Day 83 - Mastering Web Application Deployment with Docker Swarm on AWS 🚀
 Nilkanth Mistry
Nilkanth Mistry
Welcome to Day 83 of the #90DaysOfDevOps Challenge! 🎉 Today, we're diving into deploying a web application using Docker Swarm. Docker Swarm is a powerful orchestration tool that allows us to manage containers at scale, ensuring robustness and high performance for our applications. Let's get started! 💻✨
Project Description 📋
In this project, we will explore deploying a web application using Docker Swarm. Docker Swarm enables seamless management and scaling of containerized applications, making it ideal for production environments. By leveraging Docker Swarm’s features, such as load balancing, rolling updates, and service discovery, we aim to achieve high availability and reliability for our web application.
We will:
Pull an existing Docker image from DockerHub.
Deploy it onto a Docker Swarm cluster.
Setting up the Swarm cluster will provide us with automated failover, load balancing, and horizontal scaling capabilities, ensuring our application can handle varying workloads and demands. 📈⚖️
Let's dive into the project and learn how Docker Swarm can enhance the deployment and management of containerized applications. 🏊♂️🔧
Hands-on Project: Web Application Deployment Using Docker Swarm 🛠️
Before we begin, ensure you have a Docker image of your web application stored on DockerHub. Here’s the step-by-step guide to deploy it using Docker Swarm.
Pre-requisites 📦
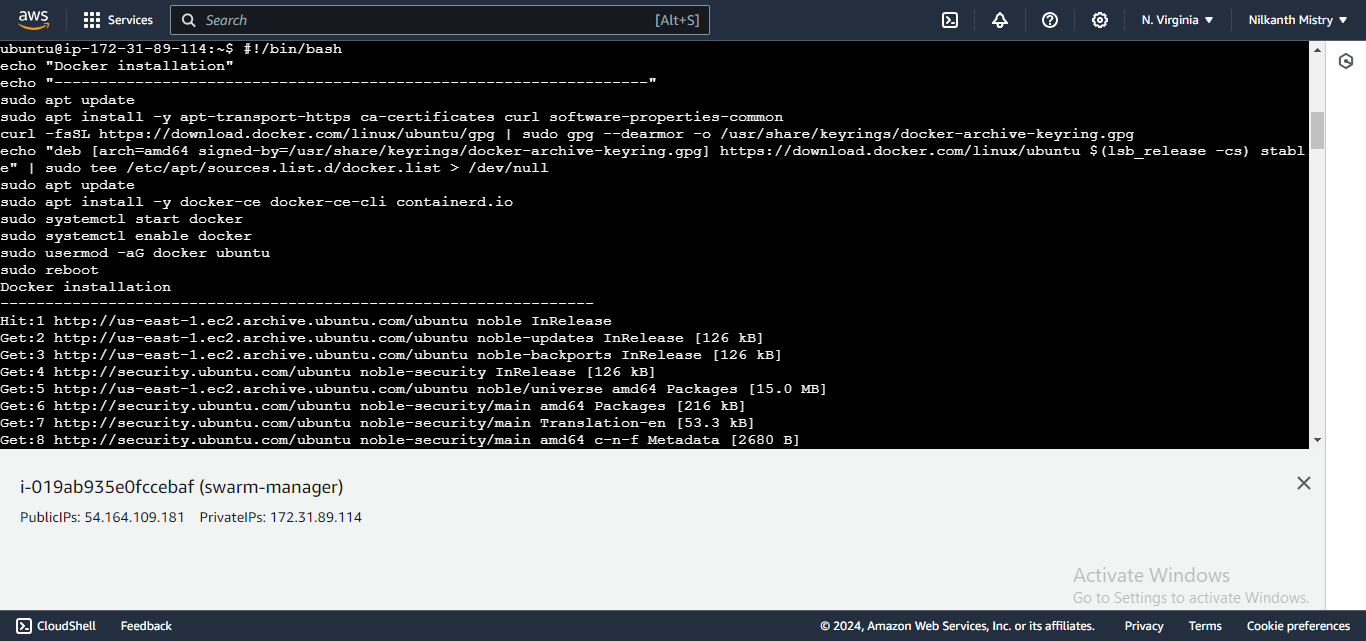
Access the AWS portal and set up three new EC2 instances with Docker pre-installed. Use the following shell script and provide it in the EC2 User Data field:
#!/bin/bash echo "Docker installation" echo "------------------------------------------------------------------" sudo apt