𝑫𝙚𝒗𝙊𝒑𝙨𝒊𝙛𝒊𝙘𝒂𝙩𝒊𝙤𝒏 𝒐𝙛 𝙂𝒐 𝑾𝙚𝒃 𝑨𝙥𝒑𝙡𝒊𝙘𝒂𝙩𝒊𝙤𝒏
 Gopi Vivek Manne
Gopi Vivek Manne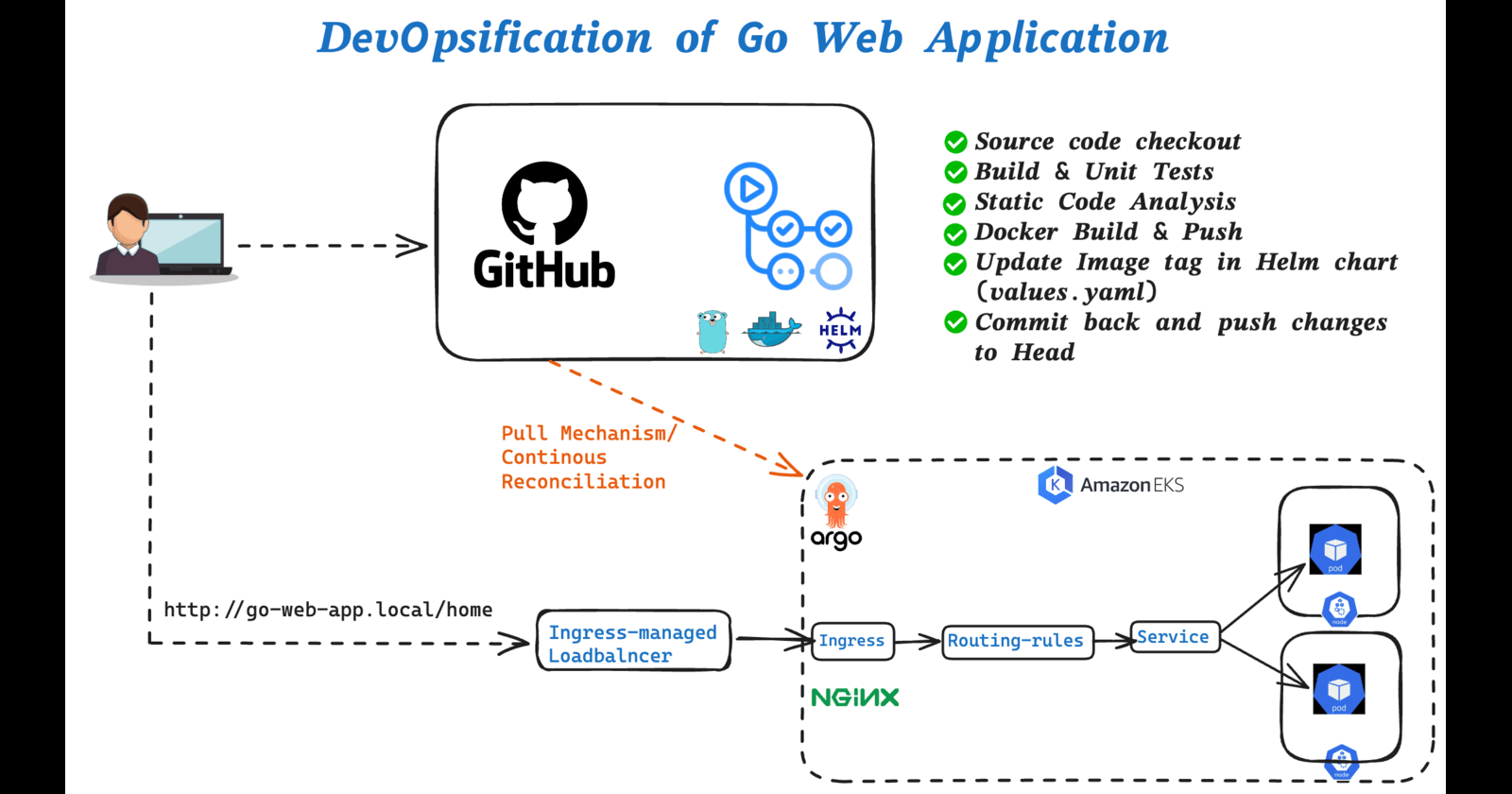
💁 Overview
This project demonstrates how to deploy a Go based web application to Amazon EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service) with a complete CI/CD pipeline using GitHub Actions, Helm, and ArgoCD.
❇ Implementation
💠 Clone the Repository
Firstly, clone the repository to your local using this command
git clone https://github.com/gmanne11/go-web-app.git
# change directory to go-web-app-devops
cd go-web-app-devops
💠 Prerequisites
Ensure you have the following tools installed and configured:
eksctl
kubectl
AWS CLI
Docker
Docker Scout
Helm
💠 Project Overview
This project includes:
A Go web application
Dockerfile for containerization
Kubernetes manifests
Helm chart for deployment
GitHub Actions workflow for CI
ArgoCD configuration for CD
💠 Local Development
Build the Docker image: Build the Docker image out of Dockerfile locally using the command
docker build -t vivekmanne/go-web-app:v1 .Check for the image created locally,
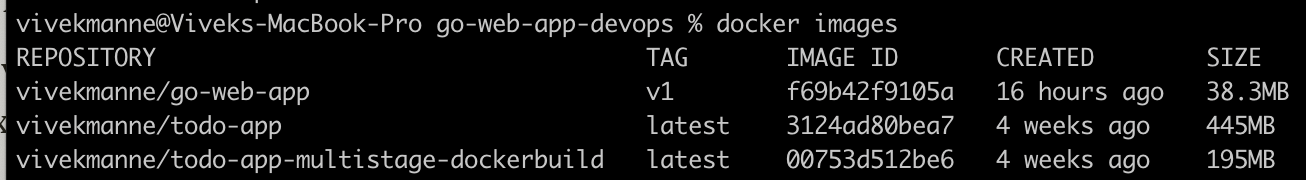
As you can see, the image named go-web-app of size less than 40MB. Since we used Multi-stage-Dockerfile with Distroless base image during the run time stage helps to build leaner and more secured image.
Run the application locally:
docker run -it -p 8080:8080 vivekmanne/go-web-app:v1Access the application at
http://localhost:8080/courses
Push the image to Docker Hub using the command like
docker push vivekmanne/go-web-app:v1
💠 Kubernetes Deployment
Now, change the directory to view the Kubernetes manifests (Deployment, Service, Ingress)
