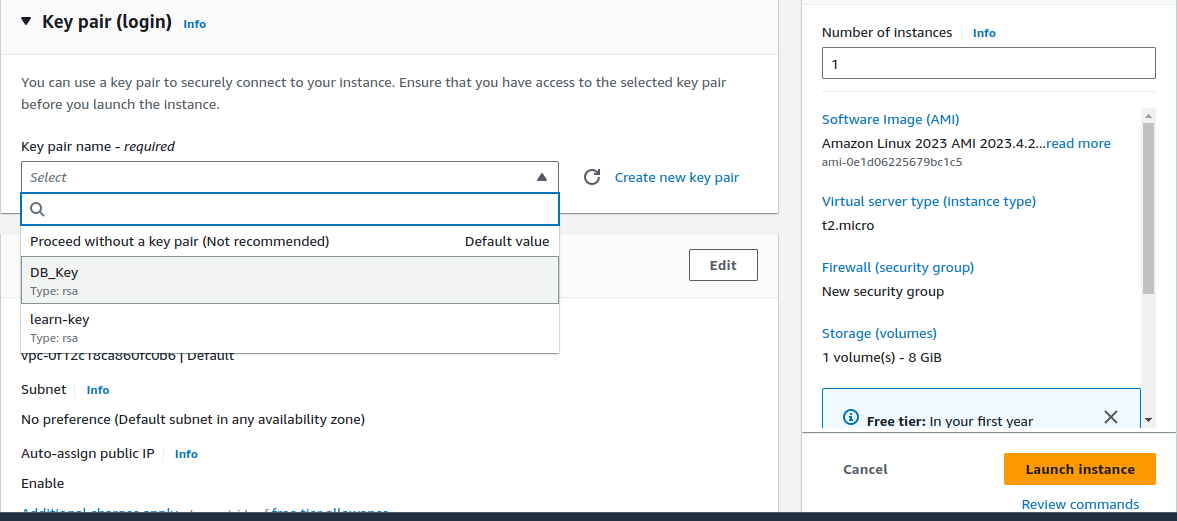
Use an Existing Key Pair:
If you already have a key pair, you can select it from the "Key pair name" dropdown list.
You can create the Key pair by navigate to the EC2 dashboard, choose "Key Pairs," and create a new key pair.
Step 5 :
Configure other details :
- Like security groups , storage , number of instances, advance details.
Best practices for Key Pairs
Secure Storage :
Encryption : Use tools like AWS KMS or other third-party solutions to store private keys in an encrypted format.
Access Control : Limit who has access to the private key to those who actually need it.
Regular Rotation :
Schedule Key Rotations : Rotate important pairs on a regular basis to reduce the chance of long-term exposure.
Automate Rotation : To automate key distribution and rotation, use tools or scripts.
Backup :
Secure Backup : Private key backups should be stored in safe, encrypted places.
Disaster Recovery : Make sure your disaster recovery plan includes backups.
Access Control :
Least Privilege Principle : Give people only the minimal amount of rights they need to complete their tasks.
IAM Policies : To restrict who can generate, use, and maintain key pairs, utilize AWS IAM policies.
Monitoring and Auditing :
Log Access : To keep track of who accesses and uses your key pairs, enable logging.
Review Logs : Check logs on a regular basis for any odd or unwanted access attempts.
Key Pair Management :
Tagging : To make managing key pairs easier, use tags to identify and arrange them.
Documentation : Keep records of the creation dates and usage contexts for each key pair.
Environment Segregation :
Separate Keys for Different Environments : To isolate access, use different key pairs for development, testing, and production environments.
Project-specific Keys : Limit the scope of access by creating key pairs that are unique to teams or projects.
Emergency Access Procedures :
Backup Admin Key : Maintain a safe backup pair of administrative keys for access in case of emergency.
Emergency Plans : Create and record protocols for handling compromised key pairs.
Avoid Hardcoding Keys :
Configuration Management : Instead of hardcoding keys into scripts or apps, use configuration management technologies to control key distribution.
Environment Variables : Save key paths in secure configuration stores or environment variables.
Use Cases
SSH Access : Secure SSH access to EC2 instances running Linux/Unix.
Remote Administration : Remote server management and administration.
Automated Scripts : Deployment scripts that are automated yet need protected access.
Multi-Factor Authentication : Multi-factor authentication for instance access enhances security.
Pros and Cons
Pros :
Enhanced Security : Offers a high degree of protection while gaining access to instances.
Simplicity : Easy to set up and use.
No Passwords : Reduces the risk of password-related attacks.
Cons :
Key Management : Requires that private keys be handled and stored with caution.
Loss of Key : You risk being locked out of the instance if you misplace the private key.
Initial Setup : Requires initial setup and configuration.
Conclusion
Summary : EC2 instances must be accessed securely using AWS Key Pairs, which use public-private key encryption for strong security.
Recommendation : Make key pairs a crucial component of your cloud security plan by sticking to best practices to ensure their safe and effective use.
References
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from N Chandra Prakash Reddy directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

N Chandra Prakash Reddy
N Chandra Prakash Reddy
-> I'm an enthusiastic DevOps professional with over 3+ years of hands-on expertise in cloud infrastructure management and orchestrating the deployment of applications which are ready for production. -> Excellent problem-solving skills and a proactive learner, staying updated with the latest trends in DevOps and Cloud Computing. 𝐆𝐞𝐭 𝐢𝐧 𝐓𝐨𝐮𝐜𝐡 -> 𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐜𝐭 𝐨𝐧 𝐋𝐢𝐧𝐤𝐞𝐝𝐢𝐧 : If you're interested in engaging in technical discussions or connecting professionally, please feel free to connect with me on LinkedIn. -> 𝐄𝐦𝐚𝐢𝐥 : ncpr.0912@gmail.com