Python version of commodity futures intertemporal hedging strategy
 FMZ Quant
FMZ Quant
Ported from the JavaScript version of Commodity Futures Intertemporal Hedging-Hundred Lines of Code Implementation, this strategy is a simple teaching strategy, intended to show the design of commodity futures strategies in Python language. Mainly used for learning strategy writing and reference design ideas.
class Hedge:
'Hedging control class'
def __init__(self, q, e, initAccount, symbolA, symbolB, hedgeSpread, coverSpread):
self.q = q
self.initAccount = initAccount
self.status = 0
self.symbolA = symbolA
self.symbolB = symbolB
self.e = e
self.isBusy = False
self.hedgeSpread = hedgeSpread
self.coverSpread = coverSpread
self.opAmount = OpAmount
def poll(self):
if (self.isBusy or not exchange.IO("status")) or not ext.IsTrading(self.symbolA):
Sleep(1000)
return
insDetailA = exchange.SetContractType(self.symbolA)
if not insDetailA:
return
tickerA = exchange.GetTicker()
if not tickerA:
return
insDetailB = exchange.SetContractType(self.symbolB)
if not insDetailB:
return
tickerB = exchange.GetTicker()
if not tickerB:
return
LogStatus(_D(), "A sell B buy", _N(tickerA["Buy"] - tickerB["Sell"]), "A buy B sell", _N(tickerA["Sell"] - tickerB["Buy"]))
action = 0
if self.status == 0:
if (tickerA["Buy"] - tickerB["Sell"]) > self.hedgeSpread:
Log("open position A sell B buy", tickerA["Buy"], tickerB["Sell"], "#FF0000")
action = 1
elif (tickerB["Buy"] - tickerA["Sell"]) > self.hedgeSpread:
Log("open position B sell A buy", tickerB["Buy"], tickerA["Sell"], "#FF0000")
action = 2
elif self.status == 1 and (tickerA["Sell"] - tickerB["Buy"]) <= self.coverSpread:
Log("close position A buy B sell", tickerA["Sell"], tickerB["Buy"], "#FF0000")
action = 2
elif self.status == 2 and (tickerB["Sell"] - tickerA["Buy"]) <= self.coverSpread:
Log("close position B buy A sell", tickerB["Sell"] - tickerA["Buy"], "#FF0000")
action = 1
if action == 0:
return
self.isBusy = True
tasks = []
if action == 1:
tasks.append([self.symbolA, "sell" if self.status == 0 else "closebuy"])
tasks.append([self.symbolB, "buy" if self.status == 0 else "closesell"])
elif action == 2:
tasks.append([self.symbolA, "buy" if self.status == 0 else "closesell"])
tasks.append([self.symbolB, "sell" if self.status == 0 else "closebuy"])
def callBack(task, ret):
def callBack(task, ret):
self.isBusy = False
if task["action"] == "sell":
self.status = 2
elif task["action"] == "buy":
self.status = 1
else:
self.status = 0
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
LogProfit(account["Balance"] - self.initAccount["Balance"], account)
self.q.pushTask(self.e, tasks[1][0], tasks[1][1], self.opAmount, callBack)
self.q.pushTask(self.e, tasks[0][0], tasks[0][1], self.opAmount, callBack)
def main():
SetErrorFilter("ready|login|timeout")
Log("Connecting to the trading server...")
while not exchange.IO("status"):
Sleep(1000)
Log("Successfully connected to the trading server")
initAccount = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
Log(initAccount)
n = 0
def callBack(task, ret):
Log(task["desc"], "success" if ret else "fail")
q = ext.NewTaskQueue(callBack)
if CoverAll:
Log("Start closing all remaining positions...")
ext.NewPositionManager().CoverAll()
Log("Operation complete")
t = Hedge(q, exchange, initAccount, SA, SB, HedgeSpread, CoverSpread)
while True:
q.poll()
t.poll()
Just transplanting the code, it feels a bit too simple, we continue to do some transformations, add charts to this trading strategy.
Add the following code before the position where the LogStatus function is called to make the real-time price difference into a K-line statistics. self.preBarTime is a member added by the Hedge class to record the latest BAR timestamp. For drawing, we use "Drawing Class library", directly call the drawing interface, you can easily draw charts.