cd k8s/manifestsCreate EKS cluster using the command like
eksctl create cluster --name demo-cluster-1 --region ca-central-1Ensure the cluster is up and running with 2 Nodes
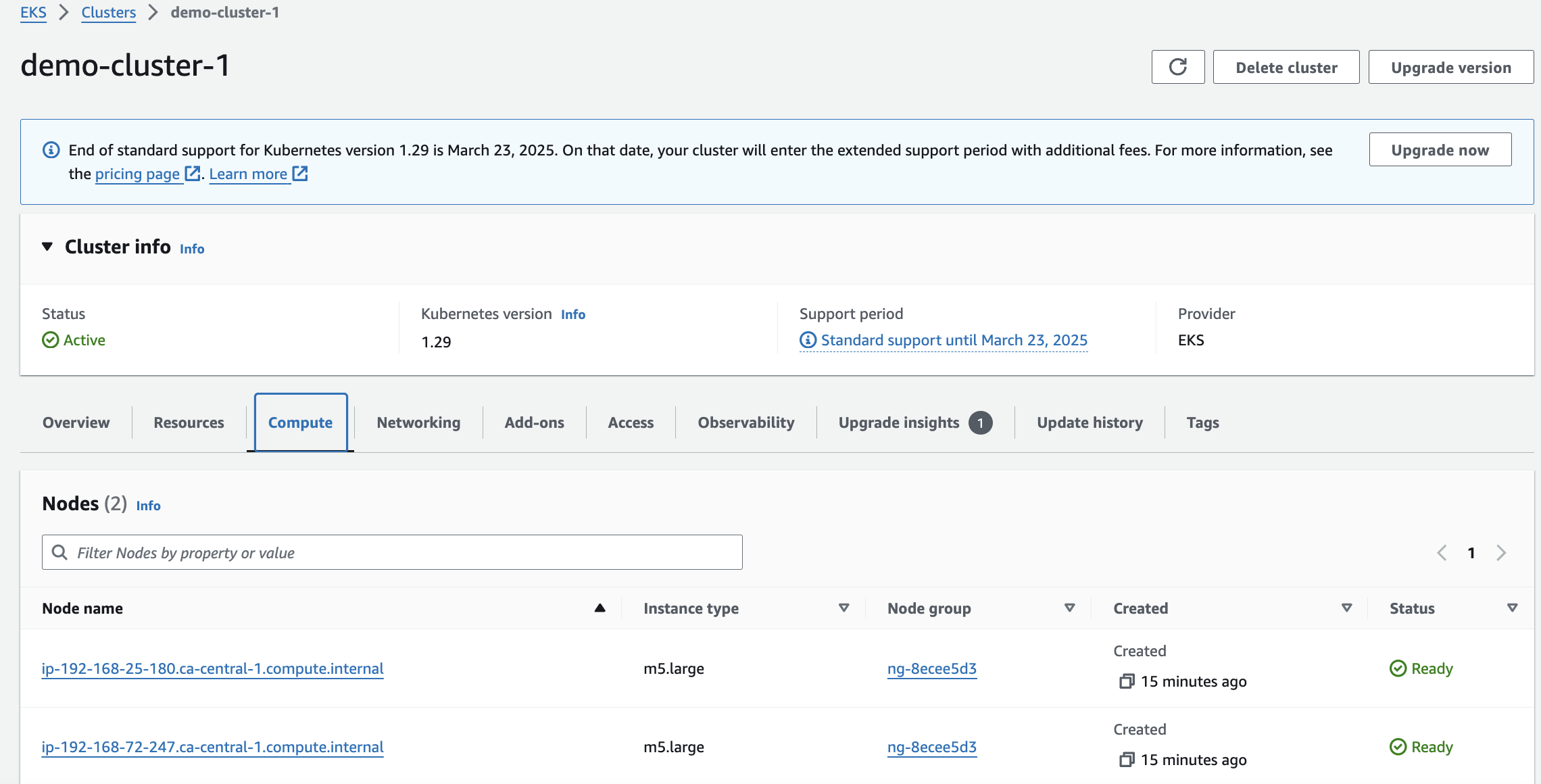
Verify that you are using the correct cluster context
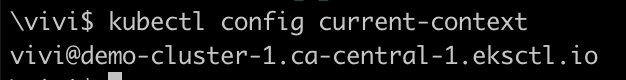
Deploy the manifests to EKS cluster
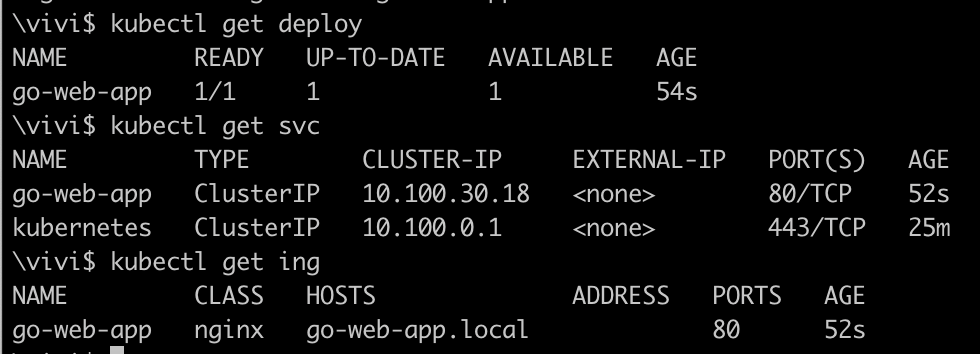
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml kubectl apply -f service.yaml kubectl apply -f ingress.yamlVerify the deployment, service and ingress are created
Let's edit the service
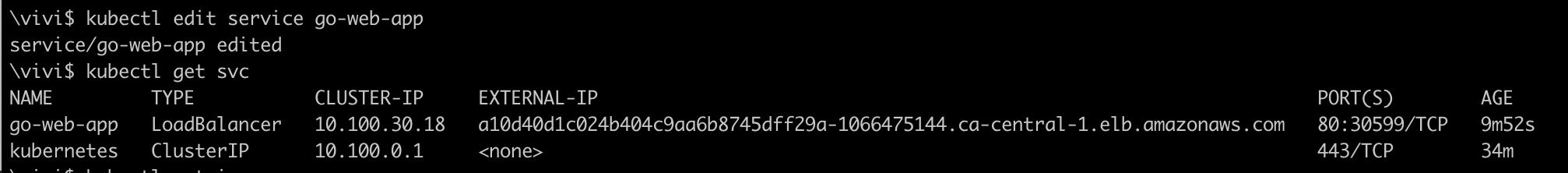
go-web-appto make itLoadBalancertypekubectl edit service go-web-app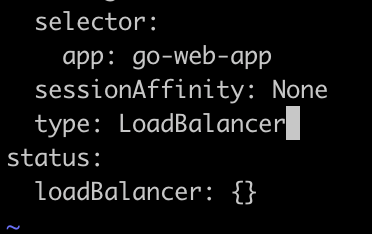
Make the change of LoadBalancer type as shown above.
Now, get the Load balancer DNS name assigned to the service and access it from browser
Deploy NGINX Ingress Controller on AWS using the below manifest
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.11.1/deploy/static/provider/aws/deploy.yamlThis will ensure the NGINX ingress controller is deployed inside the EKS cluster. By default all the resources for ingress controller will be deployed in namespace
ingress-nginx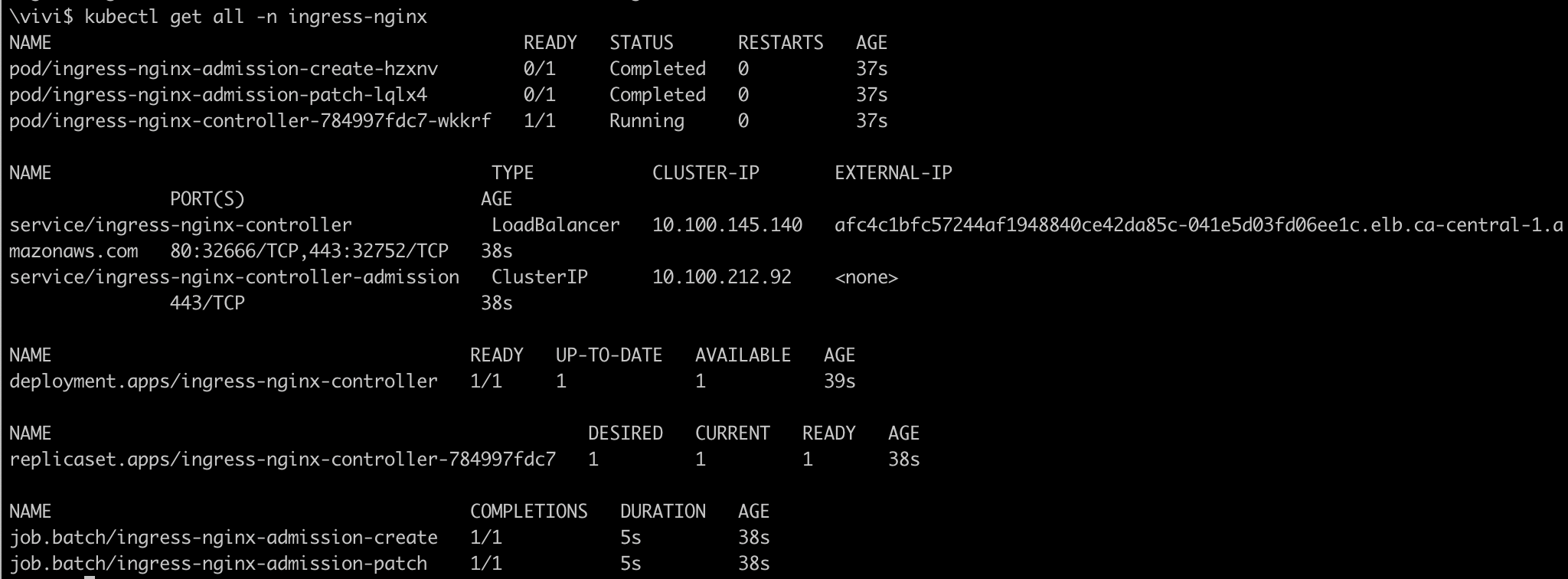
Now, the NGINX ingress controller will create NLB(Network load balancer) in AWS and attach to ingress. Ingress controller will watch out for Ingress resource and implements the rules defined and also assigns load balancer DNS to the ingress.
The NLB will route the incoming traffic to the NGINX Ingress Controller, which will then process the requests based on the Ingress rules and forward them to the appropriate services within your Kubernetes cluster.
