Basic of Python
 ashwini purwat
ashwini purwat
What is Python? What are the benefits of using Python
Python is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language. Being a general-purpose language, it can be used to build almost any type of application with the right tools/libraries. Additionally, python supports objects, modules, threads, exception-handling, and automatic memory management which help in modelling real-world problems and building applications to solve these problems.
Benefits of using Python:
- Python is a general-purpose programming language that has a simple, easy-to-learn syntax that emphasizes readability and therefore reduces the cost of program maintenance. Moreover, the language is capable of scripting, is completely open-source, and supports third-party packages encouraging modularity and code reuse.
Python Data Types
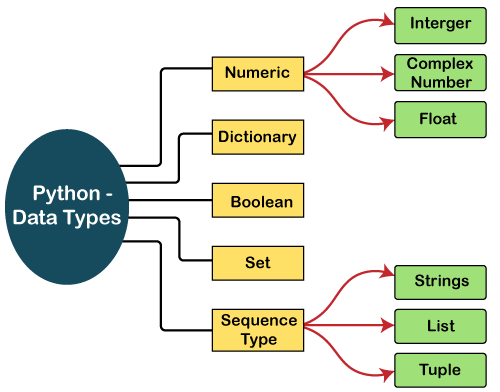
In Python, we have several types of data:
- Numeric : You can use integers, floating-point numbers, and complex numbers.
COPY
COPY
integer = 10
print(integer, 'is of type', type(integer))
floating_point = 20.5
print(floating_point, 'is of type', type(floating_point))
complex_num = 1j
print(complex_num, 'is of type', type(complex_num))
Dictionaries: Dictionaries are used to store data in key:value pairs.
COPY
COPY
dictionary = {"name": "Python", "age": 30}Booleans: These represent one of two values: True or False.
COPY
COPY
boolean_1 = True boolean_2 = FalseSet
The Set is an unordered collection of unique items. Set is defined by values separated by commas inside braces { }.
COPY
COPY
#Create a set named Student ID student_id = {111, 115, 113, 114, 110, 116, 117} #Display elements of it print(student_id) #Display Type of Student ID print(type(student_id))Sequences
Strings: These are sequences of character data. Enclose them in single or double quotes.
COPY
COPY
string_1 = 'Hello, World!' print(string_1)Lists: These are collections of items (strings, integers, or even other lists). 📝
COPY
COPY
list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry'] print(list[0]) print(list[2])Tuple: Tuple is an ordered sequence of items same as a list. The only difference is that tuples are immutable. Tuples once created cannot be modified.
We use the parentheses () to store items of a tuple.
COPY
COPY
#Create a Tuple product = ('Microsoft' , 'Linux-Ubuntu' , 'other') #Access Element at Numbber1 print(product[0]) #It will print Microsoft print(product[1]) #It will print Linux-UbuntuBasic Operations in Python
Python supports all the mathematical operations you would expect:
Addition (
+)Subtraction (
-)Multiplication (
*)Division (
/)Modulus (
%)
COPY
COPY
# Store input numbers
num1 = input('Enter first number: ')
num2 = input('Enter second number: ')
# Add two numbers
addition = float(num1) + float(num2)
print(addition)
subtraction = float(num1) - float(num2)
print(subtraction)
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from ashwini purwat directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
