Decoding Video Data: Understanding File Formats and Codecs
 ritiksharmaaa
ritiksharmaaa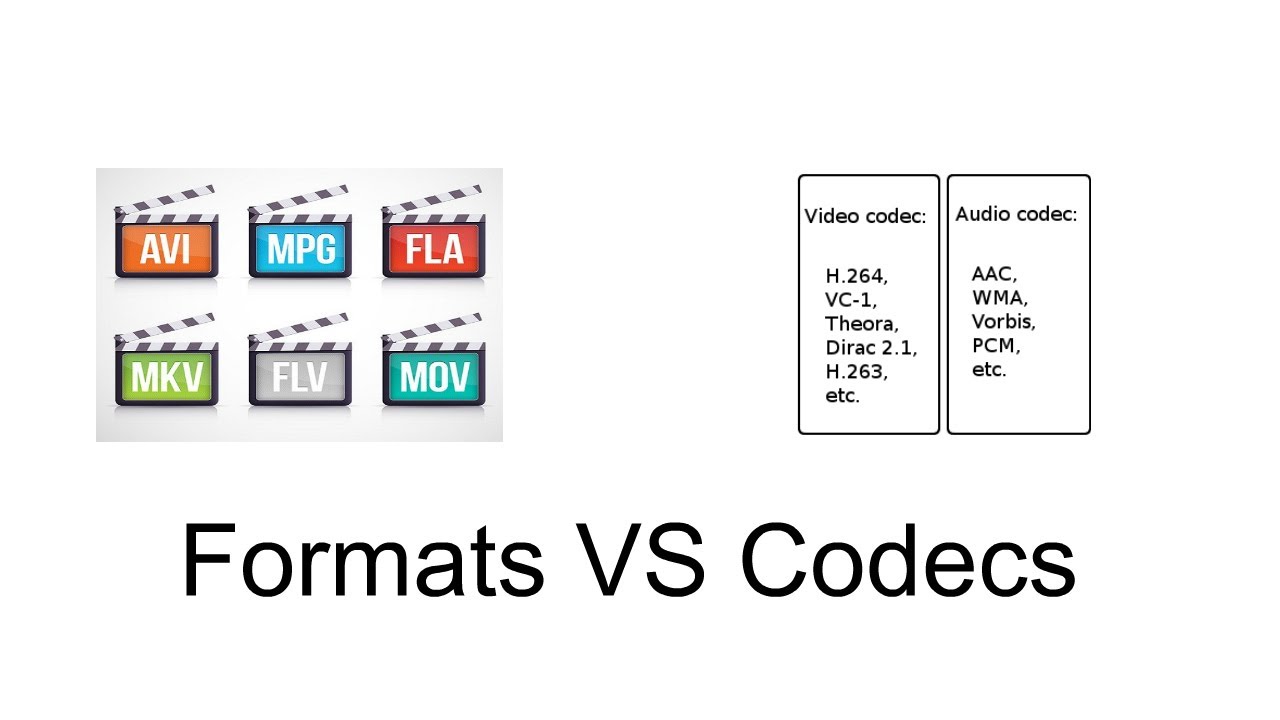
Understanding Video Recording Information and File Formats
Recording a video involves capturing a variety of data types beyond just the visual content. To effectively store and play back this information, we use various file formats and encoding methods. This article delves into the essential components of recorded video data, the role of codecs, the diversity of file formats, and what each file format typically stores
Components of Recorded Video Data

A recorded video comprises several types of data, each serving a distinct purpose:
Video Data: The visual content captured by the camera.
Audio Data: The sound recorded during the video.
Metadata: Information about the video such as date, time, and camera settings.
Subtitles and Captions: Text overlays that provide dialogue or descriptions.
Thumbnails: Small preview images of the video content.
The Role of Codecs
Codecs (short for compressor-decompressor) are essential for encoding and decoding video and audio data. They compress the data to reduce file sizes and decompress it for playback. Codecs are vital because raw video and audio files are extremely large and impractical for storage and transmission.
Video Codecs: Examples include H.264, H.265 (HEVC), and VP9. These codecs compress video data by removing redundant information and predicting motion between frames.
Audio Codecs: Examples include AAC, MP3, and Opus. These codecs compress audio data by eliminating sounds that are inaudible to the human ear.
Diversity of File Formats

There are numerous video file formats, each designed to serve different purposes and support various types of data. Here’s why we have a variety of file formats:
Compatibility: Different devices and platforms support different formats.
Quality: Some formats offer higher quality at the expense of larger file sizes.
Flexibility: Certain formats support a wide range of codecs and data types.
Efficiency: Some formats are optimized for specific use cases, such as streaming or editing.
Common Video File Formats and Their Content
MP4 (.mp4)
Purpose: Versatile, widely supported format for video and audio storage.
Contents:
Video data (encoded with codecs like H.264)
Audio data (encoded with codecs like AAC)
Subtitles
Metadata
MOV (.mov)
Purpose: Commonly used for professional video editing.
Contents:
High-quality video data
Audio data
Metadata
Subtitles
MKV (.mkv)
Purpose: Flexible format supporting multiple audio tracks and subtitles.
Contents:
Video data (supports various codecs)
Multiple audio tracks
Subtitles
Metadata
AVI (.avi)
Purpose: Older format, less efficient for modern use.
Contents:
Video data (supports various codecs)
Audio data
Metadata
WebM (.webm)
Purpose: Optimized for web streaming.
Contents:
Video data (encoded with VP8/VP9)
Audio data (encoded with Opus)
Metadata
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of video recording information and the role of codecs and file formats is crucial for anyone working with video content. The variety of file formats available ensures that we can choose the right one for our specific needs, balancing factors such as quality, file size, and compatibility. By comprehensively grasping these concepts, we can better manage, store, and share video content effectively.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from ritiksharmaaa directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

ritiksharmaaa
ritiksharmaaa
Hy this is me Ritik sharma . i am software developer