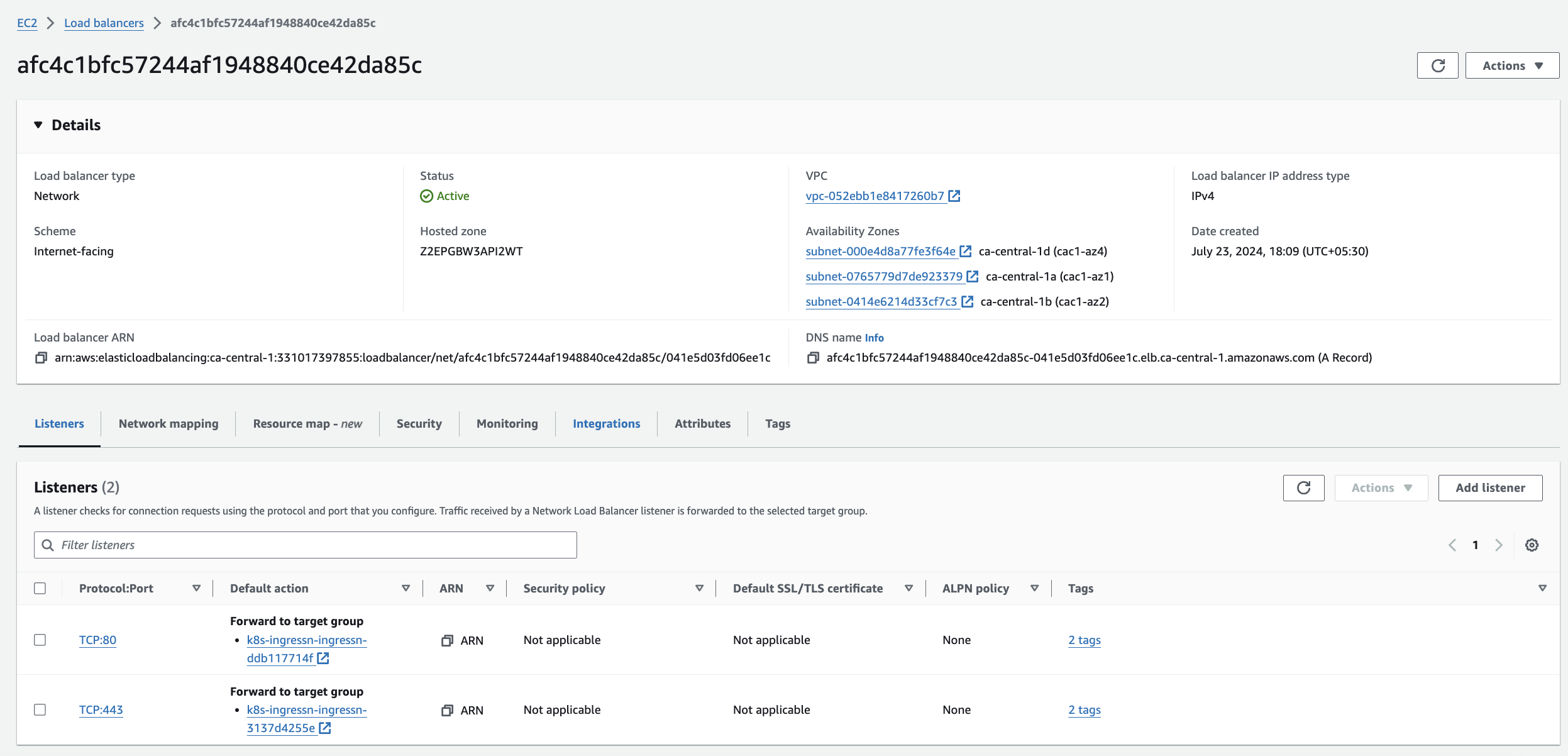
Verify that NLB is created in AWS
Here is ingress.yaml file
# Ingress resource for the application apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: go-web-app annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: / spec: ingressClassName: nginx rules: - host: go-web-app.local http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: go-web-app port: number: 80

In our case, The Load balancer DNS route the traffic to ingress controller where ingress resource rules are validated and we used host based routing rules as you can see in the ingress.yaml. when you access