Stream API in Java
 Nitish Sonkar
Nitish Sonkar
It can be classify into two operation.
Intermediate operation
Transform a stream into another stream.
Examples: filter, map, distinct, sorted, limit, etc.
Terminal operation
It's provide the result and terminate the stream.
Example: forEach, collect, reduce, count, toArray, etc.
The Java 8 Stream API Tutorial
Filter
syntax:
Stream filteredSteream=orinalStream.filter(element->/*predicate*/);
Predicate: It returns true or false
Question: Find out even number from the arrayList using Stream?
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(4,5,6,7);
List<Integer> filteredList= list.stream().filter(n->n%2==0).toList();
input: 10 elements
output: 0 to 10 elements
Map
syntax:
Stream filteredSteream=orinalStream.map(element->/*transformation fuction*/);
Predicate: It returns true or false
It takes function as an argument, return type is based on type of data.
Question: Multiply by 2 to each element from a list?
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(4,5,6,7);
List<Integer> mapList= list.stream().map(n->n*2).toList();
Question: Select only passed students and add 5 grace mark to all failed students?
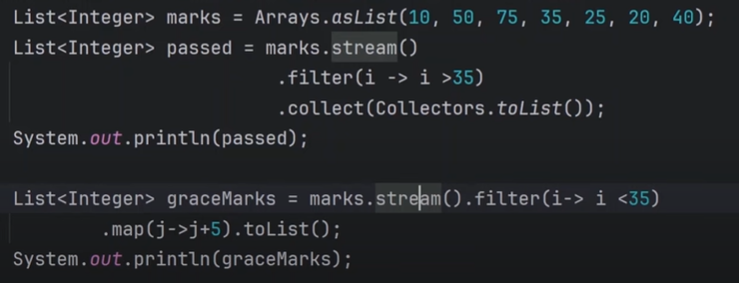
input: 10 elements
output: 10 elements
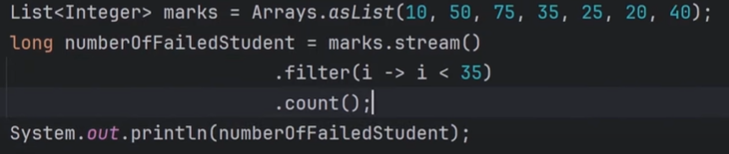
Count
To count the number of element in the stream.
Question: Find out total number of failed students?
Sorted
To sort order of element in stream.
Sorting in descending order
Customizing the sorting order then you have to use Comparator. Comparator is functional Interface. It has a compare(obj1, obj2) method. you can also use lambda expression.
return -ve: obj1 has come before obj2
return +ve: obj1 has come after obj2;


min() and max()


toArray()

Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nitish Sonkar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Nitish Sonkar
Nitish Sonkar
Hi All, Currently, I'm working as Developer.