Authentication Methods Overview
 KALPESH MOHANTA
KALPESH MOHANTA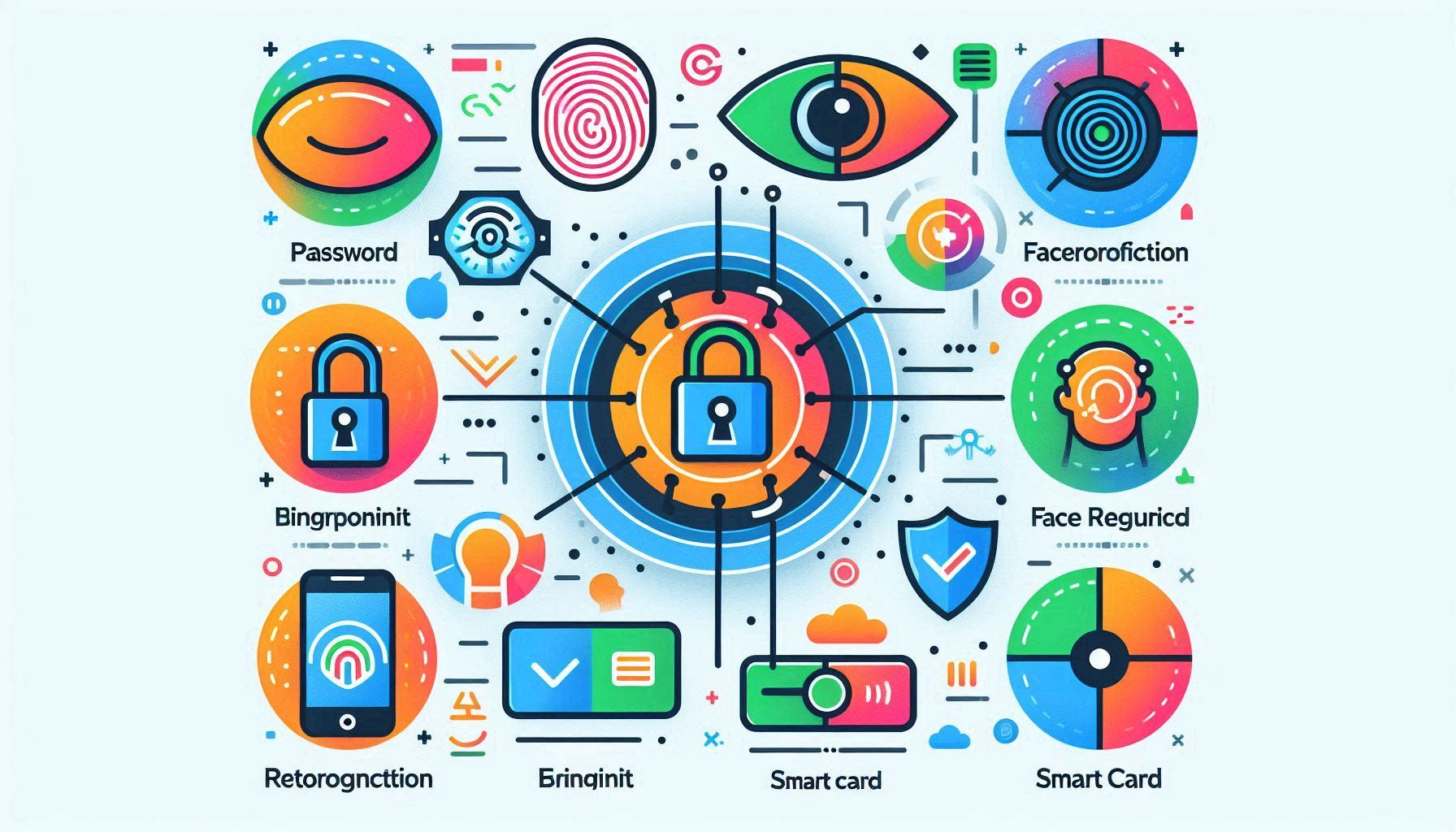
Password Authentication
Users authenticate with a username and password.
Simple to implement but less secure if passwords are weak or intercepted.
Certificate-based Authentication
Utilizes digital certificates signed by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
Scalable and manageable in large environments, offers higher security assurance.
Example: PEM file(private key).
Process:Download the PEM file when creating the EC2 instance.
Connect to the remote server using:
ssh -i <path of .pem file to access> <username of AMI>@<ip address of remote server>
scp(Secure Copy Protocol):scp -i <path of .pem file to access> <path of file you are transferring from your local machine> <username of AMI>@<ip address of remote server>:<directory on the remote server where the file will be copied>
Public Key Authentication
Uses asymmetric cryptography with a key pair: public (server-side) and private (client-side) keys.
More secure than passwords, especially with strong key management.
SSH-KEYGEN:
- Public Key: This can be freely shared with others. It's used to encrypt data that can only be decrypted by the corresponding private key.- Private Key: This should be kept secret. It's used to decrypt data encrypted with the public key and proves your identity for SSH logins.
Process:
Client:
Generate SSH keys using
ssh-keygenNavigate to the
.sshdirectory and copy the public key (e.g.,id_rsa.pub).
Remote Server:
Generate SSH keys using
ssh-keygenNavigate to the
.sshdirectory.Paste the client's public key into the
authorized_keysfile.
Final Step in Client:
ssh <private ip of remote server if within VPC, otherwise public ip of remote server>
Keyboard-Interactive Authentication
The server customizes prompts to challenge the client.
Often used for multi-factor authentication with OTPs or biometric data.
Biometric Authentication
Uses biological traits like fingerprints or facial recognition for verification.
Provides strong security but requires specialized hardware and software.
Token-based Authentication
Uses physical tokens (e.g., smart cards or USB tokens) with digital certificates or OTPs.
Ensures strong authentication and protects against unauthorized access.
Feel free to share and spread the knowledge! 🌟😊 Enjoy Learning! 😊
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from KALPESH MOHANTA directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

KALPESH MOHANTA
KALPESH MOHANTA
👋 Hi there! Welcome to my DevOps adventure! 🚀 I'm Kalpesh, a DevOps Engineer, and I'm thrilled to share my journey in the dynamic world of DevOps and Cloud Technologies. 🌐 🔧 Tech Arsenal: CI/CD Automation: Streamlining workflows for seamless deployments. Containers & Orchestration: Docker & Kubernetes. Cloud Platforms: Azure, AWS. Version Control: Git. Configuration Management: YAML, Linux commands. 🚀 My Journey: I've had the privilege to work on diverse projects, including a notable deployment for PepsiCo. My expertise spans CI/CD automation, containerization, cloud services, and scripting to enhance system performance and reliability. 💡 Why Follow Me? Join me as I delve into: Cutting-edge DevOps practices. Automation techniques. Cloud innovations. Tips & tricks for aspiring DevOps professionals. 🤝 Connect & Collaborate: Let's build, learn, and innovate together. Whether you're a fellow tech enthusiast, a professional looking to share insights, or someone eager to learn, let's connect and grow in this vibrant community. 📢 Follow my LinkedIn & Hashnode blog for insights, tutorials, and updates. Together, we'll embrace the ever-evolving DevOps landscape!