go-web-app.local to forwards the traffic to service named go-web-app and eventually to target pods.
Configure DNS mapping in
/etc/hostslocallyLook for the IP address of Load Balancer DNS using the following command
nslookup afc4c1bfc57244af1948840ce42da85c-041e5d03fd06ee1c.elb.ca-central-1.amazonaws.comThen, add the DNS mapping in
/etc/hostsfile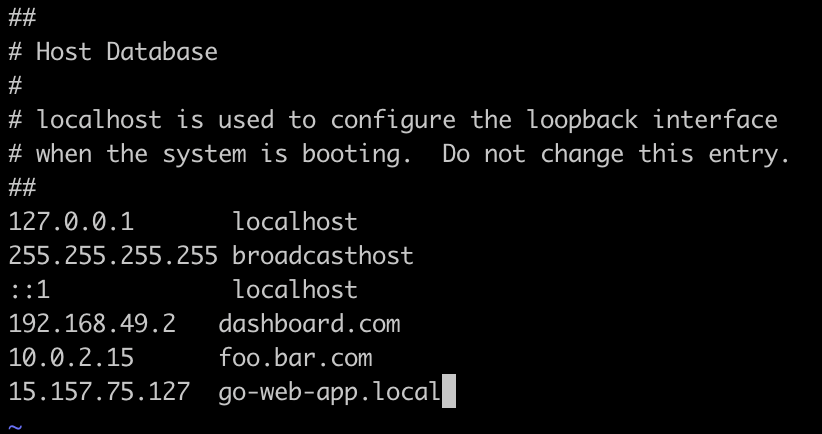
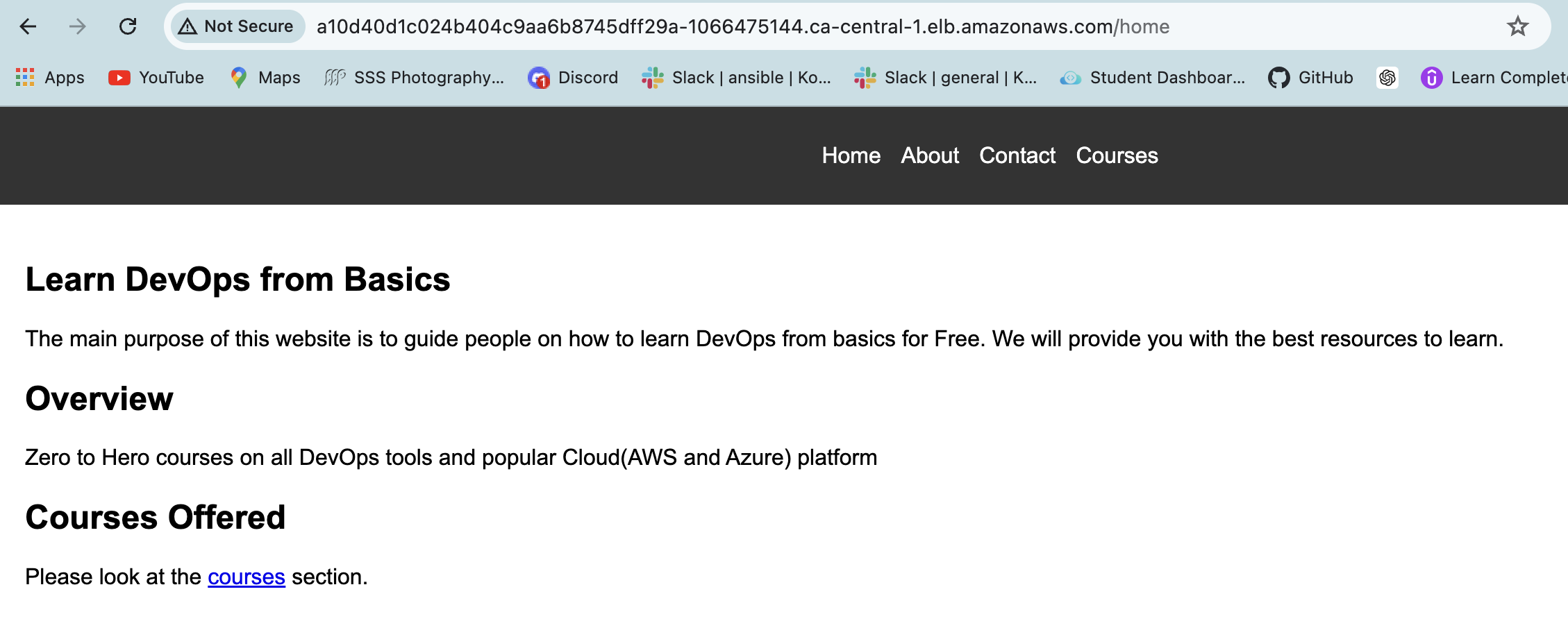
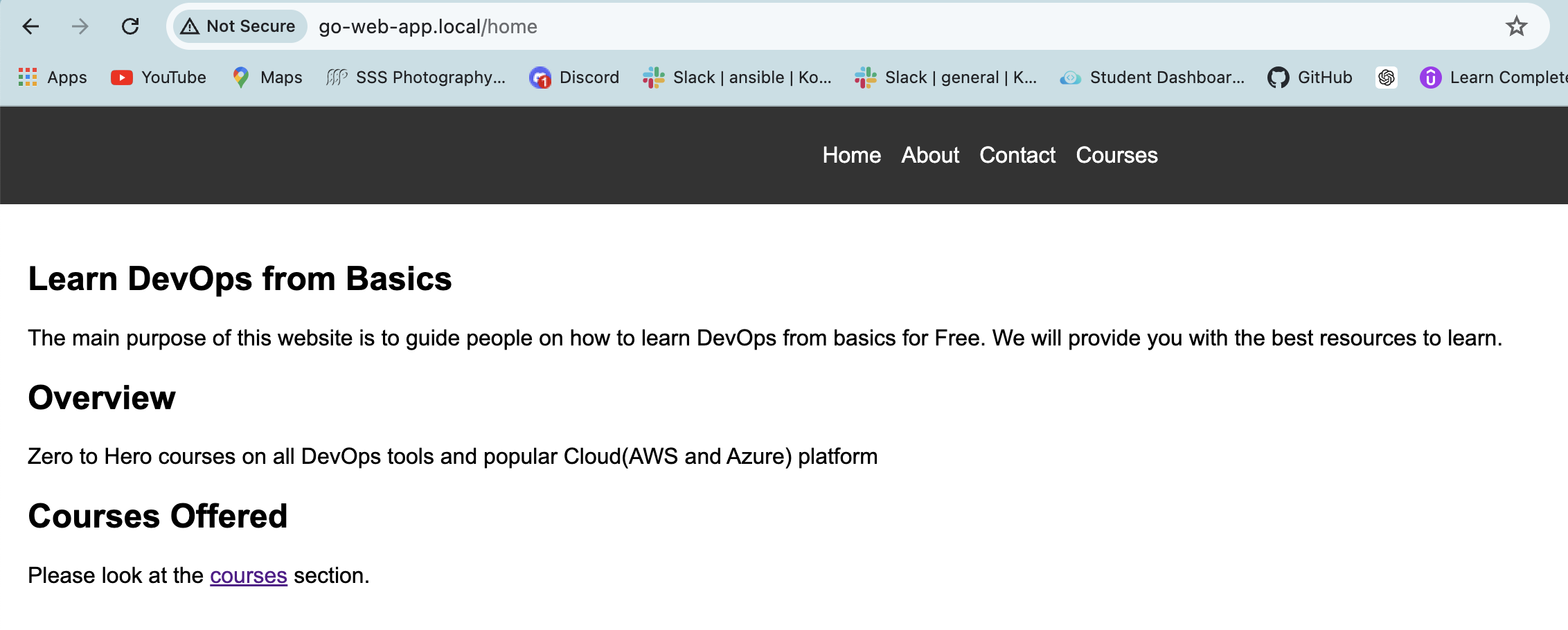
Now, Access the application using go-web-app.local/home
💠 Helm Chart Deployment
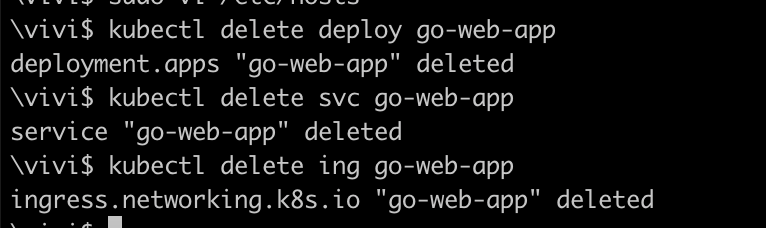
