Introduction to Kubernetes Objects
 Gaurav Kumar
Gaurav Kumar
Kubernetes is an open-source platform designed to automate deploying, scaling, and operating application containers. Kubernetes provide features of multiple object creation which represent the state of our cluster. In this blog, we will explore some of the most fundamental Kubernetes objects: Pods, ReplicaSets, Services, DaemonSets, Jobs, StatefulSets, Deployment, and Namespace. These are very essential topics for the Interview Preparation.
Pods
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: my-container
image: nginx
Here we have created a Pod named my-pod using single container image of nginx. We can have more than one containers also in a Pod. We can create this object in our cluster by below command.
kubectl apply -f <pod-object-file-name>
Once we will apply the file we will get below output which will show that Pod is created and running.

ReplicaSets
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: my-replicaset
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: my-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: my-app
spec:
containers:
- name: my-container
image: nginx
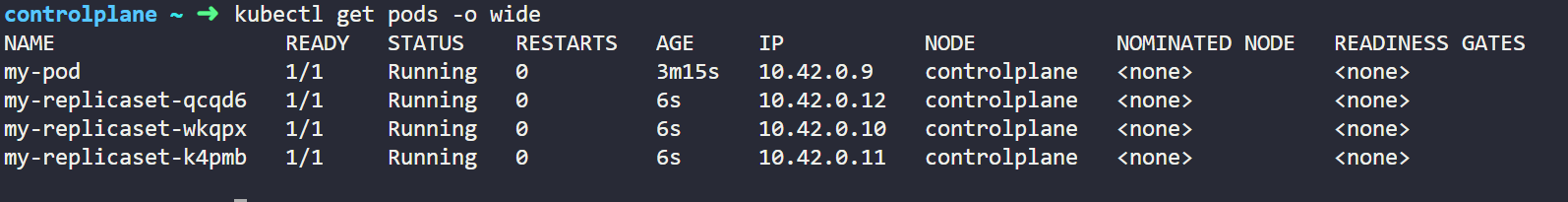
Here in above code we have mentioned replicas as 3 so it means 3 pod of my-app pod will always be running. If a Pod fails, the ReplicaSet automatically creates a new one to maintain the desired state. We can create this object in our cluster by below command.
kubectl apply -f <replicaset-object-file-name>
Once we will apply the file we will get below output which will show that 3 pod of ReplicaSet named my-replicaset is created and running.
Service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-service
spec:
selector:
app: my-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
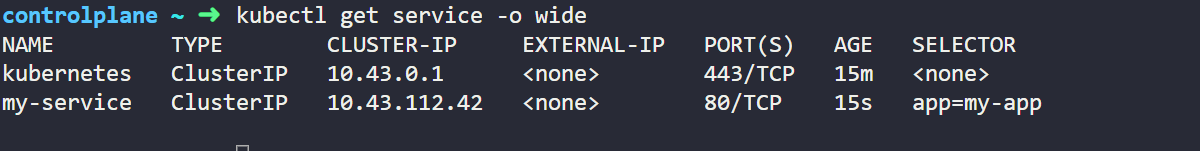
Here we have created Service named my-service, which targets Pods based on selector we have added here app: my-app, it will search for this label and add this Service definition to the Pod which matches the label. We can create apply this object by writing below code.
kubectl apply -f <service-object-file-name>
Once we will apply the file we will get below output which will show that it has created service named my-service for pod and has provided IP address also to it.
DaemonSets
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: my-daemonset
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: my-daemon
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: my-daemon
spec:
containers:
- name: my-daemon-container
image: fluentd
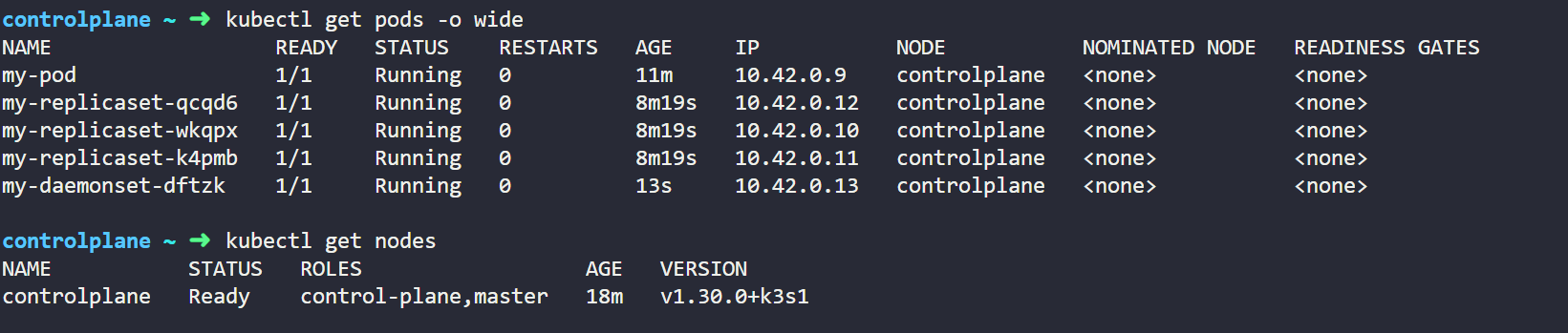
Here our DaemonSets runs a fluentd container which will ensures that this container will runs on every node and will used in centralized logging. We can create this object in our cluster by below command.
