Day 24. Create Kubernetes Cluster
 Ashvini Mahajan
Ashvini MahajanTable of contents

Prerequisites
Before diving into the installation, ensure that your environment meets the following prerequisites:
An Ubuntu 22.04 system.
Minimum 2GB RAM or more.
Minimum 2 CPU cores (or 2 vCPUs).
20 GB of free disk space on /var (or more).
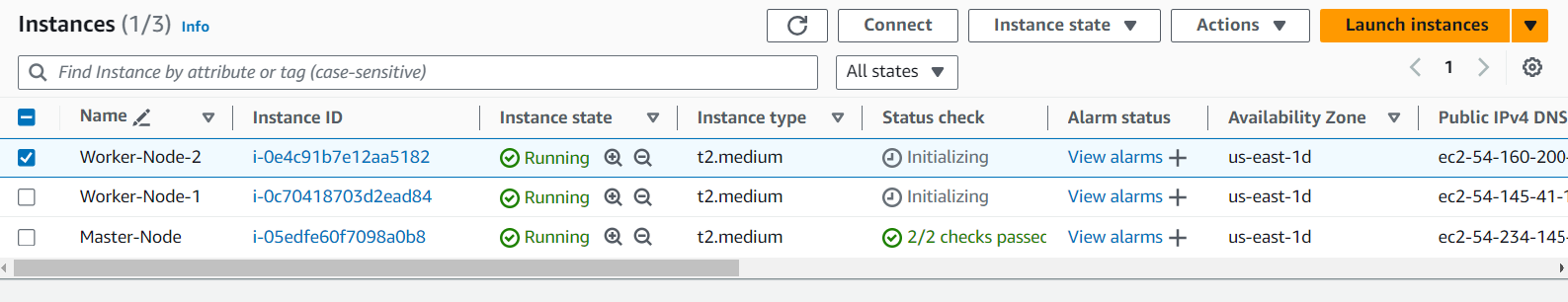
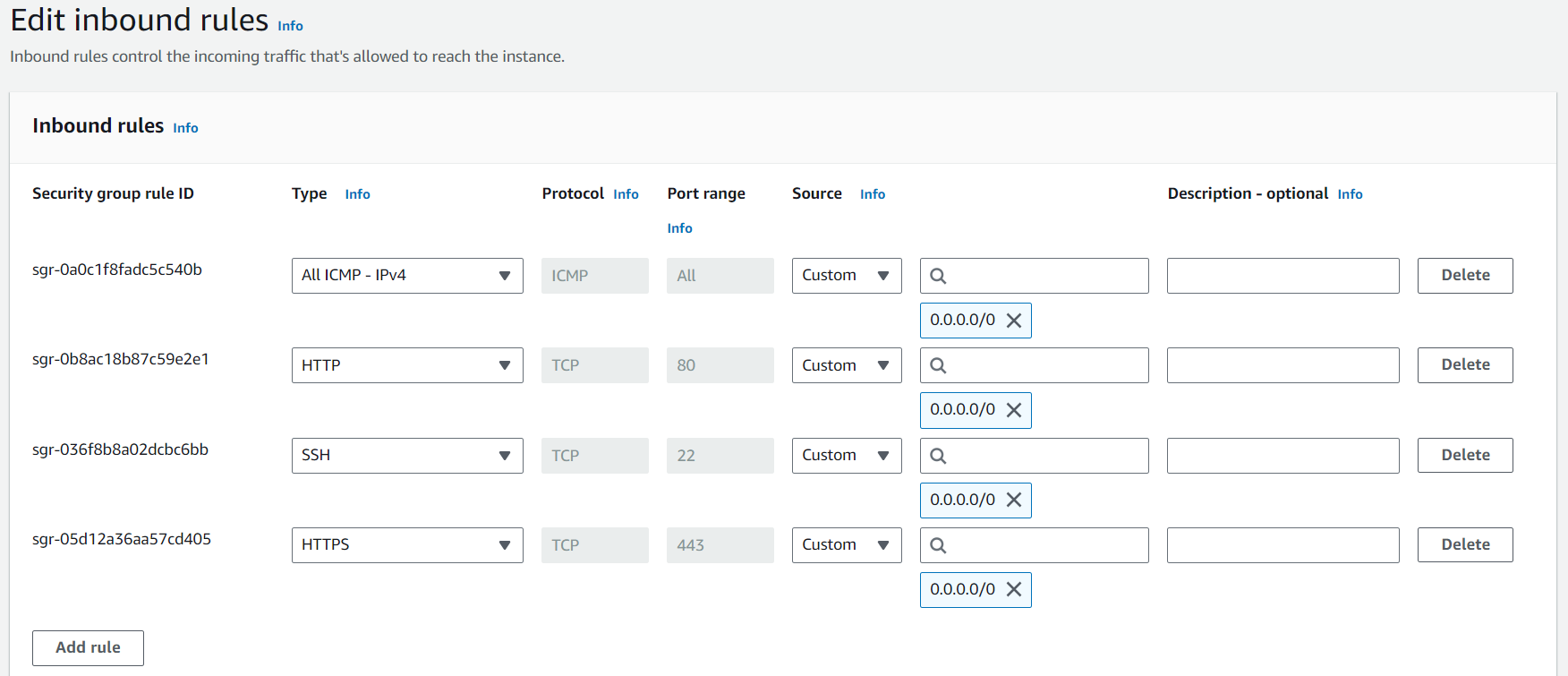
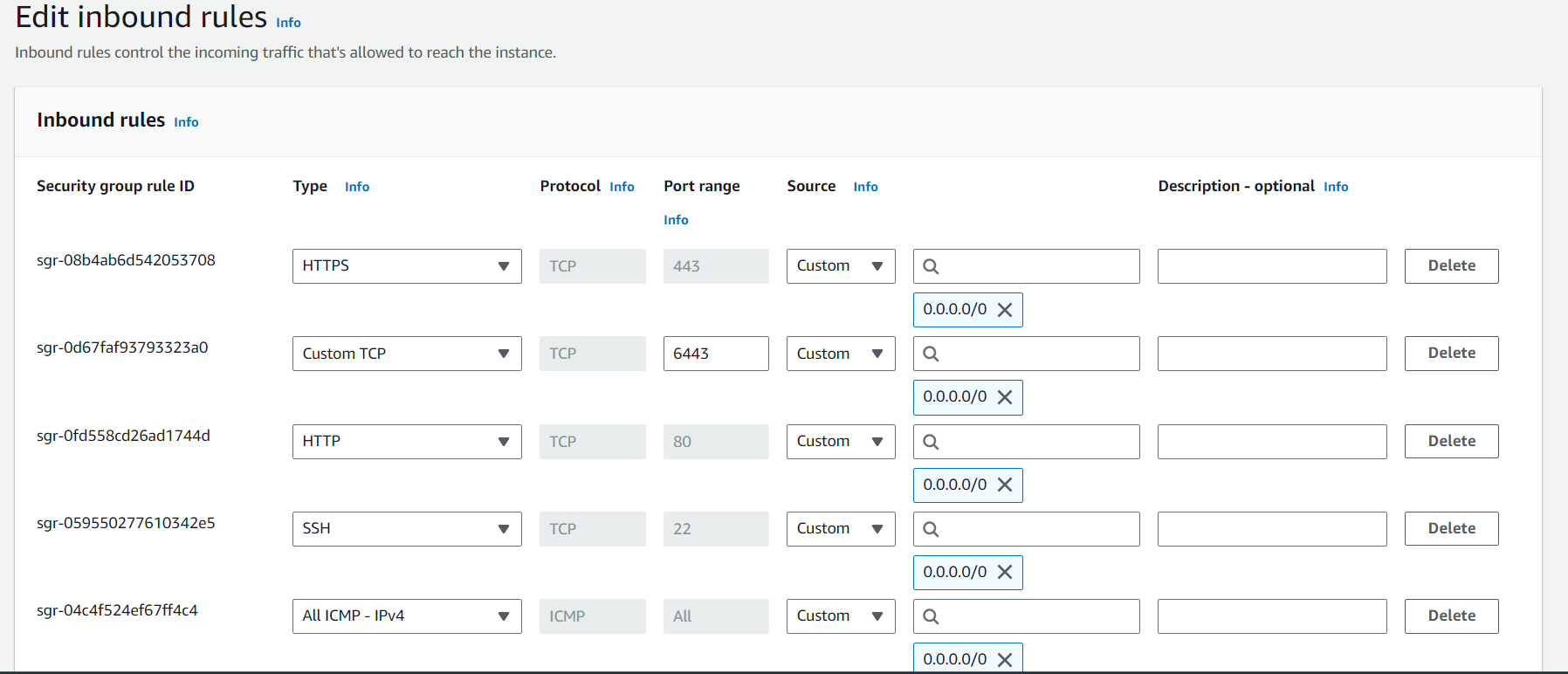