update sudo apt install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null sudo apt update sudo apt install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io sudo systemctl start docker sudo systemctl enable docker sudo usermod -aG docker ubuntu sudo reboot
Ensure the instances are up and running. 🎉
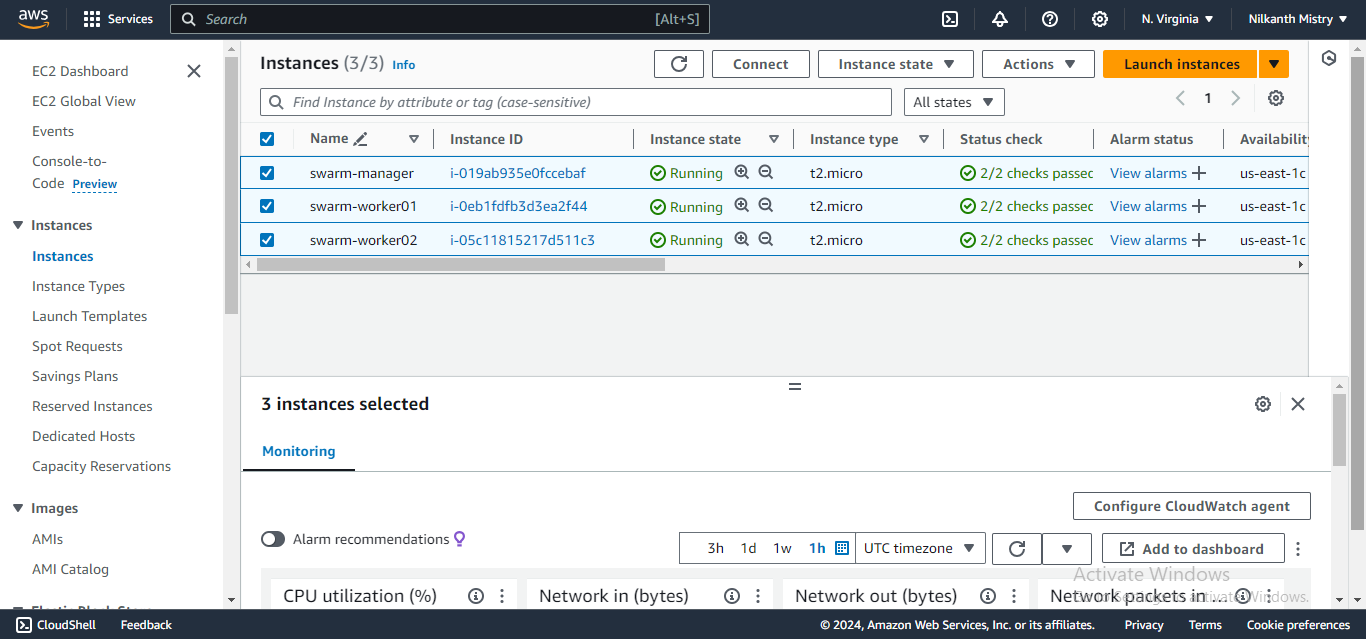
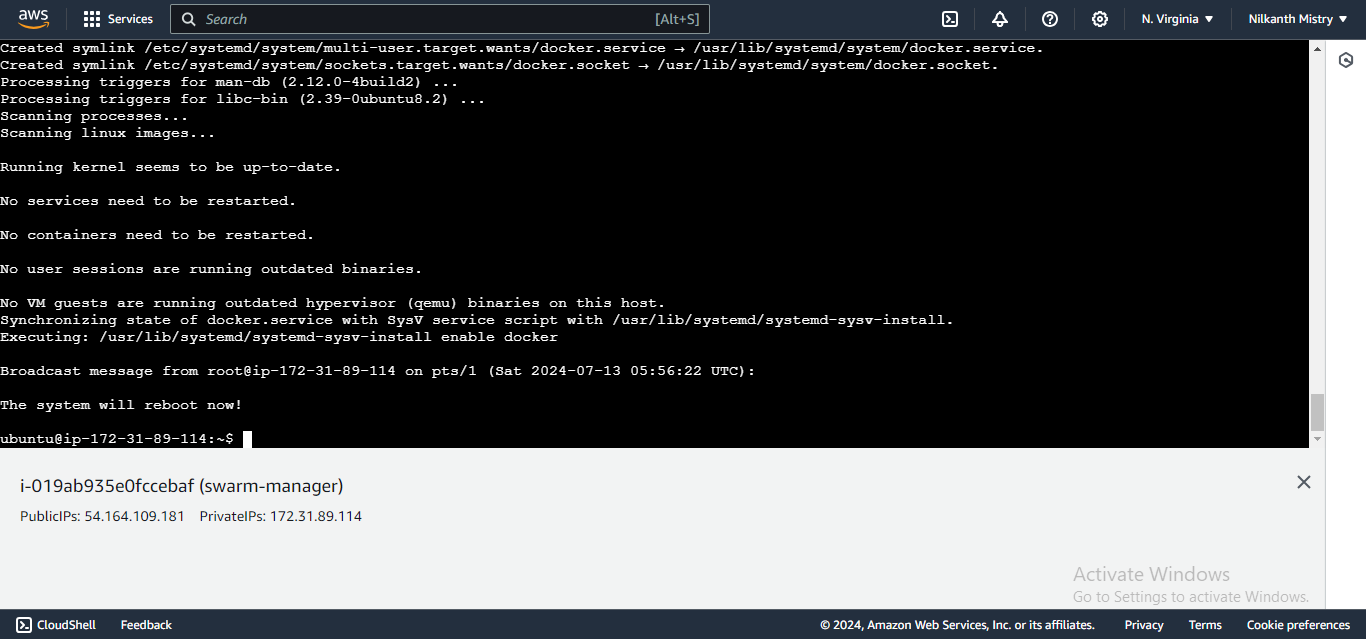
Step 1: Set Up Docker Swarm Cluster 🐋
SSH into your manager node.
Initialize the Docker Swarm cluster by running:
docker swarm initA key will be generated to add additional nodes as workers to the swarm. Copy and execute this key on the remaining servers to join them to the swarm. 🔑
