cmd Delete Folder – How to Remove Files and Folders in Windows
 Kristofer Koishigawa
Kristofer Koishigawa
Sometimes it's just faster to do things with the command line.
In this quick tutorial we'll go over how to open Command Prompt, some basic commands and flags, and how to delete files and folders in Command Prompt.
If you're already familiar with basic DOS commands, feel free to skip ahead.
How to open Command Prompt
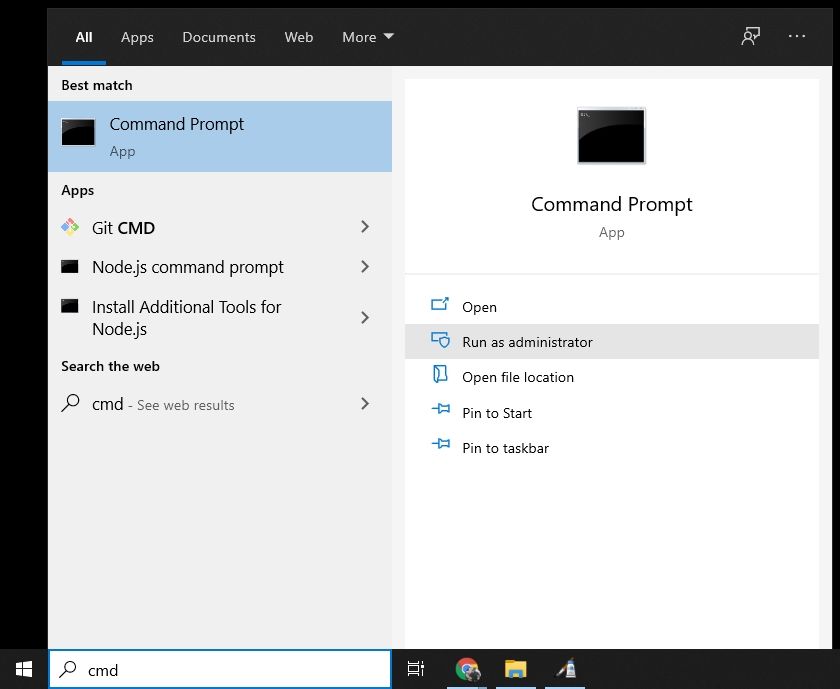
To open Command Prompt, press the Windows key, and type in "cmd".
Then, click on "Run as Administrator":
After that, you'll see a Command Prompt window with administrative privileges:
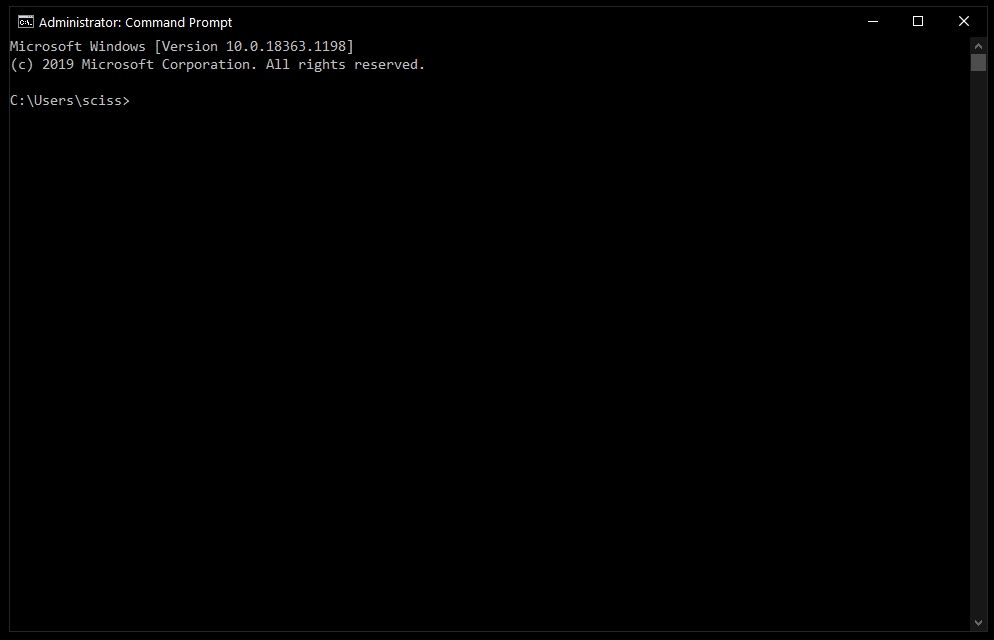 Screenshot of Command Prompt window
Screenshot of Command Prompt window
If you can't open Command Prompt as an administrator, no worries. You can open a normal Command Prompt window by clicking "Open" instead of "Run as Administrator".
The only difference is that you may not be able to delete some protected files, which shouldn't be a problem in most cases.
How to delete files with the del command
Now that Command Prompt is open, use cd to change directories to where your files are.