- Custom ICMP rule for all nodes in Security Group
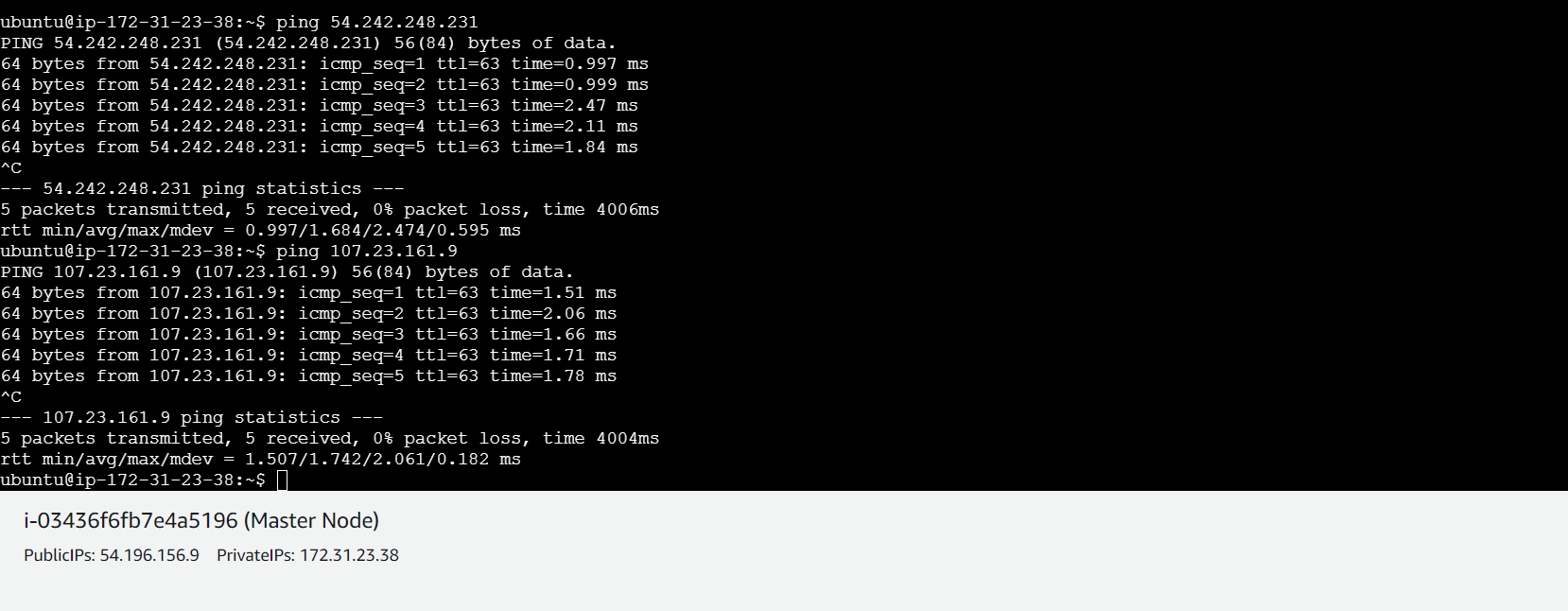
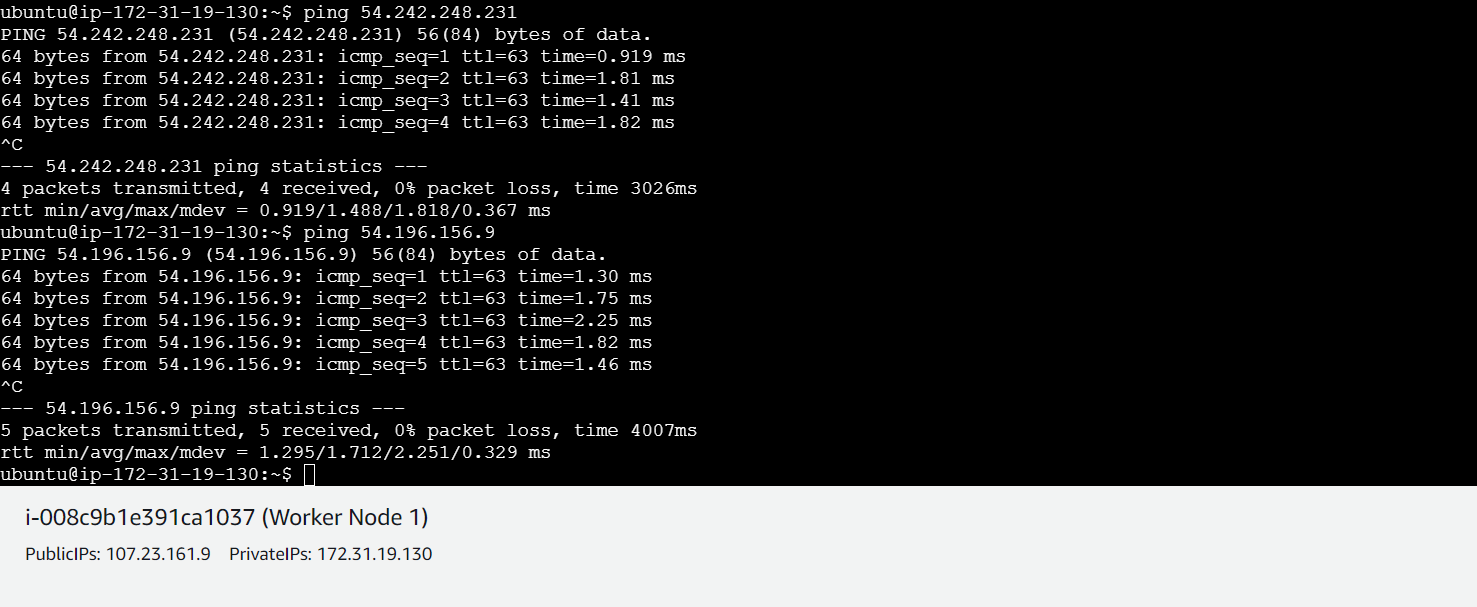
- Ensure machines in the cluster can ping each other via IP and hostname.