kubectl apply -f <daemonsets-object-file-name>
Once we will apply the file we will get below output which will show that it has created DaemonSets named my-daemonsets for fluentd. For now we only have one nodes that's the reason it is showing only one instance of DaemonSets otherwise we will see more.
Job
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: my-job
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: my-container
image: busybox
command: ["sh", "-c", "echo Hello Kubernetes! && sleep 30"]
restartPolicy: OnFailure
Here we have created Job named my-job which runs a busybox container that will print a messages and sleeps for 30 seconds. Once this work will be completed it will terminate the Pod and will be completed state. We can create this object in our cluster by below command.
kubectl apply -f <job-object-file-name>
Once we will apply the file we will get below output which will show that it has created Job named my-job for busybox container.
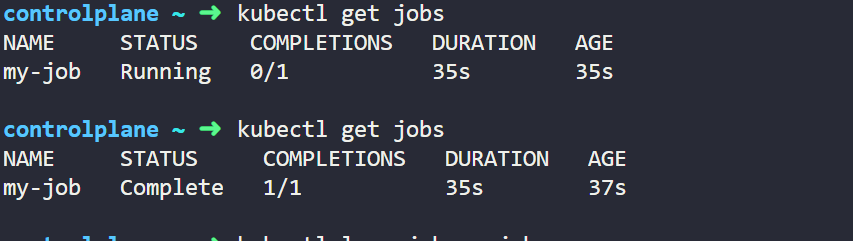
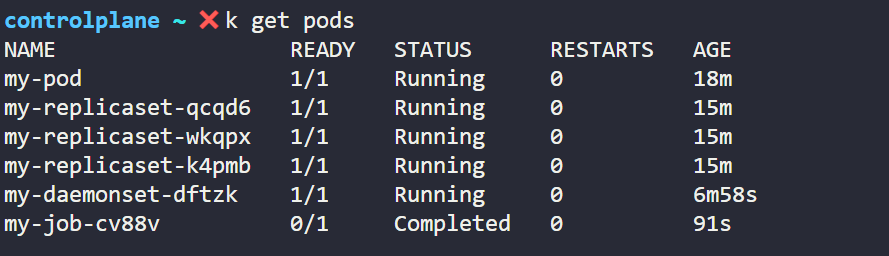
In the above two pictures we can see that when Job hasn't finished its work completed it is showing Status as 0/1, but when it completes it work it is showing Status as 1/1 which we can also verify from Pod Status which is showing Status as Completed for my-job and for other Pod it is showing Running.
StatefulSets
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: my-statefulset
spec:
serviceName: "my-service"
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: my-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: my-app
spec:
containers:
- name: my-container
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: my-volume
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: my-volume
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
Here we have created StatefulSets with 3 replicas of the nginx container with persistent storage. We can create this object in our cluster by below command.
kubectl apply -f <statefulsets-object-file-name>
Here we have created StatefulSets named my-statefulset which runs a nginx container.
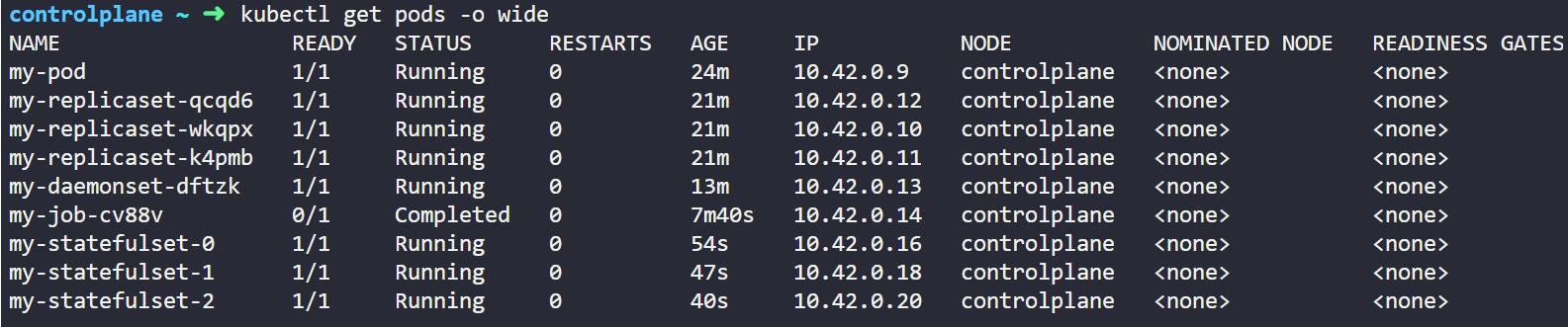
Here we can see that 3 StatefulSets has been created with unique named and stable IP address.
Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 1
maxUnavailable: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Here we have created Deployment with 3 replicas, strategy as RollingUpdate for nginx container. It will also ensures that 3 pods will always be running. We can create this object in our cluster by below command.
kubectl apply -f <deployment-object-file-name>
Here we have created Deployment named my-deployment which runs a nginx container. We can verify this from below.
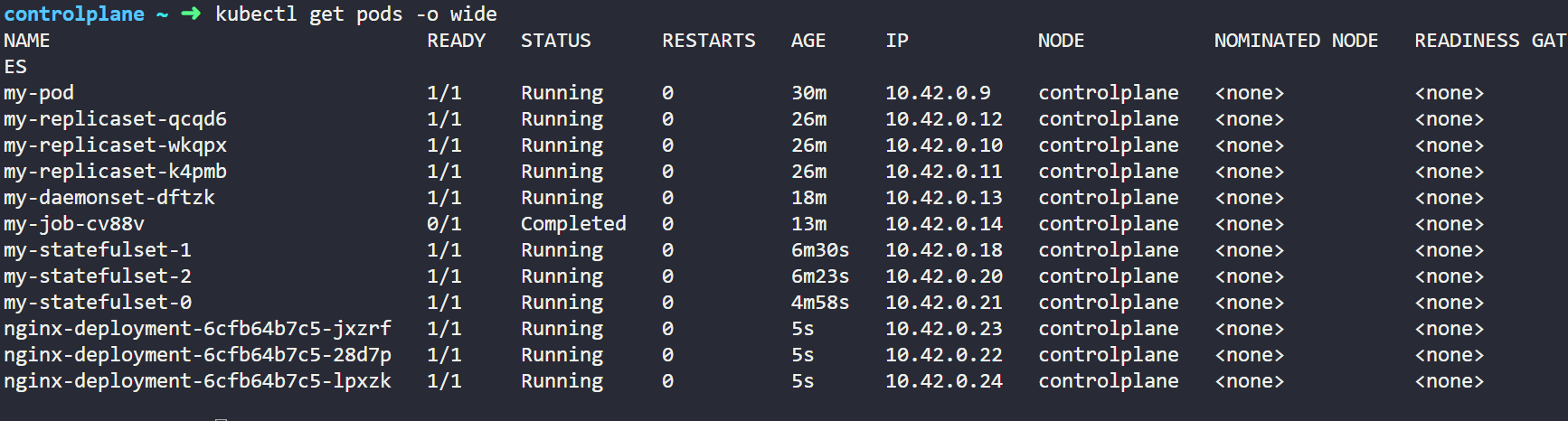
Namespace
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: my-namespace
Here we are creating Namespace named my-namespace. We can apply this by below command.
kubectl apply -f <namespace-object-file-name>
Once applied we can view the Namespace details as below output.
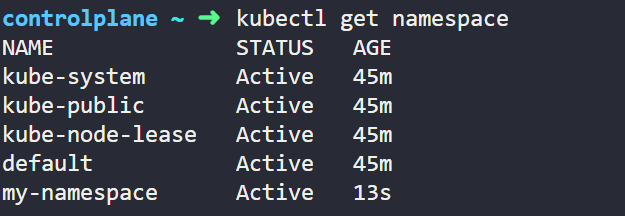
We can see that my-namespace named Namespace created 13 seconds ago and also we have default and some other namespace already available. These other namespace by default got created at the time of cluster setup.
That's all from my side for Kubernetes Objects.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Gaurav Kumar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Gaurav Kumar
Gaurav Kumar
I am working as a full time DevOps Engineer at Tata Consultancy Services from past 2.7 yrs, I have very good experience of containerization tools Docker, Kubernetes, OpenShift. I have good experience of using Ansible, Terraform and others.