Make sure the k8s resources are deleted before proceeding with deployment using helm chart
Ensure you are in the correct directory of
helmcd helm/Deploy using Helm and verify the objects are deployed
helm install go-web-app ./go-web-app-chart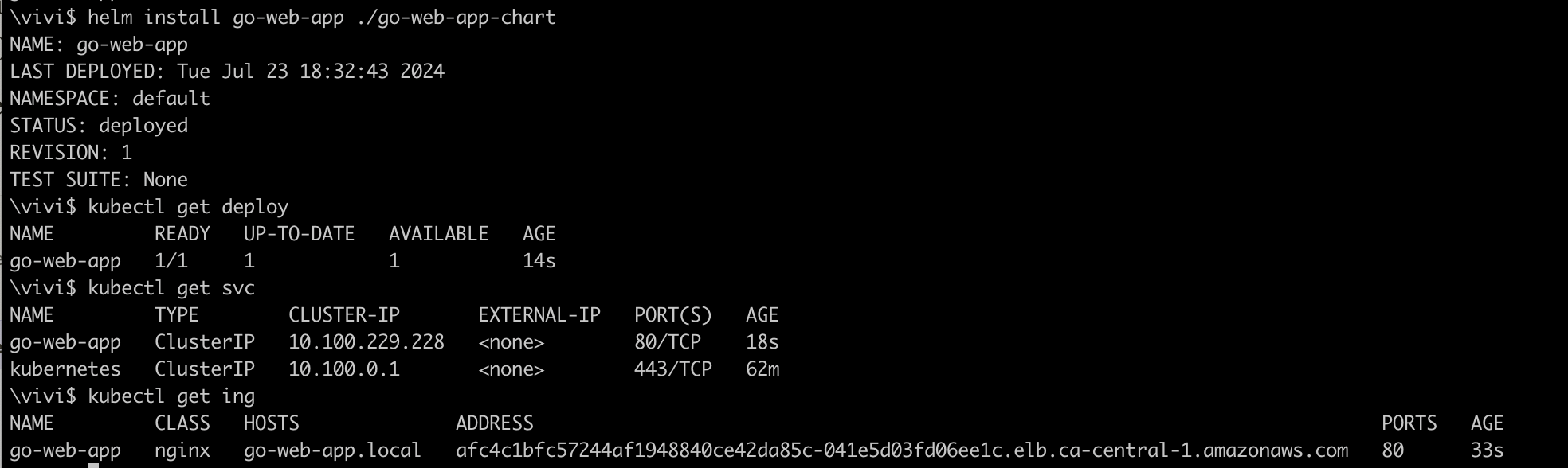
The NLB automatically assigns Load Balancer DNS name to ingress hosts as u can see above.
Try accessing the application again using
go-web-app.local/home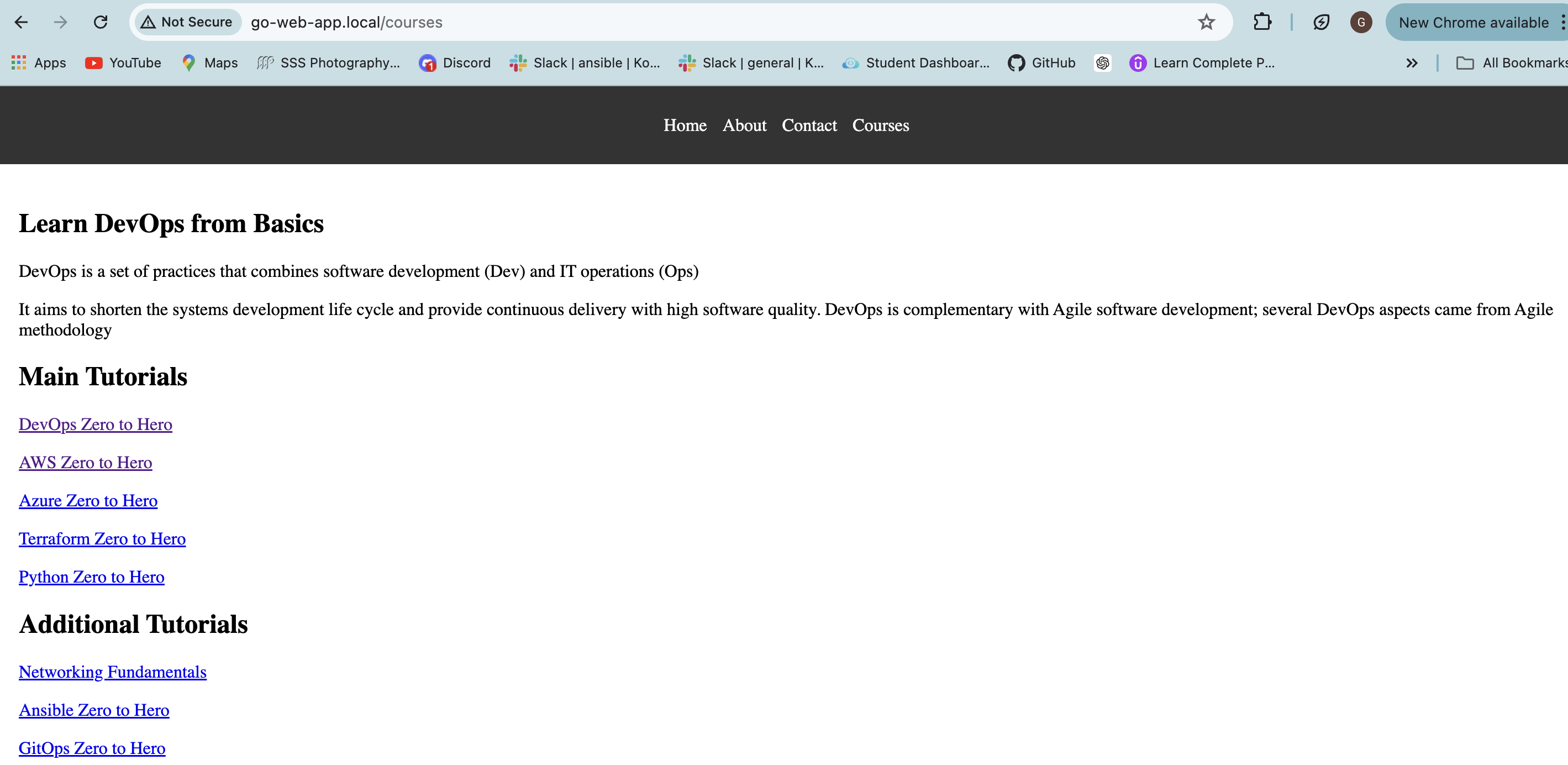
💠 CI/CD Pipeline
✅ CI with GitHub Actions
Check
.github/workflows/cicd.yamlwith the following stages:
✅ Checkout code✅ Build and run unit tests
✅ Perform static code analysis
