Steps for comprehensive literature survey
 Jyoti Maurya
Jyoti MauryaTable of contents

Conducting a comprehensive literature survey when the scope, objectives, and research questions are already defined involves several systematic steps to ensure you cover all relevant literature.
Steps for Comprehensive Literature Survey
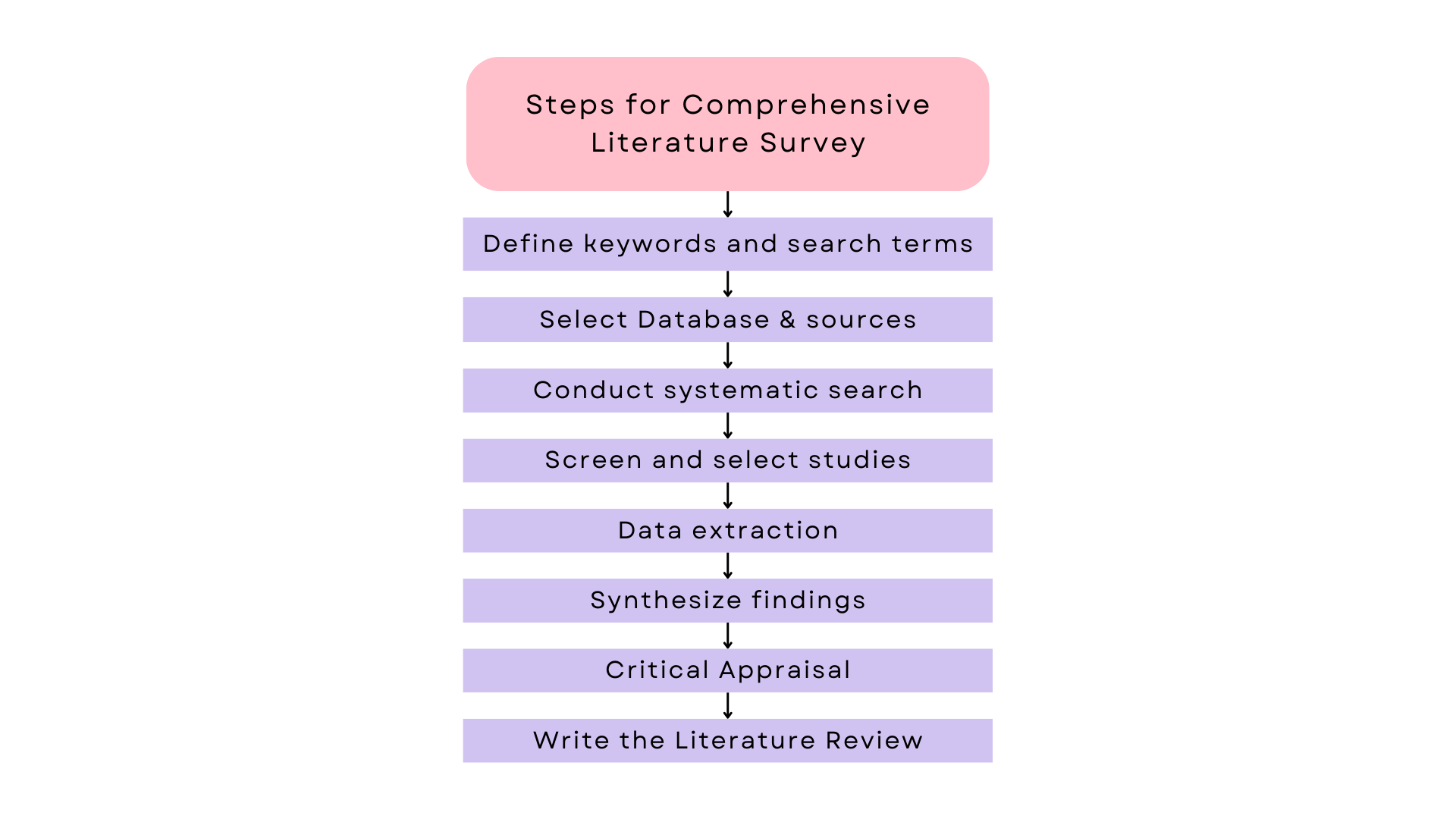
1. Define Keywords and Search Terms
Keywords: Identify main keywords related to your scope, objectives, and research questions.
Synonyms and Related Terms: List synonyms and related terms to ensure a broad search.
Boolean Operators: Use Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) to combine keywords and refine searches.
2. Select Databases and Sources
Choose relevant academic databases (e.g., Google Scholar, PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science).
Include gray literature (e.g., theses, dissertations, conference papers, technical reports).
You will need access to these databases. Use your university or company subscription access.
3. Conduct Systematic Searches
Database Searches: Perform searches in selected databases using defined keywords and search terms.
Backward Searching: Review references of identified articles to find additional relevant papers.
Forward Searching: Use citation analysis to find newer papers that cite identified key articles.
4. Screen and Select Studies
Title and Abstract Screening: Quickly screen titles and abstracts to exclude irrelevant studies.
Full-Text Screening: Read full texts of potentially relevant studies to confirm their relevance.
5. Data Extraction
Key Information: Extract key information such as authors, publication year, study design, methodology, findings, and relevance to your research questions.
Organize Data: Use spreadsheets or reference management tools (e.g., EndNote, Mendeley, Zotero) to organize and manage extracted data.
6. Synthesize Findings
Thematic Analysis: Identify common themes, trends, and gaps in the literature.
Comparison and Contrast: Compare and contrast findings from different studies.
Conceptual Framework: Develop a conceptual framework or model if applicable.
7. Critical Appraisal
Quality Assessment: Critically appraise the quality of included studies using appropriate checklists or criteria.
Bias and Limitations: Identify potential biases and limitations in the studies reviewed.
8. Write the Literature Review
Introduction: Introduce the scope, objectives, and research questions of your review.
Body: Present the synthesized findings thematically or chronologically, addressing each research question.
Conclusion: Summarize key findings, highlight gaps, and suggest future research directions.
Tips for Effective Literature Survey
Keep Track of Search Terms and Strategies: Document your search terms and strategies for transparency and reproducibility.
Stay Organized: Use reference management tools to keep track of your sources and notes.
Be Comprehensive but Selective: Aim to cover all relevant literature but focus on high-quality and most pertinent studies.
Regularly Update: Literature reviews are dynamic; periodically update your review to include the latest research.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Jyoti Maurya directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Jyoti Maurya
Jyoti Maurya
I create cross platform mobile apps with AI functionalities. Currently a PhD Scholar at Indira Gandhi Delhi Technical University for Women, Delhi. M.Tech in Artificial Intelligence (AI).