Open port 2377 in your Security Group to allow Docker Swarm communication. 🔓
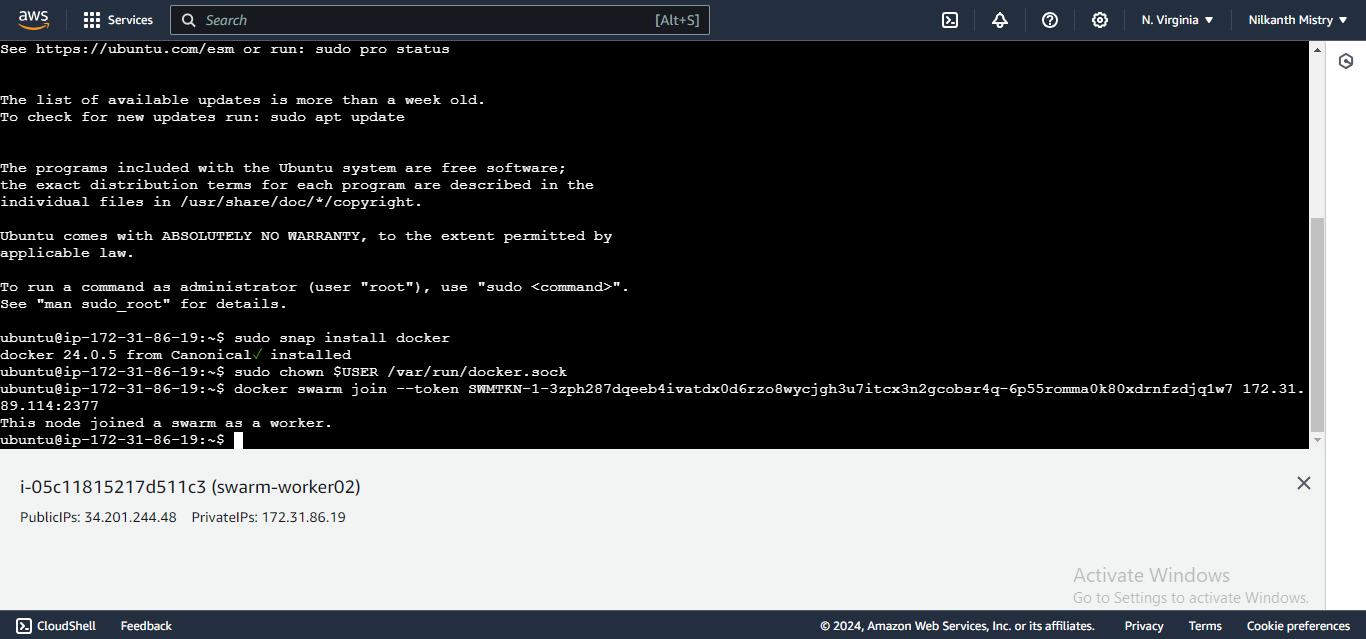
Verify the connected worker and manager nodes:
docker node ls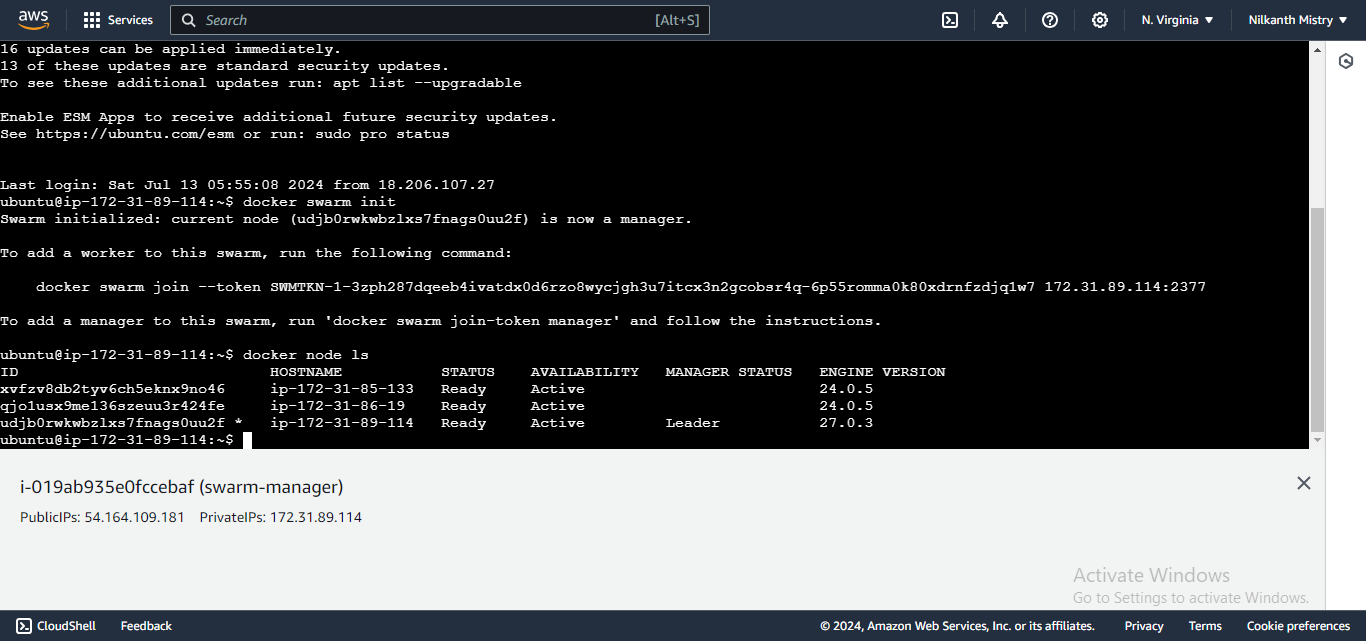

Step 2: Deploy the Web Application 🚀
With the Docker Swarm cluster ready, deploy your web application using the Docker image stored on DockerHub:
docker service create --name django-notes-app --replicas 3 -p 8000:8000 samsorrahman/django-notes-app:latest
Step 3: Verify the Deployment 🕵️♂️