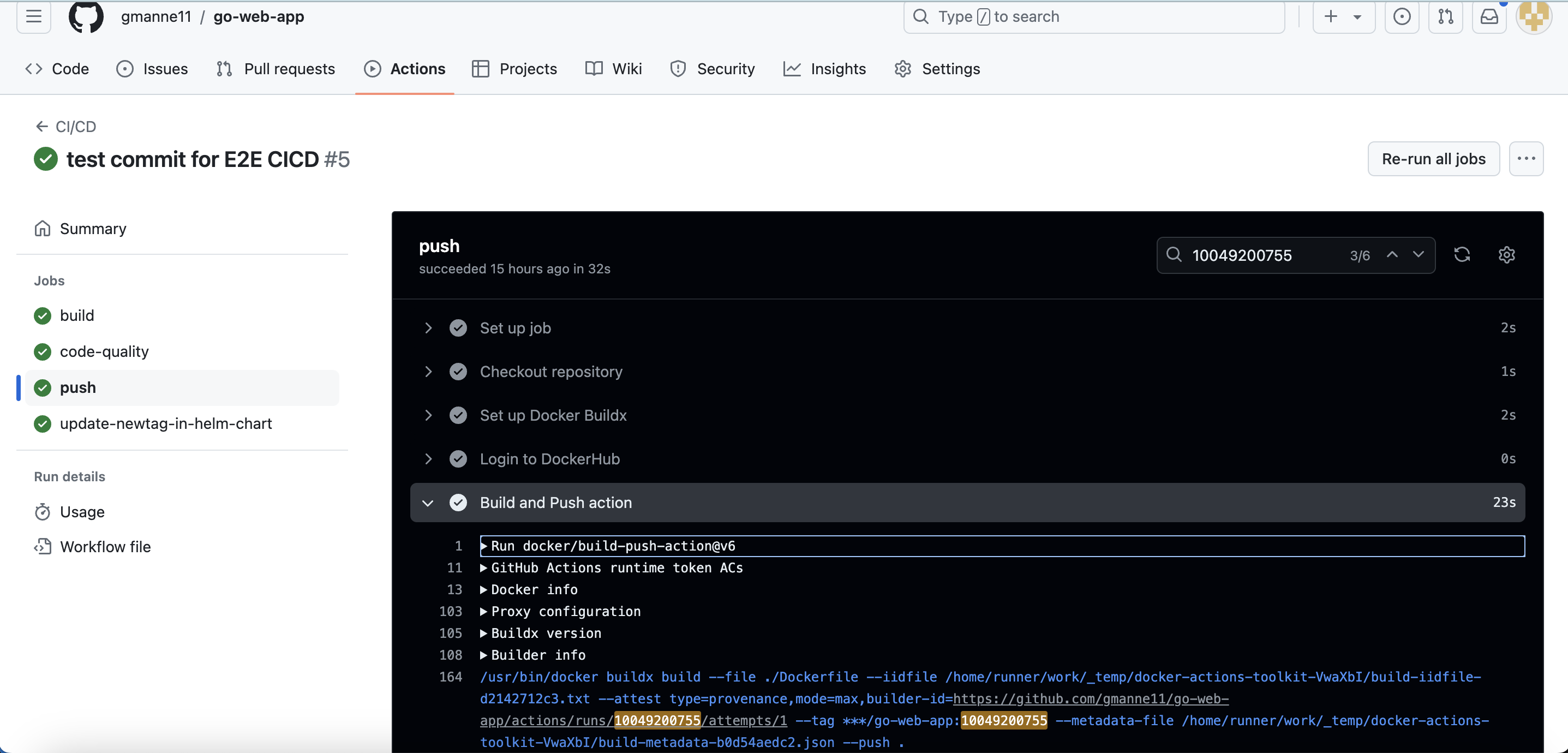
✅ Build and push Docker image
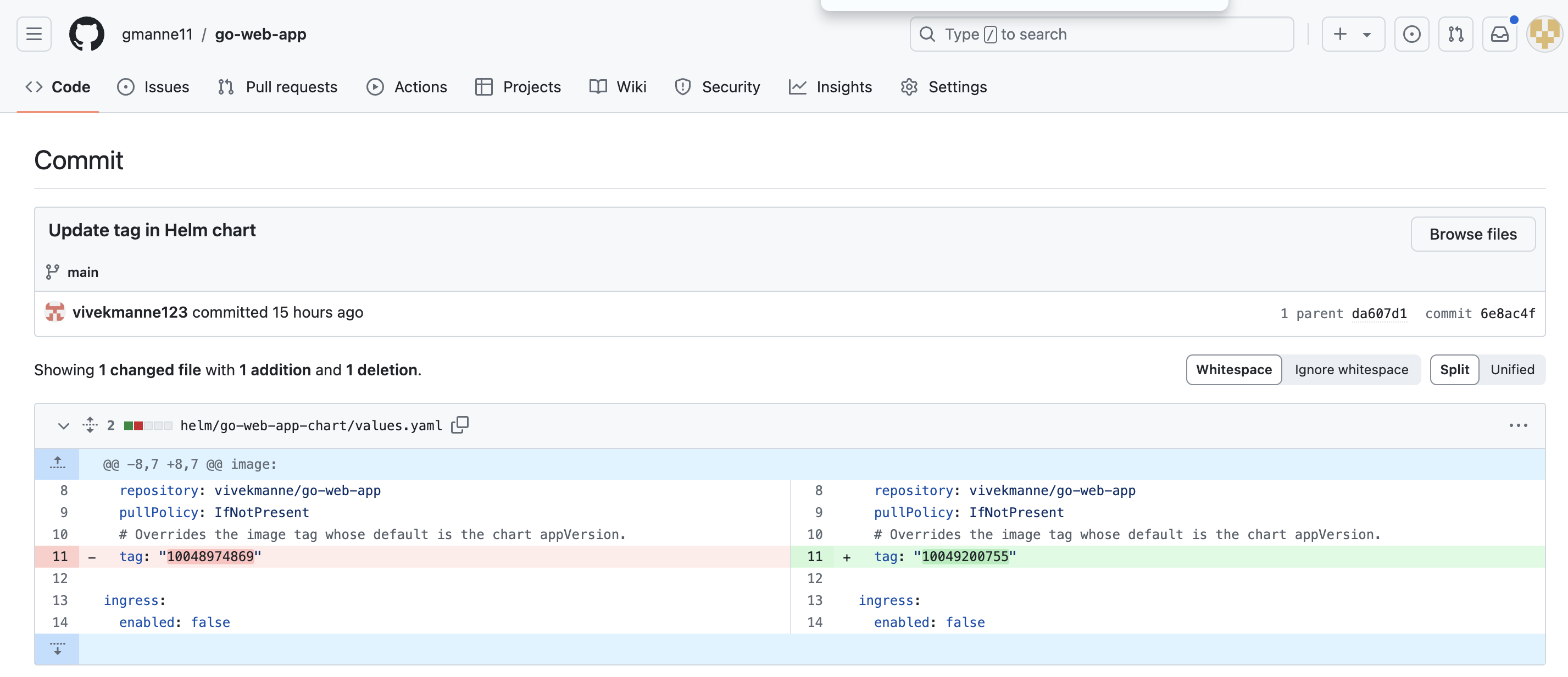
✅ Update image tag in Helm values.yaml
✅ Commit back to the repo Head
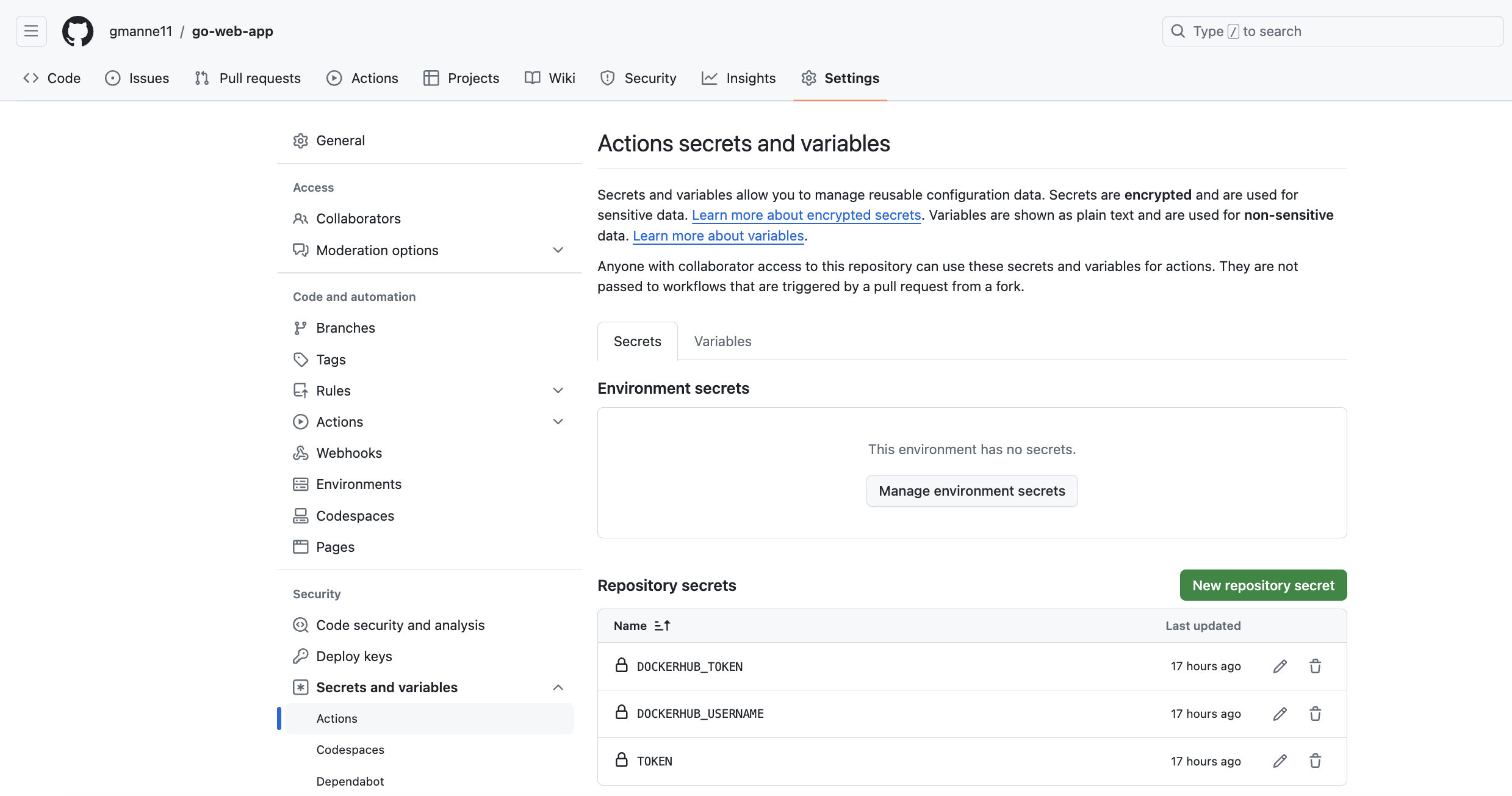
Ensure the secrets defined in workflow file are added to Repository secrets.
NOTE:
Create DOCKERHUB_TOKEN in Dockerhub in case if you didn't have one
Create Github Token and add the value for secret named TOKEN
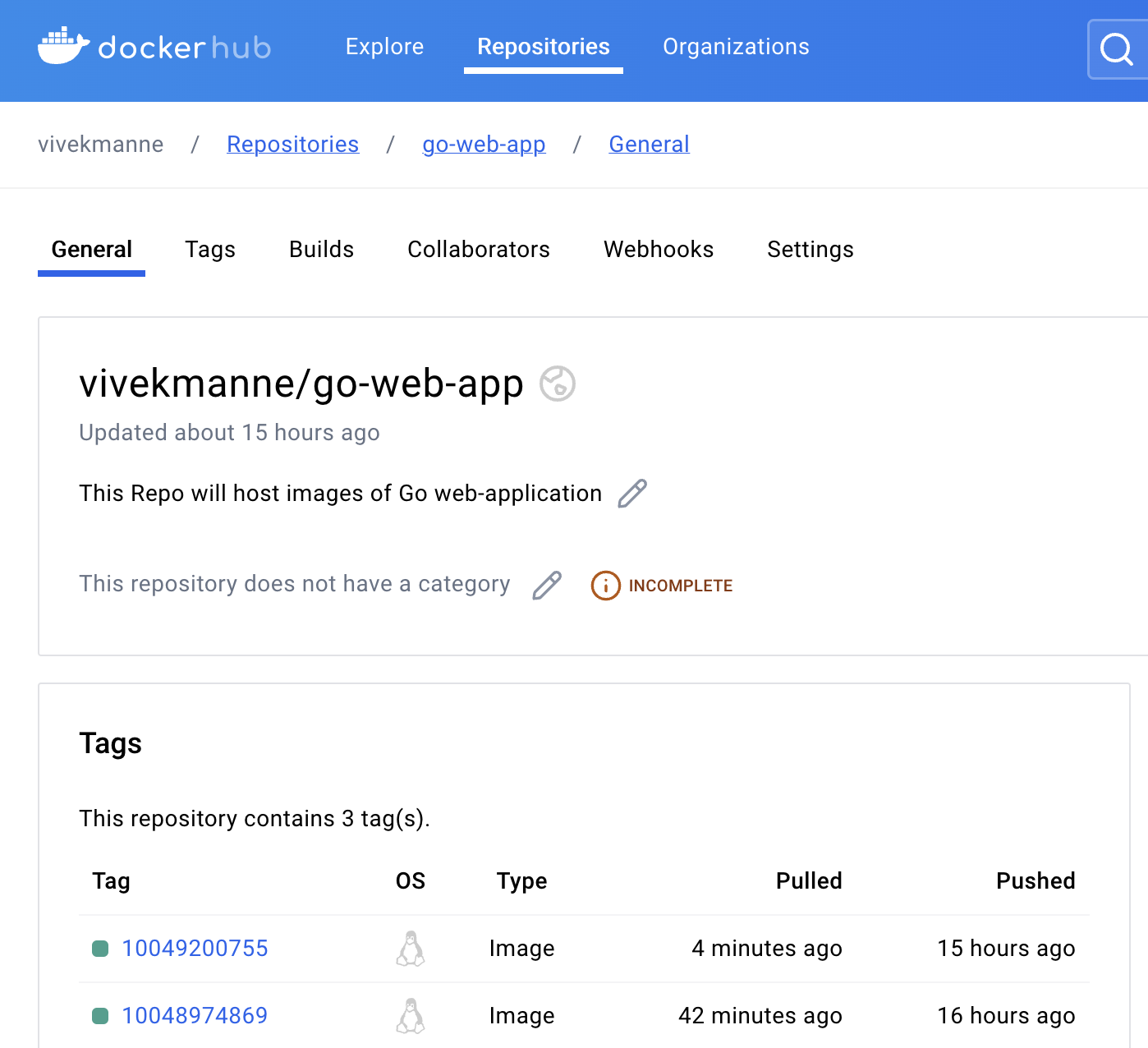
Perform a Dummy commit that should trigger workflow to build the image and pushed to Dockerhub and then update the image tag in values.yaml file.
