Web 3.0 Unleashed: Dive into the Tech That's Shaping Our Future!
 Anushree Mehta
Anushree Mehta
Web 3.0, often referred to as the decentralized web, represents the next phase of internet evolution. It promises to bring more user control, privacy, and decentralization. In this blog we will explore the core technologies behind this transformation.
1. Blockchain
Blockchain is the backbone of Web 3.0. It is a distributed ledger technology that ensures transparency, security, and immutability of data. Here's how it works:
Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchain stores data across a network of computers, making it resistant to censorship and hacking.
Transparency: Every transaction on a blockchain is visible to all participants, fostering trust and accountability.
Immutability: Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity of information.
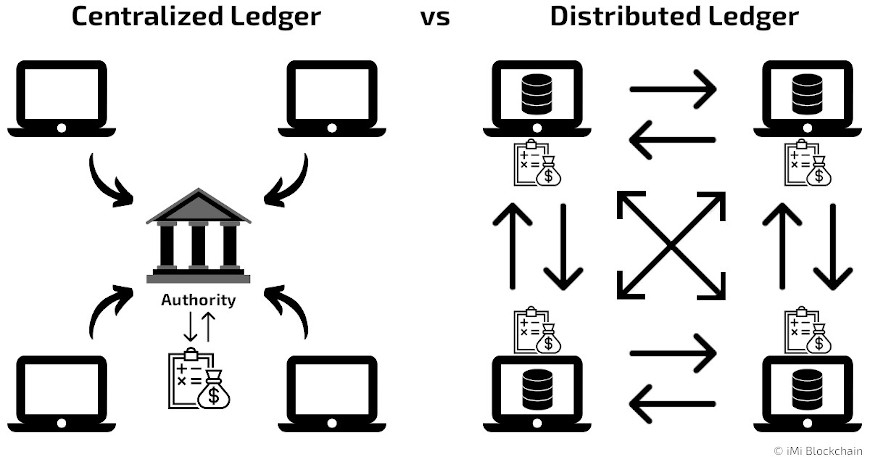
Blockchain technology can seem complex, but let's break it down with a simple, relatable example.
Simplest Example: The Digital Notebook
Imagine a group of friends, aman, harry, and Rahul, who decide to keep a shared digital notebook to record their transactions with each other. Here's how it works:
The Digital Notebook: This is the blockchain. It's a public, shared document that everyone in the group can see and verify.
Transactions: Each time aman, harry, or Rahul makes a transaction, it gets written in the notebook. For example, aman pays harry $10. This transaction is written down
Blocks: Transactions are grouped together into blocks. Imagine that every page of the notebook can only hold a certain number of transactions. Once the page is full, it's closed, and a new page starts. Each page is like a block in the blockchain.
Hashing: To ensure the integrity of the notebook, a special code called a hash is created from the contents of each page. This code acts like a fingerprint for the page. If even a single letter on the page is changed, the fingerprint changes completely, making it obvious that tampering has occurred.
Chaining: Each new page (block) includes the fingerprint (hash) of the previous page. This links the pages together in a chain, hence the name "blockchain."
Decentralization: The digital notebook isn't kept by just one person. Instead, every friend in the group has a copy. When a new page is filled, everyone updates their copy of the notebook. This way, if someone tries to cheat and write false transactions in their own copy, it won't match everyone else's copies, and the cheating attempt will be obvious.

Real-World Application: Bitcoin
Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, uses blockchain technology. Here’s a simplified look at how it works:
When Aman sends 1 Bitcoin to Harry, the transaction is recorded in a block.
This block is added to the Bitcoin blockchain, a public ledger.
Miners (people with powerful computers) validate the transaction by solving complex mathematical problems, ensuring its legitimacy.
Once validated, the block is added to the blockchain, and everyone’s copy of the ledger is updated.
Each block contains a list of transactions, and each new block includes a reference to the previous block, forming a secure, unalterable chain of transaction history.
By using blockchain, Bitcoin ensures that transactions are transparent, secure, and decentralized, preventing issues like double-spending or fraud.
2. Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
Cryptocurrencies and digital assets are transforming the way we think about money and ownership. Here's a straightforward explanation of what they are and how they work.
What are Cryptocurrencies?
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (like the US dollar or the euro), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology.
Scenario: aman wants to send 1 Bitcoin (BTC) to harry.
Transaction Creation: aman uses her digital wallet to create a transaction, specifying that she wants to send 1 BTC to harry. This transaction is broadcast to the entire Bitcoin network.
Transaction Validation: Miners pick up the transaction and validate it by solving a complex mathematical problem. This process, known as proof of work, ensures that the transaction is legitimate.
Adding to the Blockchain: Once validated, the transaction is grouped with others into a block, which is added to the Bitcoin blockchain. All participants in the network update their copies of the blockchain to include the new block.
Transaction Finalization: Harry receives the 1 BTC from aman. The transaction is now part of the blockchain, visible to all participants and immutable.
Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum is a blockchain platform that supports not only a cryptocurrency (Ether, or ETH) but also smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
Scenario: aman wants to create a smart contract to pay harry 10 ETH if he completes a task.
Smart Contract Creation: aman writes a smart contract in Ethereum's programming language, Solidity. The contract specifies that harry will receive 10 ETH upon completion of a specific task.
Deployment: aman deploys the smart contract on the Ethereum blockchain. This makes the contract visible and accessible to all network participants.
Task Completion: harry completes the task. The smart contract automatically verifies the completion and transfers 10 ETH from aman's wallet to harry's wallet.
Blockchain Update: The Ethereum blockchain updates to include the execution of the smart contract. All participants in the network can see that the contract conditions were met and that the transaction occurred.
Digital Assets: Beyond Cryptocurrencies
Digital assets include more than just cryptocurrencies. They encompass any asset that exists in digital form and has value, including:
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Unique digital assets representing ownership or proof of authenticity of items such as art, music, and collectibles.
Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets like the US dollar to minimize price volatility.
Utility Tokens: Digital tokens that provide access to a product or service within a blockchain ecosystem.
Example of NFTs: Digital Art
Creation: An artist creates a digital artwork and mints it as an NFT on a blockchain platform like Ethereum.
Ownership: The NFT represents the ownership of the artwork. It is unique and cannot be replicated.
Sale: The artist sells the NFT to a buyer. The transaction is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring that the buyer now owns the artwork.
Verification: Anyone can verify the authenticity and ownership of the NFT by checking the blockchain.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and digital assets are transforming the way we interact with the digital world. By breaking down these complex concepts into simple analogies, we can better understand their immense potential and real-world applications.
Together, these technologies promise a future where trust, transparency, and decentralization are integral to our digital interactions. From enhancing financial systems to securing digital art, the possibilities are vast and varied. Staying informed and engaged with these innovations will be crucial as they continue to evolve and reshape our world.
Give a follow to stay updated with our latest blogs :)
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Anushree Mehta directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Anushree Mehta
Anushree Mehta
Hii!! i am anushree mehta currently pursuing my btech degree from Poornima college of engineering in CS AI branch. i am a passionate front end developer and i am willing to contribute to the web3 market. i am working as a volunteer @dev station as a technical content writer. i love to attend and organise hackathons , this year i was the co-organiser of hack-it-sapiens - a national level hackathon.