Transcoding : part 1
 ritiksharmaaa
ritiksharmaaa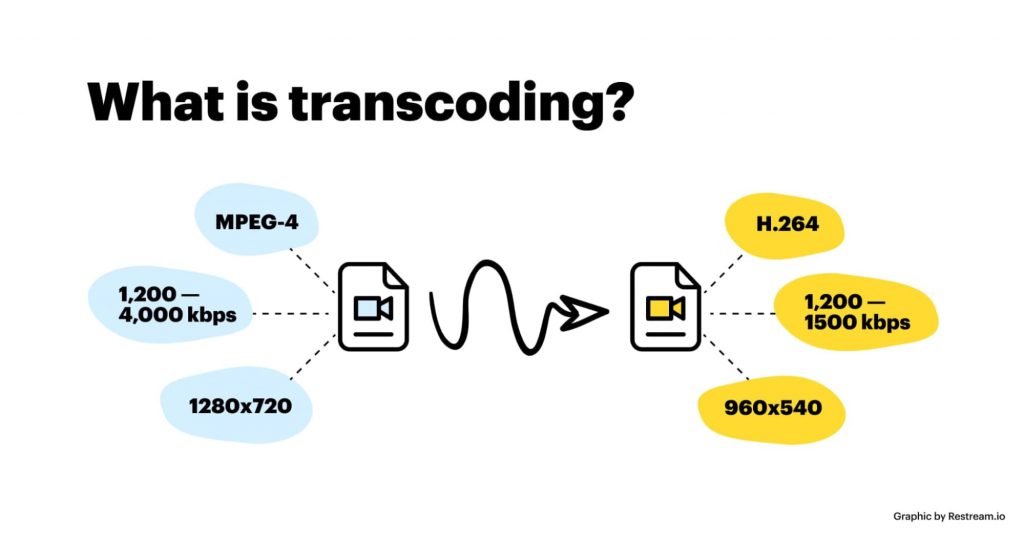
Understanding Key Terminologies in Video Production
Bitrate
Definition: The amount of data processed per unit of time, usually measured in kilobits per second (kbps) or megabits per second (Mbps).
Importance: Higher bitrates generally result in better video quality but require more bandwidth and storage.
Resolution
Definition: The number of pixels displayed on the screen, typically expressed as width x height (e.g., 1920x1080 for Full HD).
Importance: Higher resolution provides clearer and more detailed images but also increases file size and bandwidth requirements.
Frame Rate
Definition: The number of frames displayed per second (fps).
Importance: Higher frame rates result in smoother motion, important for fast-paced action and sports videos. Common frame rates are 24, 30, and 60 fps.
Aspect Ratio
Definition: The ratio of the width to the height of the video frame.
Importance: Determines the video's shape and compatibility with different display devices. Common aspect ratios include 16:9 (widescreen) and 4:3.
Codec
Definition: A software or hardware tool that compresses and decompresses digital video.
Importance: Determines the efficiency of compression and quality. Popular codecs include H.264, H.265 (HEVC), and VP9.
Color Depth
Definition: The number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel.
Importance: Higher color depth provides a greater range of colors and more accurate color representation. Common values are 8-bit, 10-bit, and 12-bit.
File Format
Definition: The container that holds the video data, such as .mp4, .mov, .mkv, etc.
Importance: Affects compatibility with different devices and software. Each format supports various features and compression methods.
Compression
Definition: The process of reducing the file size of the video.
Importance: Balances video quality and file size. Compression can be lossy (reduces quality) or lossless (maintains quality).
Bit Depth
Definition: The number of bits used to store each sample of audio or video.
Importance: Higher bit depth provides more dynamic range and detail. For video, it influences color representation and for audio, it affects sound quality.
Understanding these properties helps in optimizing video quality for different use cases, such as streaming, broadcasting, or archiving.
Frame Rate in Video Production
Frame rate, measured in frames per second (fps), is a crucial aspect of video production that determines how smoothly motion is depicted. Essentially, it refers to the number of individual frames or images displayed per second in a video.
Common Frame Rates:
24 fps: Standard for films, providing a cinematic look.
30 fps: Typical for TV and online content, offering a balance between smooth motion and file size.
60 fps: Often used for sports and video games, delivering very smooth motion.
Higher frame rates result in smoother video, which is especially important for fast-paced action. However, higher fps also means more data to process and larger file sizes. Understanding and selecting the appropriate frame rate is key to achieving the desired visual effect in your videos.
Resolution
Resolution, in the context of video and images, refers to the detail an image or video holds. Higher resolution means more image detail. Resolution can be measured in various ways depending on the medium and context.