✅ CD with ArgoCD
Install ArgoCD in the cluster
kubectl create namespace argocd kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yamlVerify that all resources are created in
argocdnamespace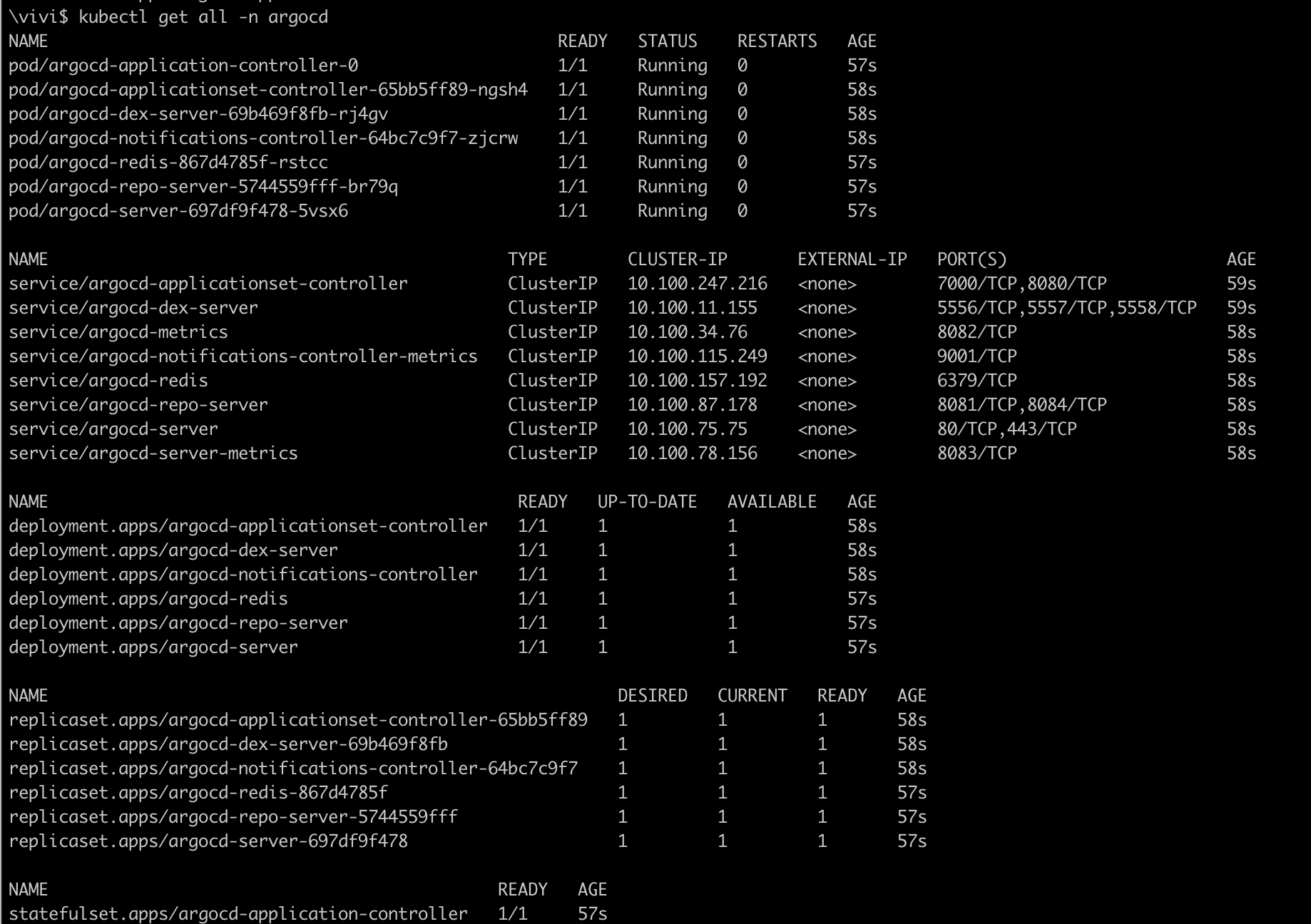
Now, edit the service
argocd-serverand make it LoadBalancer typekubectl edit service argocd-server -n argocd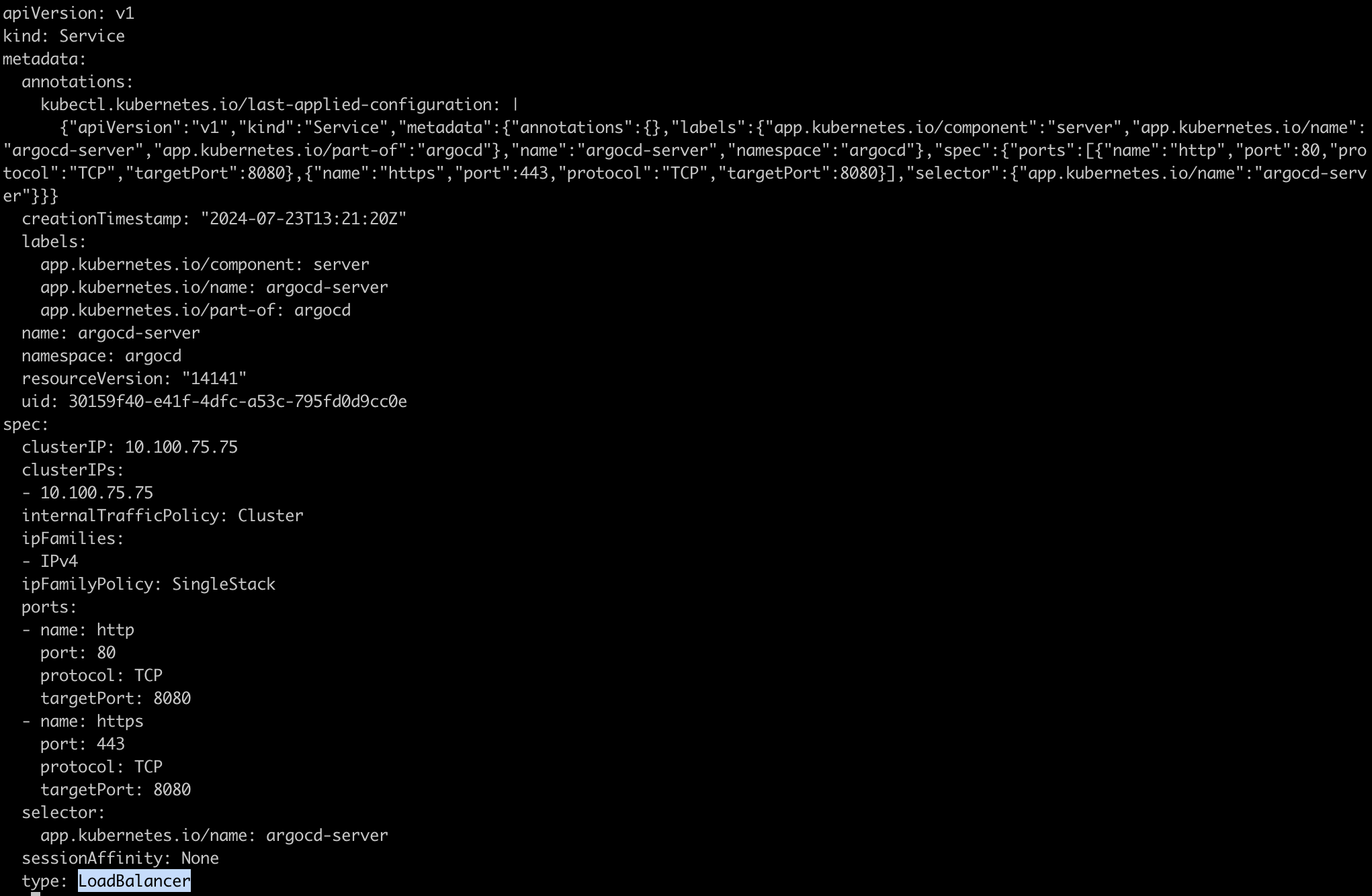
Verify the argocd service is gets the Loadbalancer DNS name

Access the ArgoCD UI using the DNS of the load balancer
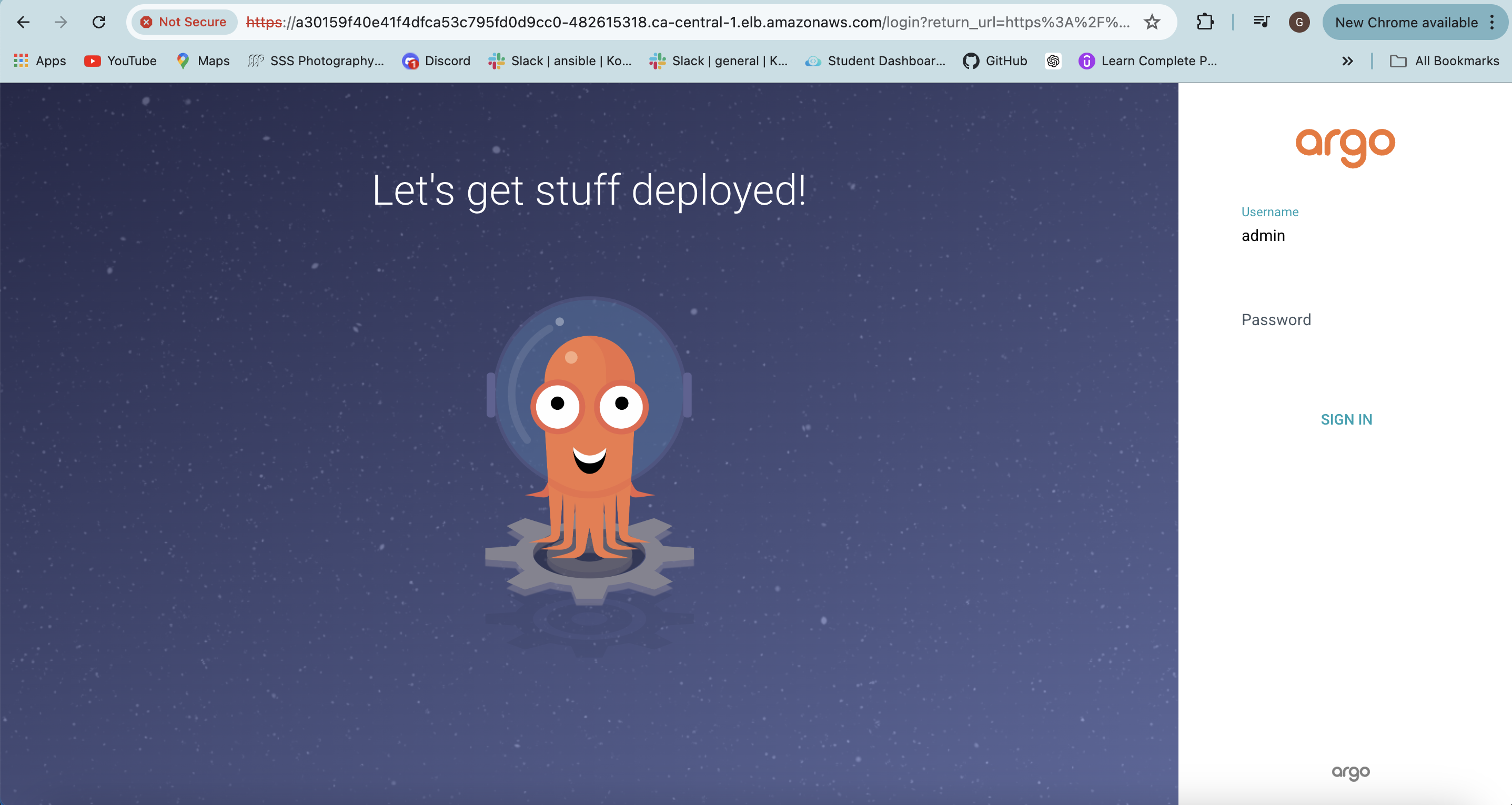
Default Username is
adminand look for the password inargocd-initial-admin-secretwhich was created out of the box.kubectl get secrets -n argocd kubectl edit secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -n argocd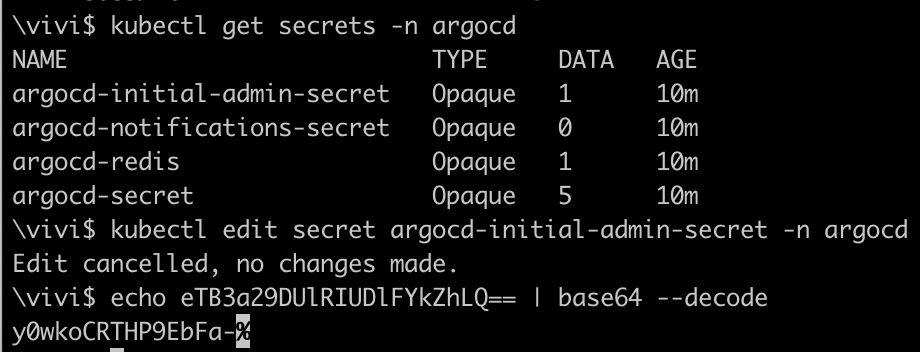
Now, access the ArgoCD UI using the decoded password
Configure the Application
Application name --> go-web-app
Project Name ---> default
Sync policy -----> Automatic
Repository URL ---> your repo URLPATH ----> helm/go-web-app-chart
Cluster URL ----> https://kubernetes.default.svc
Namespace ----> defaultvalues -----> values.yaml
ArgoCD will continuously reconcile the desired state from Git with the cluster state
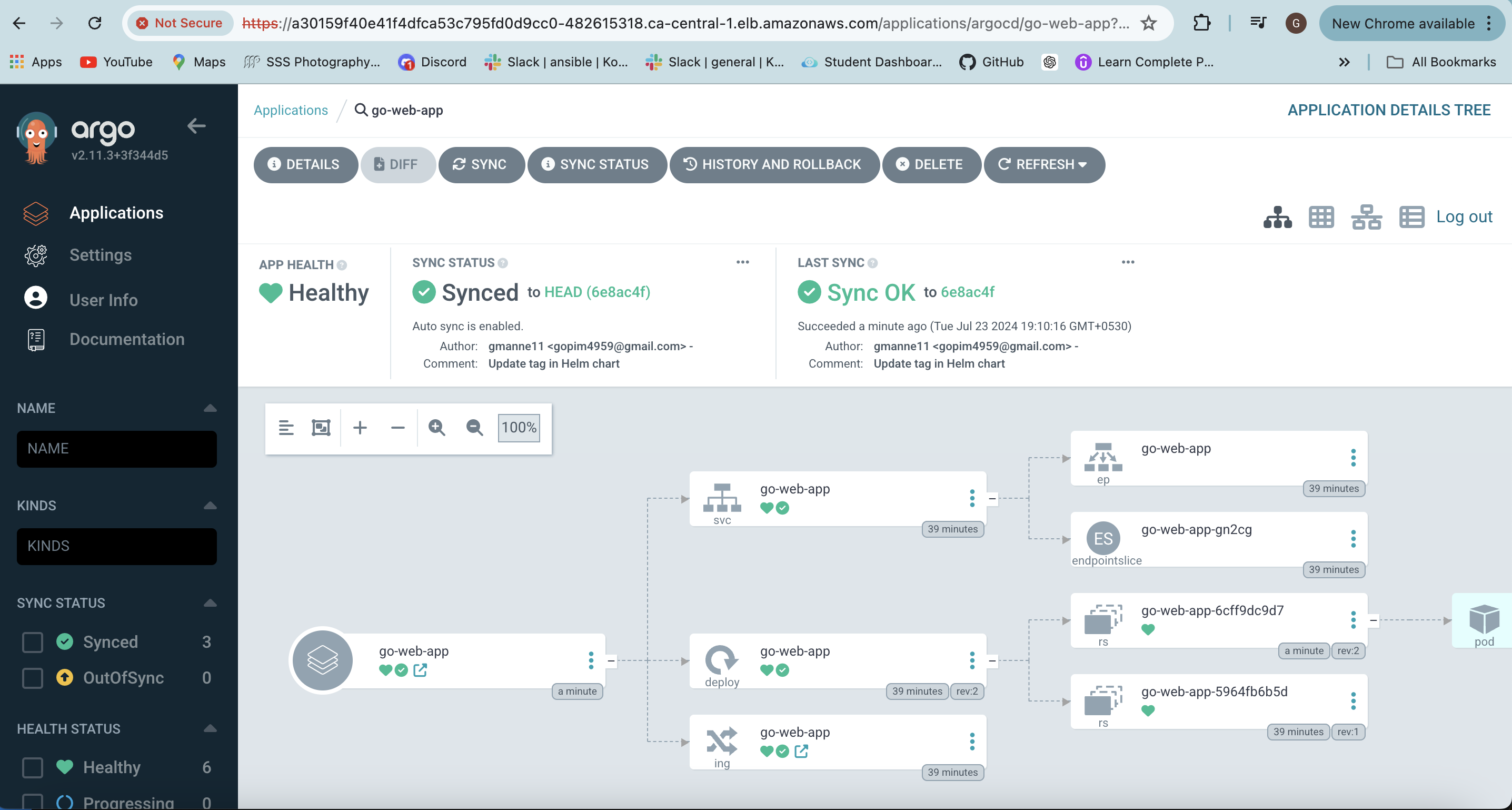