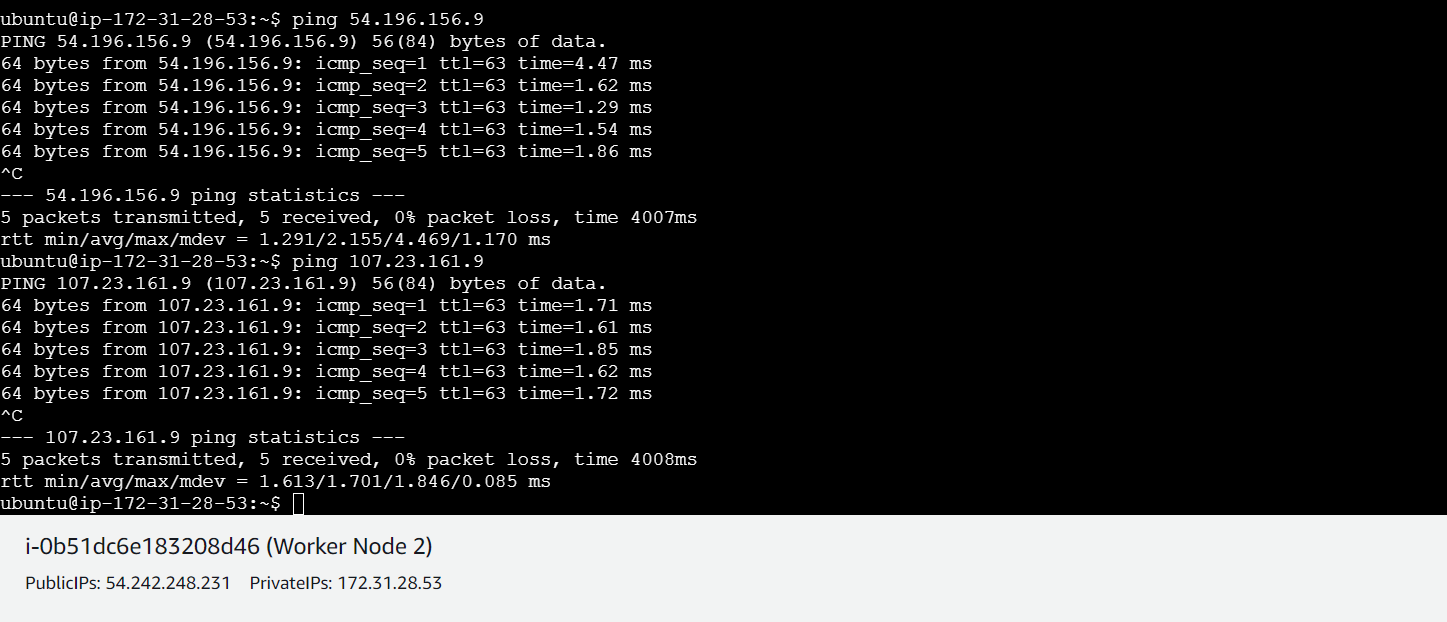
Update and Upgrade Ubuntu (all nodes)
Begin by ensuring that your system is up to date. Open a terminal and execute the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
Disable Swap (all nodes)
To enhance Kubernetes performance, disable swap and set essential kernel parameters. Run the following commands on all nodes to disable all swaps:
sudo swapoff -a
sudo sed -i '/ swap / s/^\(.*\)$/#\1/g' /etc/fstab
Add Kernel Parameters (all nodes)
Load the required kernel modules on all nodes:
sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/containerd.conf <<EOF
overlay
br_netfilter
EOF
sudo modprobe overlay
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
- Configure the critical kernel parameters for Kubernetes using the following
sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/kubernetes.conf <<EOF