Video Resolution
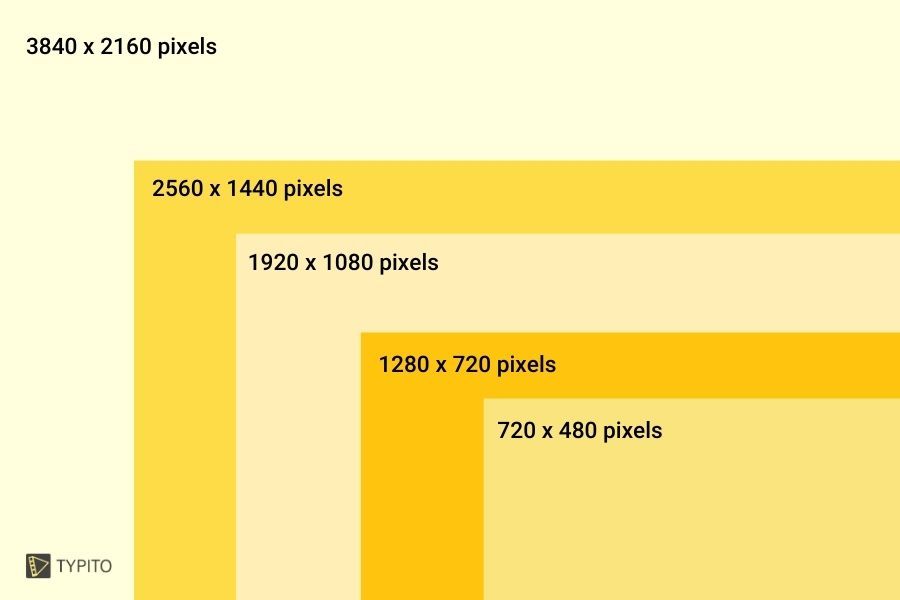
Video resolution describes the number of pixels that can be displayed on the screen, typically given as width x height. Common video resolutions include:
480p (SD - Standard Definition): 640 x 480 pixels
720p (HD - High Definition): 1280 x 720 pixels
1080p (Full HD): 1920 x 1080 pixels
1440p (2K): 2560 x 1440 pixels
2160p (4K - Ultra High Definition): 3840 x 2160 pixels
4320p (8K): 7680 x 4320 pixels
The 'p' stands for progressive scan, which means each frame is drawn in sequence. There is also 'i' for interlaced, where each frame is split into even and odd lines.
Impact on Quality
Higher resolution videos offer more detail and can be displayed on larger screens without losing clarity. However, they also require more storage space and higher bandwidth for streaming.
Image Resolution
Image resolution is typically measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI) for print. Higher PPI or DPI means more detail.
Digital Images
Low Resolution: 72 PPI, commonly used for web images.
High Resolution: 300 PPI, used for print images to ensure they are sharp and detailed.
Impact on Quality
Higher resolution images can be printed at larger sizes without becoming pixelated or blurry. For digital use, higher resolution means more detail, but also larger file sizes.
Aspect Ratio
Resolution is often discussed in conjunction with aspect ratio, which is the ratio of the width to the height of the image or video. Common aspect ratios include:
4:3: Traditional TV and computer monitors.
16:9: Widescreen TVs, most modern monitors, and smartphones.
21:9: Ultra-wide monitors and some cinema formats.ntext.
Practical Considerations
When deciding on a resolution for video or images, consider:
Purpose: Higher resolutions are better for detailed work and large displays, while lower resolutions can save on storage and bandwidth.
Device Compatibility: Ensure the resolution is supported by the devices that will display the content.
Performance: Higher resolution requires more processing power, which can impact performance on less powerful devices.
Understanding resolution is crucial for tasks like video streaming, where you need to balance quality with bandwidth and storage constraints.
In video resolution terminology, the letter "p" stands for "progressive scan." It's a term used to describe how the video image is displayed on the screen. Here's what it means in the context of resolutions like 360p, 480p, 720p, and 1080p:
Understanding the 'p' in Video Resolutions

Progressive Scan (p)
Definition: Progressive scan displays the entire frame of video in one pass, meaning each frame is made up of a complete set of lines. In other words, every frame is drawn all at once.
Advantages: Progressive scan provides smoother and more detailed images, especially for fast-moving content, because each frame is shown in its entirety. It avoids the issues related to interlacing, such as combing artifacts.
Common Resolutions with 'p'
360p (640x360): A low-resolution format often used for streaming on mobile devices or low-bandwidth scenarios.
480p (854x480): Standard definition (SD) resolution, which is higher quality than 360p and is commonly used for DVDs and older television formats.
720p (1280x720): High definition (HD) resolution providing a significant improvement in clarity and detail compared to 480p. It is widely used in HD broadcasting and online streaming.
1080p (1920x1080): Full high definition (Full HD) resolution, offering even greater clarity and detail, commonly used in Blu-ray discs, modern television broadcasts, and high-definition online content.
Progressive vs. Interlaced Scan
Progressive Scan (p):
Displays each frame as a whole.
Results in smoother motion and better quality, particularly noticeable in fast-moving scenes.
Examples: 720p, 1080p.
Interlaced Scan (i):
Displays each frame in two passes: first showing the odd lines, then the even lines.
Can lead to artifacts like combing in fast-moving scenes, as the image is split into two fields.
Examples: 480i, 1080i.
Why It Matters
Image Quality: Progressive scan generally provides better image quality than interlaced scan, especially for modern displays that are optimized for progressive content.
Compatibility: Most contemporary media and streaming services use progressive scan formats because they offer superior quality and compatibility with modern display technology.
By understanding the "p" in these resolutions, you can better appreciate the quality and performance characteristics of different video formats.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from ritiksharmaaa directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

ritiksharmaaa
ritiksharmaaa
Hy this is me Ritik sharma . i am software developer
