Unix and Linux Fundamentals: A New User’s Guide
 Anushka Bhujang Pawar
Anushka Bhujang Pawar
Operating Systems:
It is an interface Between User and Hardware
Unix Flavors
Linux
Mac OS
AIX
Solaris
HP-UX
Why Choose Linux?
Multi-User & Multi-Tasking: Supports multiple users and tasks simultaneously.
Open Source: Freely available and modifiable by anyone.
Security: Built with strong security features.
Resource Efficiency: Requires fewer resources compared to other operating systems.
Popular Linux Distributions
RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux)
CentOS
Ubuntu
Amazon Linux
Fedora
Linux Mint
OpenSUSE
Architecture of Linux
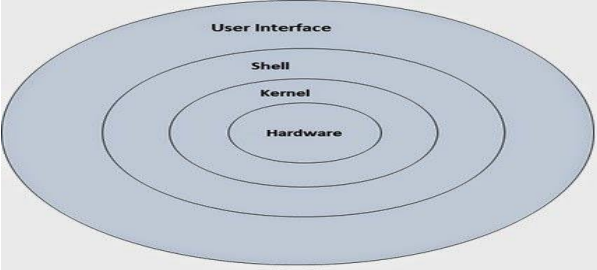
Certainly! Here are some important concepts and topics related to Linux that can enhance your blog:
1. Kernel vs. User Space
Kernel: The core component of Linux that manages hardware resources and system calls. It operates in privileged mode.
User Space: The area where user applications run. These applications interact with the kernel through system calls.
2. Linux Boot Process
- The boot process includes several stages: BIOS/UEFI initialization, bootloader (GRUB), kernel loading, and initialization of user space (init system).
3. Init Systems
Systemd: The most common init system in modern distributions, providing parallel startup, on-demand services, and managing system resources.
SysVinit: The traditional init system, using scripts to manage services.
4. Package Management Systems
APT (Advanced Package Tool): Used in Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu for managing software packages.
DNF (Dandified YUM): The next-generation version of YUM used in Fedora and RHEL-based systems.
5. Linux File Permissions
- The permission model (read, write, execute for user, group, and others) and use
chmod,chown, andchgrpeffectively.
6. Processes and Job Control
Processes: Instances of running programs, which can be managed using commands like
ps,top, andkill.Job Control: Background and foreground processes can be managed using
bg,fg, andjobs.
7. Networking Basics
- Networking key concepts, such as IP addressing, subnetting, DNS, and common tools like
ping,traceroute, andnetstat.
8. Shell Scripting
- Basics of writing shell scripts, including shebang (
#!/bin/bash), variables, control structures (if statements, loops), and functions.
9. System Monitoring and Logs
- Using tools like
top,htop,vmstat, andiostatfor performance monitoring. log files located in/var/log, can be used for troubleshooting.
10. Security Practices
- Important to keep the system updated, using firewalls (like
iptablesorfirewalld), and understanding SELinux/AppArmor for enhanced security.
11. Virtualization and Containers
- We can use virtualization technologies (KVM, VirtualBox) and containerization (Docker, Podman) for creating isolated environments.
12. Cloud Integration
- Linux plays a crucial role in cloud environments (AWS, Azure) and the use of cloud-init for instance initialization.
13. Common Troubleshooting Commands
- Tools and commands for diagnosing issues, such as
dmesg,journalctl,strace, andlsof.
File System Hierarchy in Linux
/ - The root directory, top level of the filesystem.
/root - Home directory for the root user.
/home - Home directories for other users.
/boot - Contains bootable files for Linux.
/etc - Stores configuration files.
/usr - Default location for installed software.
/bin - Contains user commands.
/sbin - Commands used by the root user.
Basic Linux Commands
File and Directory Operations:
cat- Create and append files.touch- Create a blank file.nano,vi/vim- Create and edit files.ls- List directory contents (-a,-lafor detailed listing).cd- Change directory.pwd- Print working directory.mkdir- Create directory, including multiple directories with-p.cp- Copy files and directories.mv- Move or rename files and directories.rm- Remove files;rm -rfto remove directories recursively.tree- View directory structure in tree format.find- Search for files and directories (-type ffor files,-type dfor directories).
Viewing and Filtering Files:
grep- Search and print matching lines in files.less,more- View file content page by page.head- Display the first 10 lines of a file.tail- Display the last 10 lines of a file.sort- Sort file content alphabetically or numerically.
User and Group Management:
useradd,usermod,userdel- Manage users.groupadd,groupmod,groupdel- Manage groups.gpasswd- Manage group membership (-ato add,-Mfor multiple users,-dto delete).passwd- Change user password.chown- Change file owner.chgrp- Change file group.chmod- Change file permissions.
Networking and System Information:
hostname- Display or set the system hostname.ifconfig- Display or configure network interfaces.cat /etc/*rele*- Display operating system version.
Package Management with YUM:
yum install <package>- Install a package.yum update <package>- Update a package.yum remove <package>- Uninstall a package.yum list installed- List installed packages.service <service> status- Check the status of a service.service <service> start- Start a service.service <service> restart- Restart a service.chkconfig <service> on- Enable a service to start at boot.chkconfig <service> off- Disable a service from starting at boot.
Miscellaneous Commands:
tar- Archive files (-cvfto create,-xvfto extract).gzip,gunzip- Compress and decompress files.wget- Download files from the web.which- Locate a command.sudo- Execute a command as the root user.whoami- Display the current user.du -h- Display disk usage in a human-readable format.
Key Shortcuts and Tips
cat: End input withCtrl+D.nano: Save and exit withCtrl+X.Creating Nested Directories: Use
mkdir -p dir1/dir2.Deleting Directories: Use
rm -rfto remove directories recursively.Using
grep: Example:grep root /etc/passwd.Viewing Files: Use
less /etc/passwd,head -3 /etc/passwd.Sorting Files: Use
sort <filename>.Creating Links:
ln -sfor soft links,lnfor hard links.Managing Tar Archives:
tar -cvfto create,tar -xvfto extract.Compressing Files: Use
gzipto compress andgunzipto decompress.
This overview provides a solid foundation for understanding and working with Linux, emphasizing its flexibility, efficiency, and security.
further detailed tutorials for your better referance:
1] https://youtu.be/_tCY-c-sPZc?si=hXVQGssvs0GblPcG
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Anushka Bhujang Pawar directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