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOF
- Then, reload the changes:
sudo sysctl --system
Install Containerd Runtime (all nodes)
We are using the containerd runtime. Install containerd and its dependencies with the following commands:
sudo apt install -y curl gnupg2 software-properties-common apt-transport-https ca-certificates
- Enable the Docker repository:
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmour -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/docker.gpg
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
- Update the package list and install containerd:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y containerd.io
- Configure containerd to start using systemd as cgroup:
containerd config default | sudo tee /etc/containerd/config.toml >/dev/null 2>&1
sudo sed -i 's/SystemdCgroup \= false/SystemdCgroup \= true/g' /etc/containerd/config.toml
- Restart and enable the containerd service:
sudo systemctl restart containerd
sudo systemctl enable containerd
Add Apt Repository for Kubernetes (all nodes)
Kubernetes packages are not available in the default Ubuntu 22.04 repositories. Add the Kubernetes repositories with the following commands:
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.28/deb/ /" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.29/deb/Release.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg
sudo apt update
Install Kubectl, Kubeadm, and Kubelet (all nodes)
After adding the repositories, install essential Kubernetes components, including kubectl, kubelet, and kubeadm, on all nodes with the following commands:
sudo apt install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl
Initialize Kubernetes Cluster with Kubeadm (master node)
With all the prerequisites in place, initialize the Kubernetes cluster on the master node using the following Kubeadm command:
sudo kubeadm init
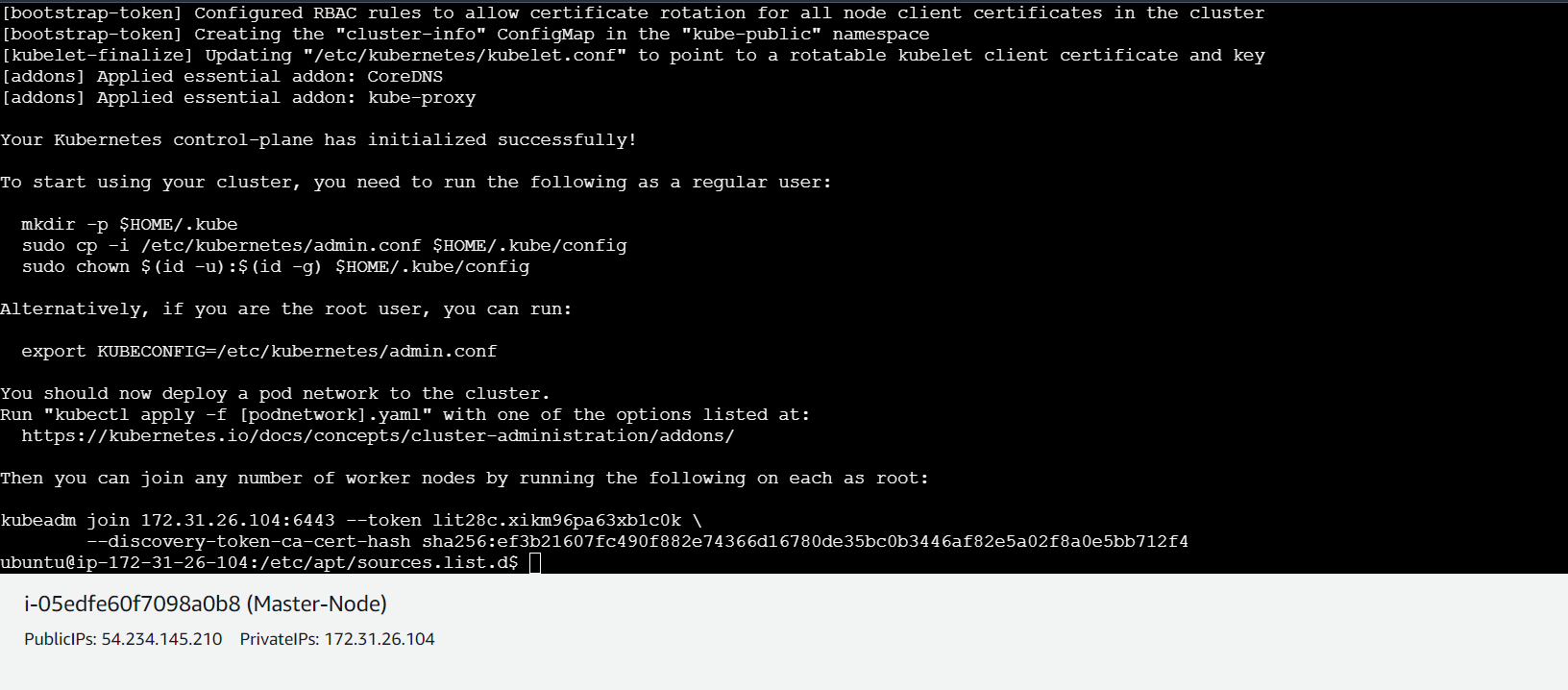
After the initialization is complete make a note of the
kubeadm joincommand for future reference.Run the following commands on the master node:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
- Next, use
kubectlcommands to check the cluster and node status:
kubectl get nodes

Add Worker Nodes to the Cluster (worker nodes)
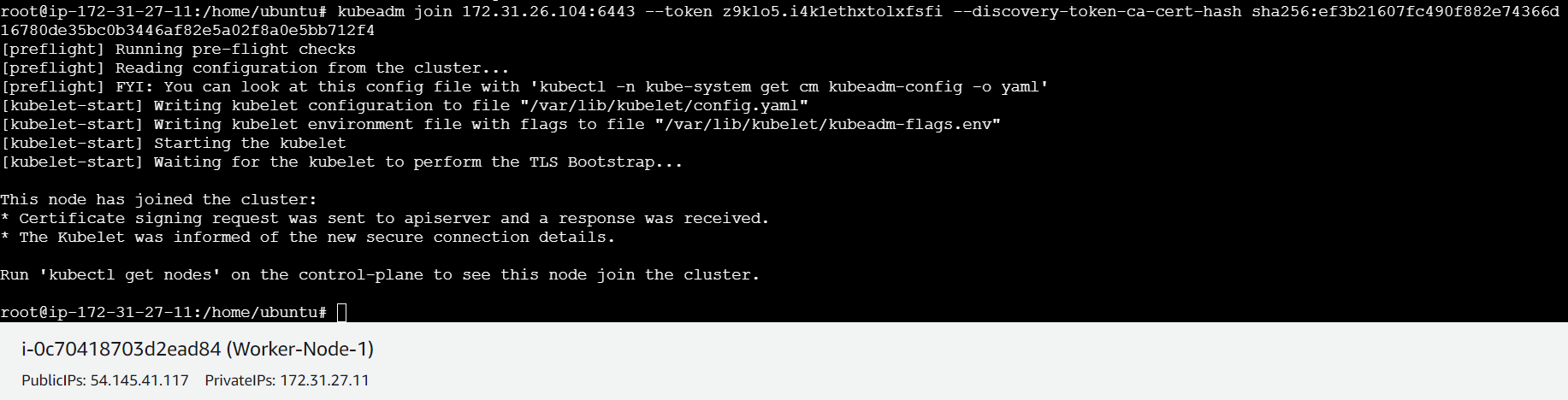
On each worker node, use the
kubeadm joincommand you noted down earlier:Open port 6443 on all nodes
kubeadm join 172.31.26.104:6443 --token lit28c.xikm96pa63xb1c0k \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:ef3b21607fc490f882e74366d16780de35bc0b3446af82e5a02f8a0e5bb712f4
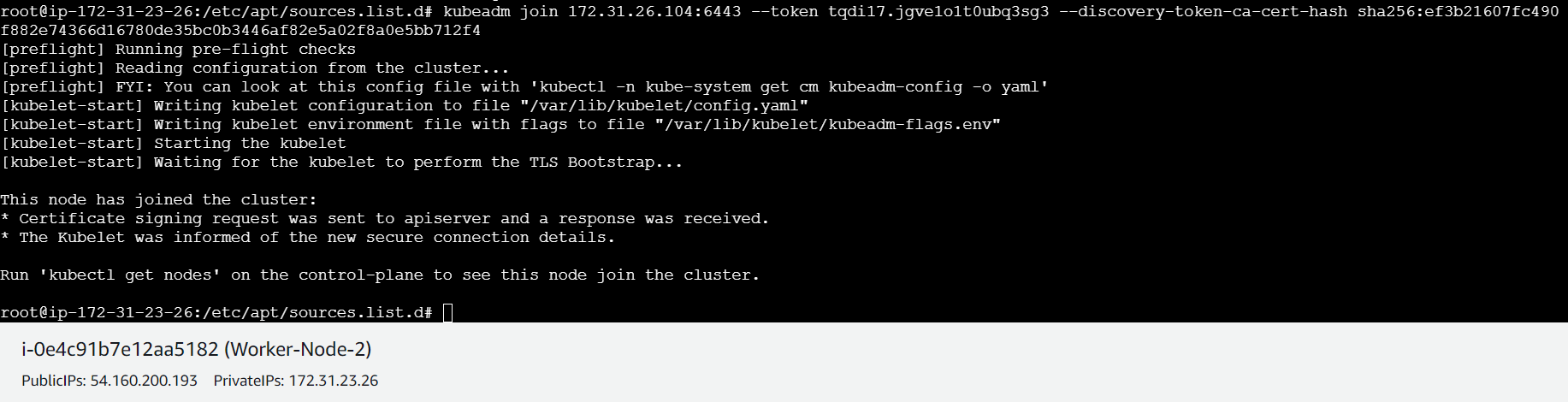
- list all nodes on master-node