# Calculate the spread K line
r = exchange.GetRecords()
if not r:
return
diff = tickerB["Last"] - tickerA["Last"]
if r[-1]["Time"] != self.preBarTime:
# Update
self.records.append({"Time": r[-1]["Time"], "High": diff, "Low": diff, "Open": diff, "Close": diff, "Volume": 0})
self.preBarTime = r[-1]["Time"]
if diff > self.records[-1]["High"]:
self.records[-1]["High"] = diff
if diff < self.records[-1]["Low"]:
self.records[-1]["Low"] = diff
self.records[-1]["Close"] = diff
ext.PlotRecords(self.records, "diff:B-A")
ext.PlotHLine(self.hedgeSpread if diff > 0 else -self.hedgeSpread, "hedgeSpread")
ext.PlotHLine(self.coverSpread if diff > 0 else -self.coverSpread, "coverSpread")
Backtesting effect:
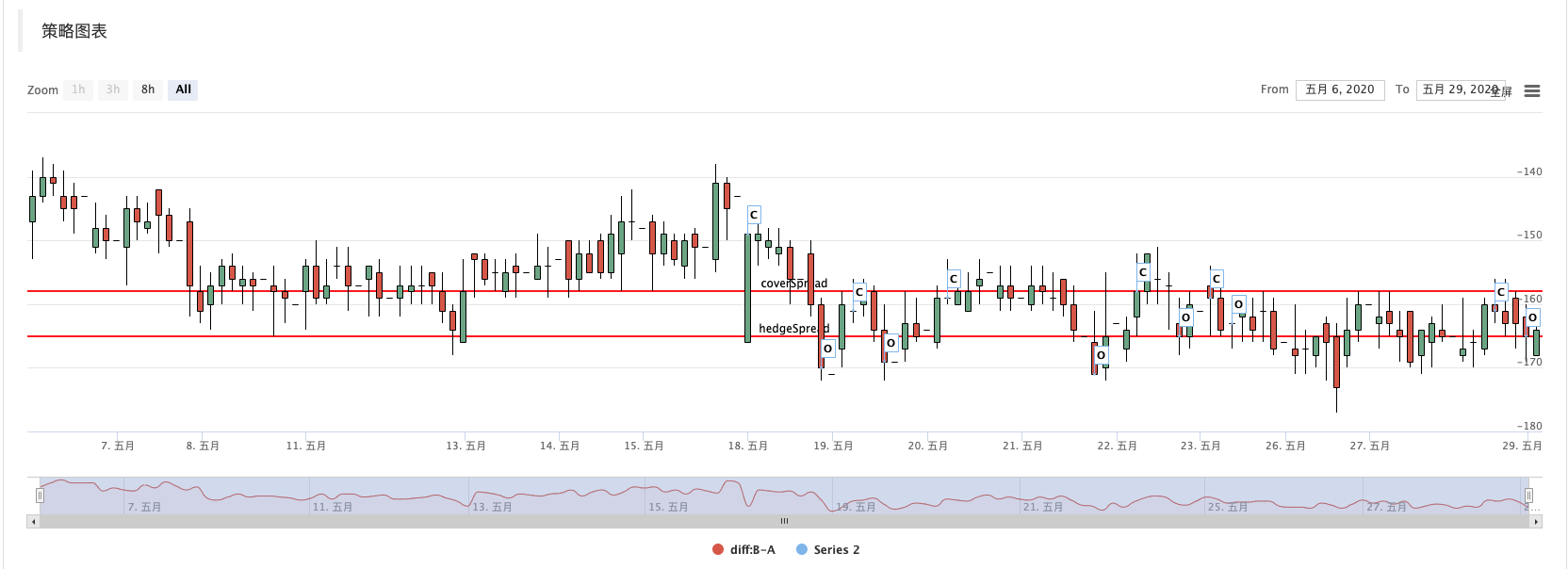
Next, we will add interactive functions, so that the strategy can modify the HedgeSpread and CoverSpread parameters at runtime to control the hedging spread and closing spread. You also need a button to close the position with one click. We add these controls on the strategy editing page.
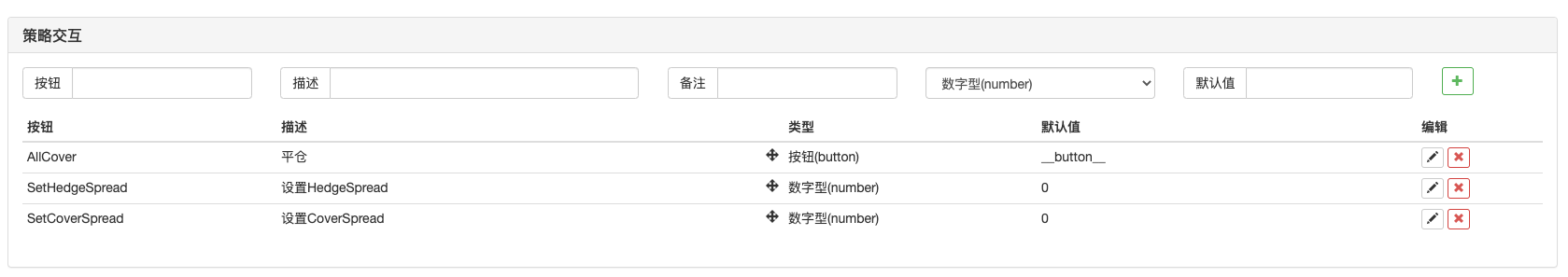
Then in the main loop of the strategy, after the q.poll(), t.poll() call, add the interactive control code.
while True:
q.poll()
t.poll()
# The following interactive control code
cmd = GetCommand()
if cmd:
arr = cmd.split(":")
if arr[0] == "AllCover":
p.CoverAll()
elif arr[0] == "SetHedgeSpread":
t.SetHedgeSpread(float(arr[1]))
elif arr[0] == "SetCoverSpread":
t.SetCoverSpread(float(arr[1]))
You can copy the whole trading strategy here: https://www.fmz.com/strategy/211504
From: Python version of commodity futures intertemporal hedging strategy (fmz.com)
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from FMZ Quant directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

FMZ Quant
FMZ Quant
Quantitative Trading For Everyone