Exploring Cloud Deployment Options: Public, Private, and Hybrid Models
 Sivasai Nukala
Sivasai Nukala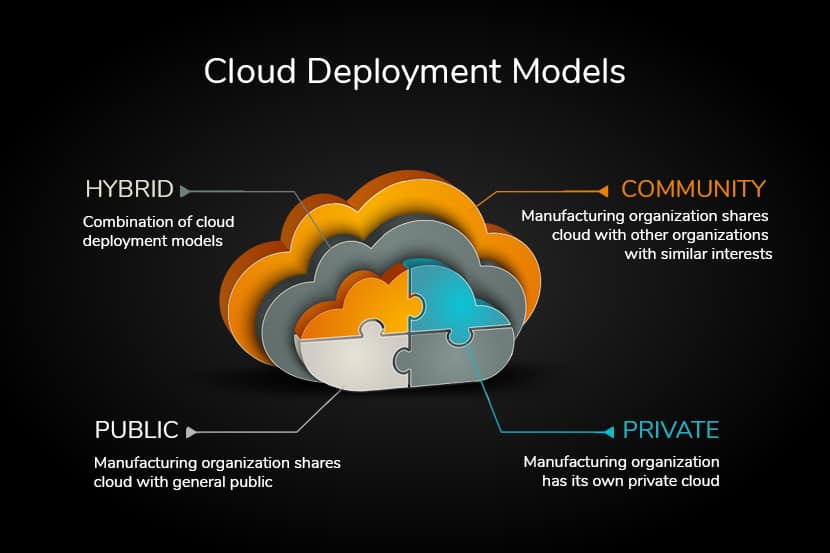
Understanding the various deployment models is essential for leveraging the cloud effectively. Today, we'll explore the three primary cloud deployment models: Public, Private, and Hybrid. Each model offers distinct advantages and is suited to different business needs.
1. Public Cloud
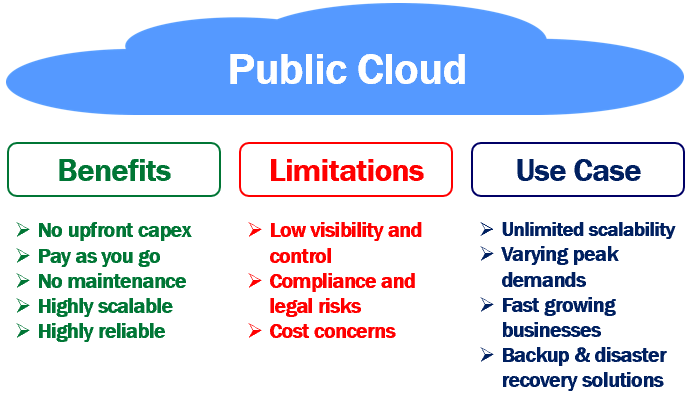
- Explanation: The public cloud is a cloud infrastructure that is shared among multiple organizations and is owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider. Resources like servers and storage are made available to the public over the internet.
Examples:
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Microsoft Azure
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Advantages: Cost-effective, scalable, and reliable.
Use Cases: Startups with limited budgets, e-commerce websites, development and testing environments.
2. Private Cloud
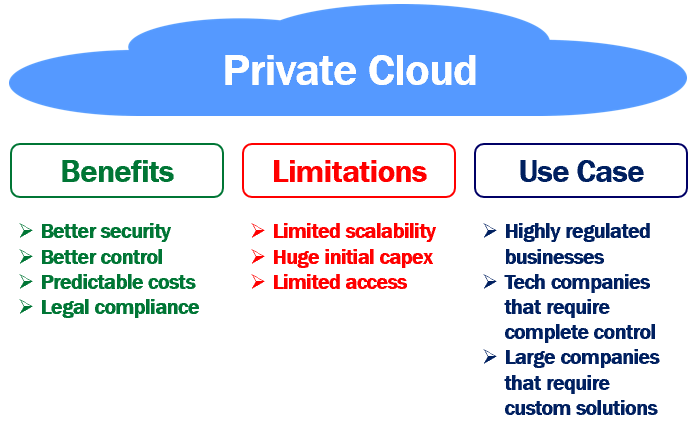
- Explanation: A private cloud is a cloud infrastructure that is used exclusively by a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party service provider. This model provides more control and customization over resources.
Examples:
VMware vSphere
OpenStack
IBM Cloud Private
Advantages: Greater control, customization, and compliance.
Use Cases: Financial institutions, healthcare organizations, large enterprises.
3. Hybrid Cloud
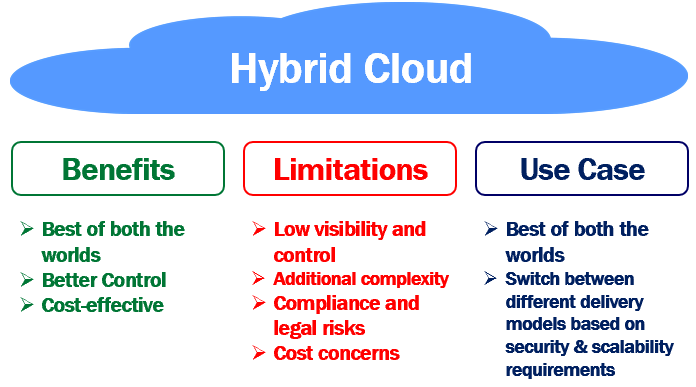
- Explanation: The hybrid cloud combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This model provides greater flexibility and optimized deployment options.
Examples:
Microsoft Azure Stack
Google Anthos
AWS Outposts
Advantages: Flexibility, cost efficiency, and scalability.
Use Cases: Disaster recovery, seasonal workloads, regulated industries.
4. Community Cloud
- Explanation: The community cloud is a collaborative model where the infrastructure is shared among several organizations from a specific group with common goals, security requirements, or compliance considerations. This cloud model is managed and used by multiple organizations, making it ideal for communities with shared concerns and interests.
Examples:
Government Cloud Solutions: Used by various government agencies to meet their specific compliance and security requirements.
Health Cloud: Shared by several healthcare providers to maintain HIPAA compliance while sharing patient data and resources.
Academic Cloud: Utilized by multiple educational institutions to share resources, research data, and collaborative tools.
Advantages:
Cost Sharing: Reduced costs as expenses are distributed among the community members.
Enhanced Security and Compliance: Tailored to meet specific industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Collaboration: Promotes cooperation and resource sharing among community members.
Use Cases:
Research Collaborations: Universities and research institutions sharing computational resources and research data.
Government Agencies: Different government bodies sharing infrastructure while maintaining high security and compliance.
Healthcare Consortia: Hospitals and healthcare providers sharing patient information and resources while complying with health regulations.
Best Regards,
Sivasai Nukala
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Sivasai Nukala directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Sivasai Nukala
Sivasai Nukala
I am a Pre Final year Computer Science student at KL University