kubectl get nodes

Install Kubernetes Network Plugin (master node)
To enable communication between pods in the cluster, you need a network plugin. Install the Calico network plugin with the following command from the master node:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v3.25.0/manifests/calico.yaml
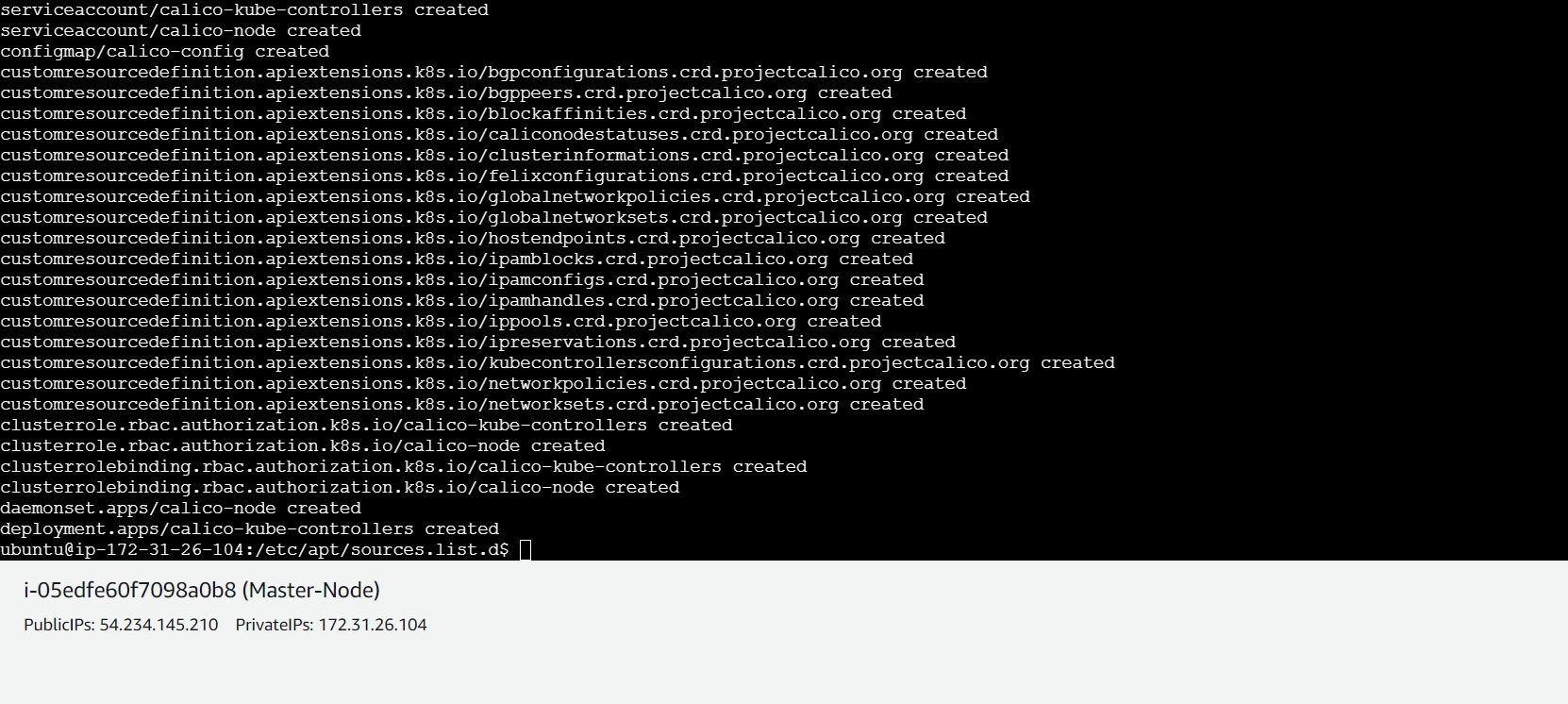
Verify the cluster and test (master node)
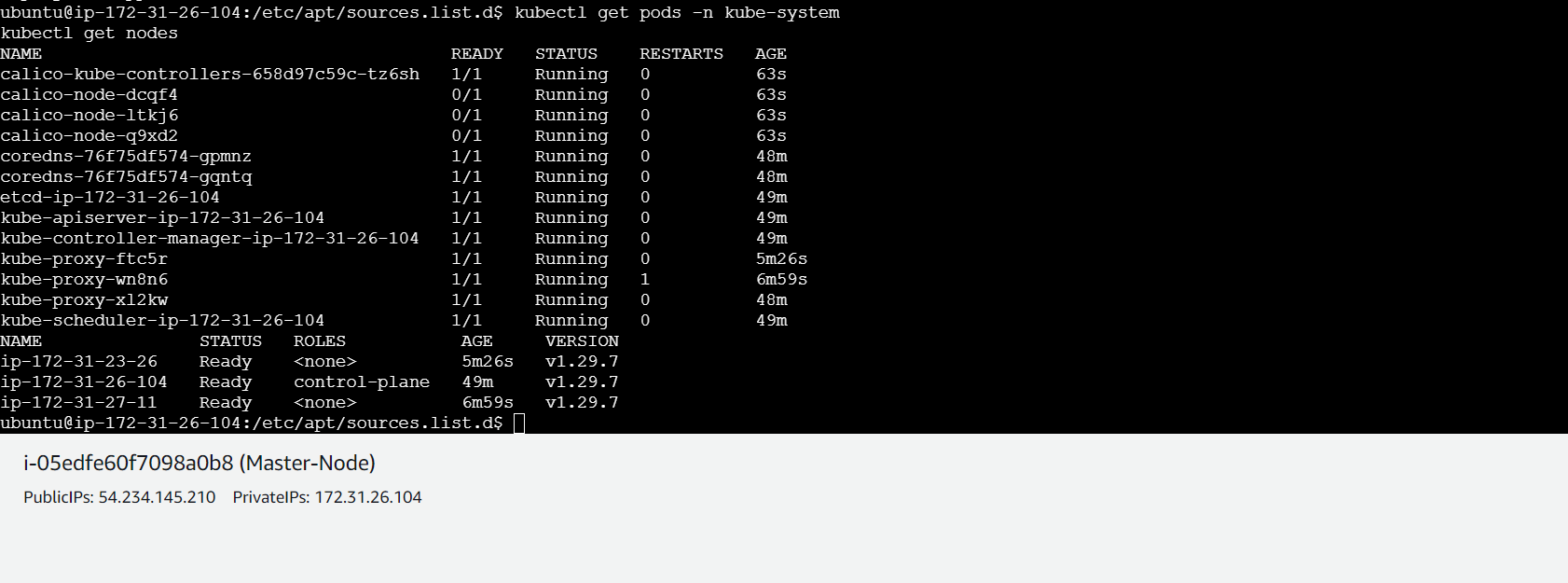
Finally, we want to verify whether our cluster is successfully created.
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
kubectl get nodes
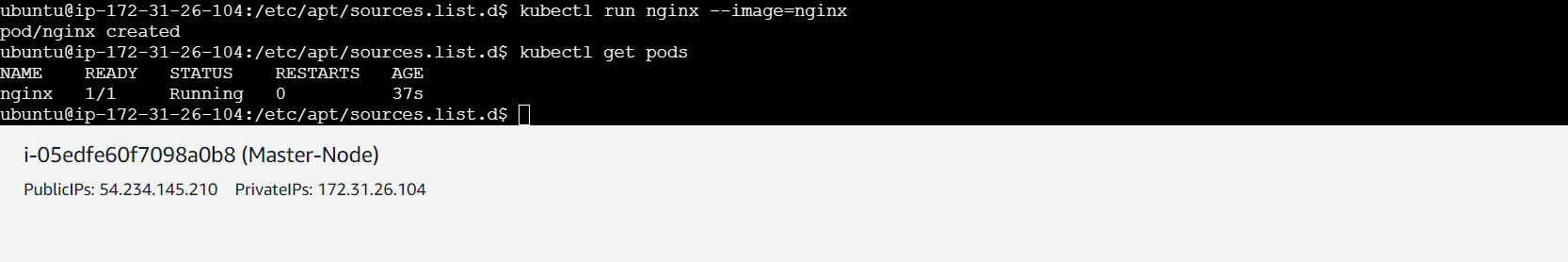
- Deploy test application on cluster (master node)
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ashvini Mahajan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
Ashvini Mahajan
Ashvini Mahajan
I am DevOps enthusiast and looking for opportunities in DevOps.