Check the status of your service and replicas:
docker service ls docker ps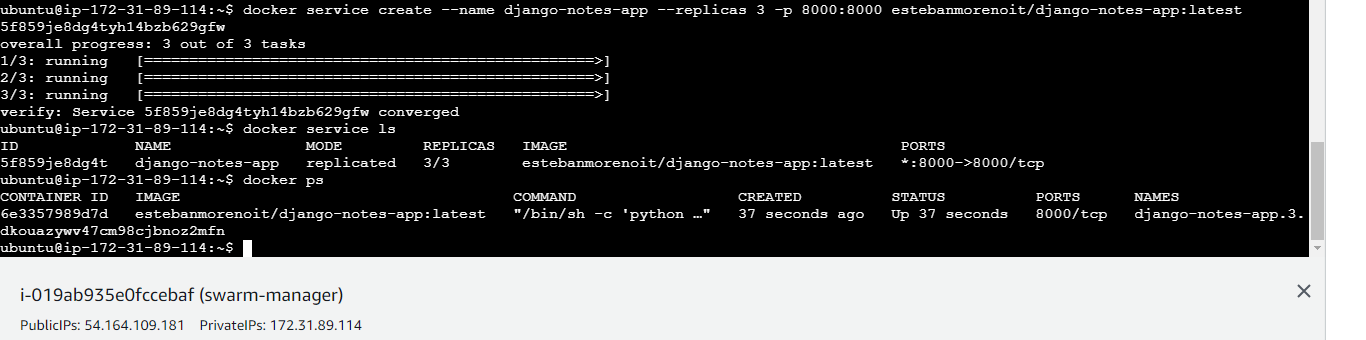
Verify the application is running by navigating to
http://<ec2-instance-public-ip-address>:8000on each instance:swarm-manager 🖥️
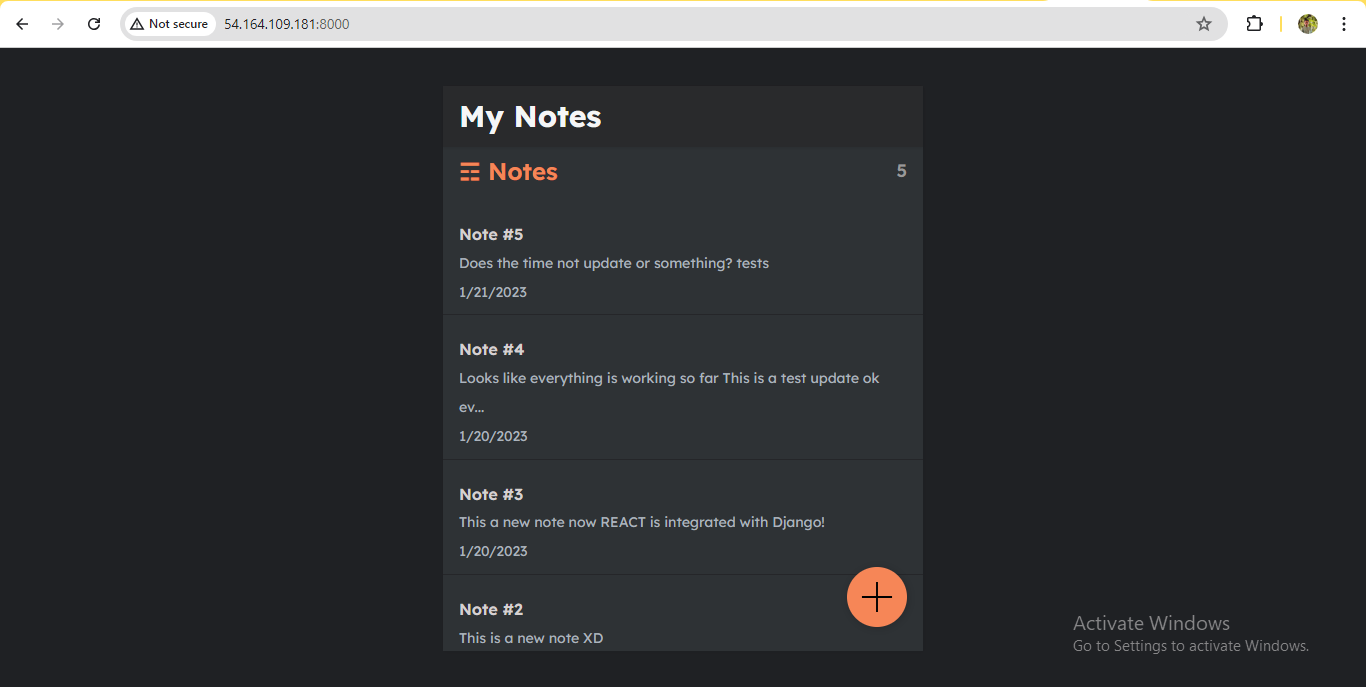
swarm-worker1 🖥️
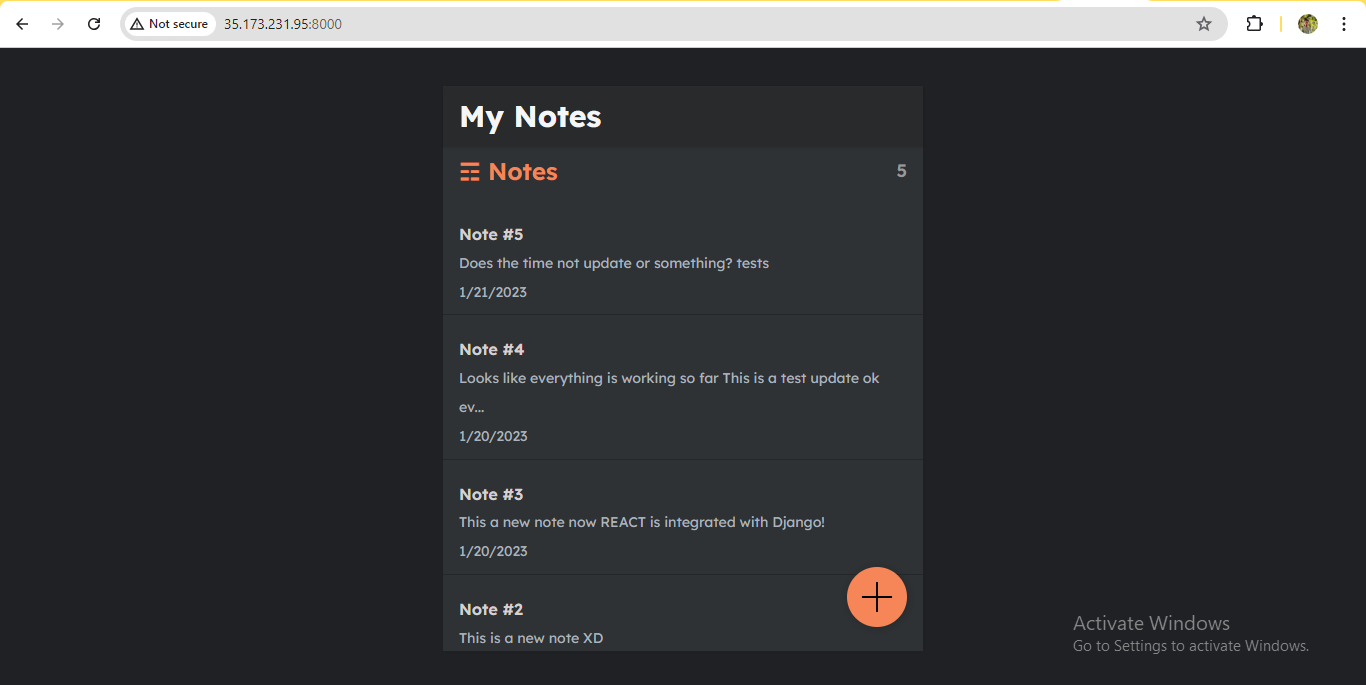
swarm-worker2 🖥️
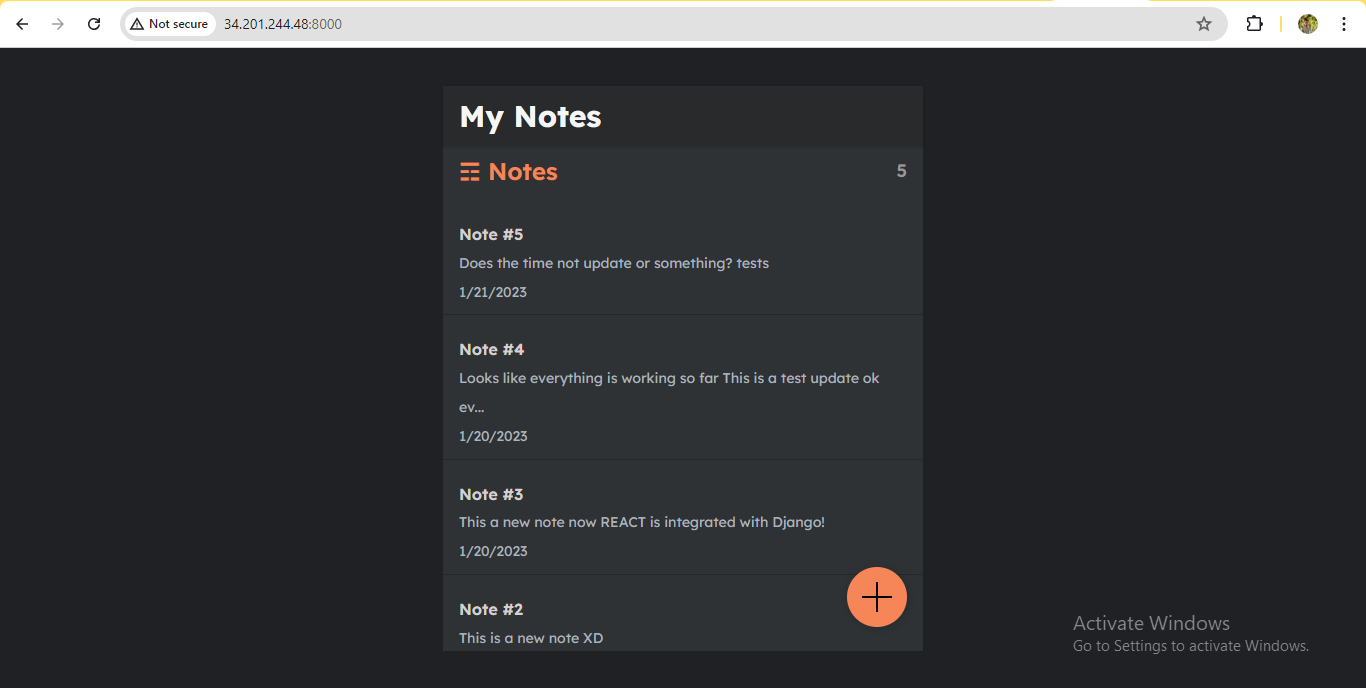
Step 4: Clean-up 🧹
Remove the service:
docker service rm django-notes-appLeave the Swarm from any worker node:
docker swarm leaveForce the manager node to leave the Swarm:
docker swarm leave --force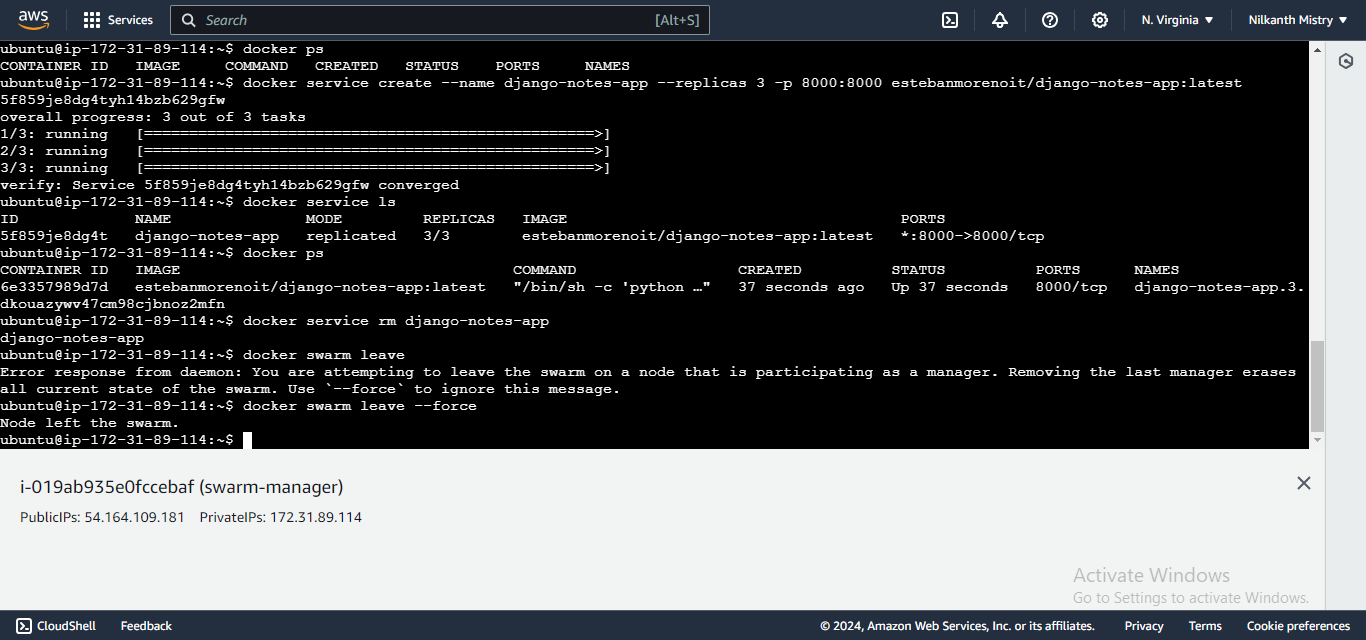
Congratulations! 🎉
You've successfully deployed a web application using Docker Swarm! This milestone enhances our understanding of container orchestration and its role in modern DevOps practices. Tomorrow, we will explore another exciting project. Stay tuned for Day 84! 🚀✨
If you enjoyed this blog, please follow and click the clap 👏 button below to show your support! Subscribe to my blogs to stay updated with future posts. If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment below. Thanks for reading and have an amazing day ahead! 🌟
Connect with me 🌐:
Happy DevOps-ing! 😄
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nilkanth Mistry directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Nilkanth Mistry
Nilkanth Mistry
Embark on a 90-day DevOps journey with me as we tackle challenges, unravel complexities, and conquer the world of seamless software delivery. Join my Hashnode blog series where we'll explore hands-on DevOps scenarios, troubleshooting real-world issues, and mastering the art of efficient deployment. Let's embrace the challenges and elevate our DevOps expertise together! #DevOpsChallenges #HandsOnLearning #ContinuousImprovement