Verify that the latest pod has pulled the most recent image and successfully started a container to run the application.
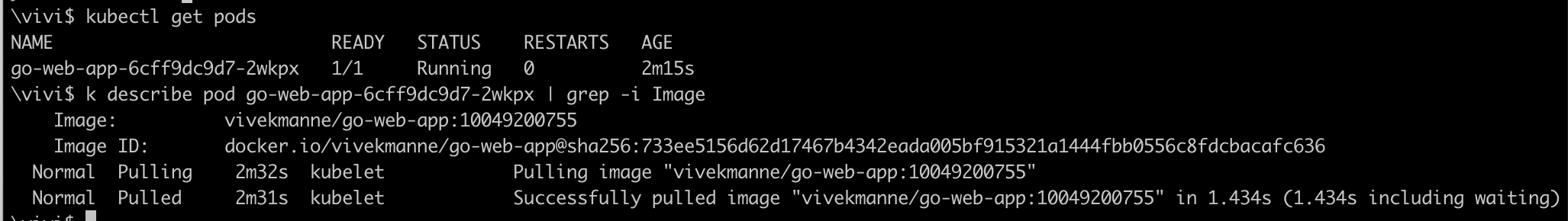
The latest image with tag 10049200755 was pulled to start a container to run the application.
💠 Accessing the Application
After successful deployment, access the application at http://go-web-app.local/home in your browser.
TASK ACCOMPLISHED.....👏 ✅
Make sure to Delete the Cluster using the command like
eksctl delete cluster --name demo-cluster-1 --region ca-central-1
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Gopi Vivek Manne directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Gopi Vivek Manne
Gopi Vivek Manne
I'm Gopi Vivek Manne, a passionate DevOps Cloud Engineer with a strong focus on AWS cloud migrations. I have expertise in a range of technologies, including AWS, Linux, Jenkins, Bitbucket, GitHub Actions, Terraform, Docker, Kubernetes, Ansible, SonarQube, JUnit, AppScan, Prometheus, Grafana, Zabbix, and container orchestration. I'm constantly learning and exploring new ways to optimize and automate workflows, and I enjoy sharing my experiences and knowledge with others in the tech community. Follow me for insights, tips, and best practices on all things DevOps and cloud engineering!