I've prepared a directory on the desktop called Test Folder. You can use the command tree /f to see a, well, tree, of all the nested files and folders:
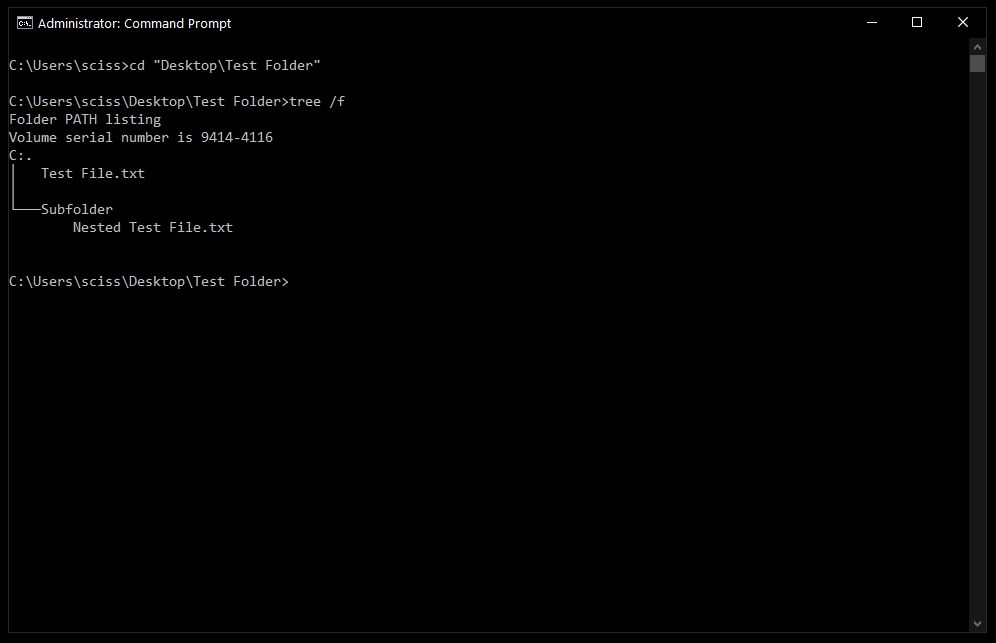
To delete a file, use the following command: del "<filename>".
For example, to delete Test file.txt, just run del "Test File.txt".
There may be a prompt asking if you want to delete the file. If so, type "y" and hit enter.
Note: Any files deleted with the del command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
After that, you can run tree /f to confirm that your file was deleted:

Also, bonus tip – Command Prompt has basic autocompletion. So you could just type in del test, press the tab key, and Command Prompt will change it to del "Test File.txt".
How to force delete files with the del command
Sometimes files are marked as read only, and you'll see the following error when you try to use the del command:
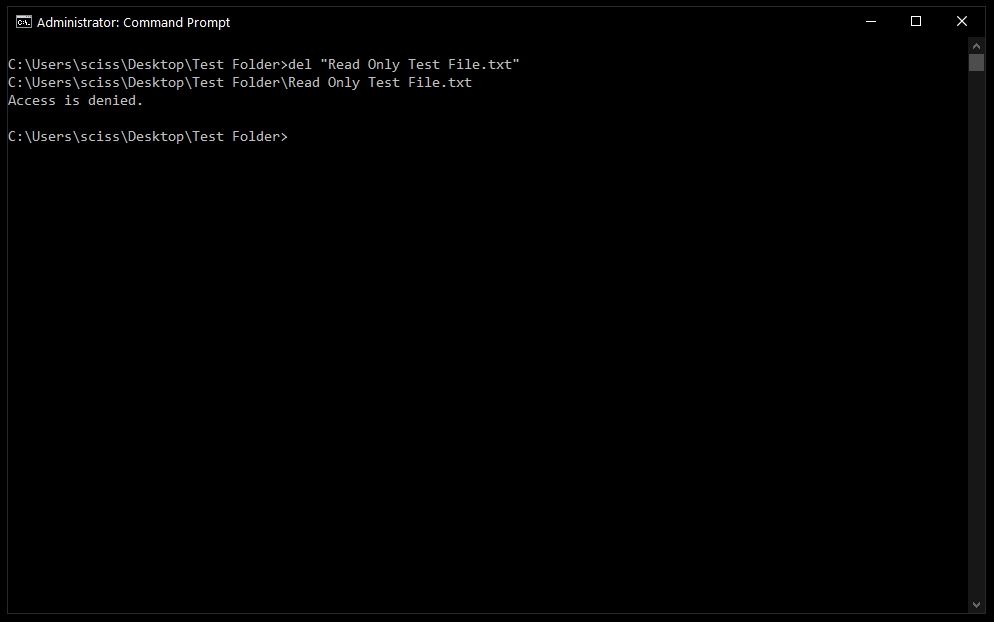
To get around this, use the /f flag to force delete the file. For example, del /f "Read Only Test File.txt":
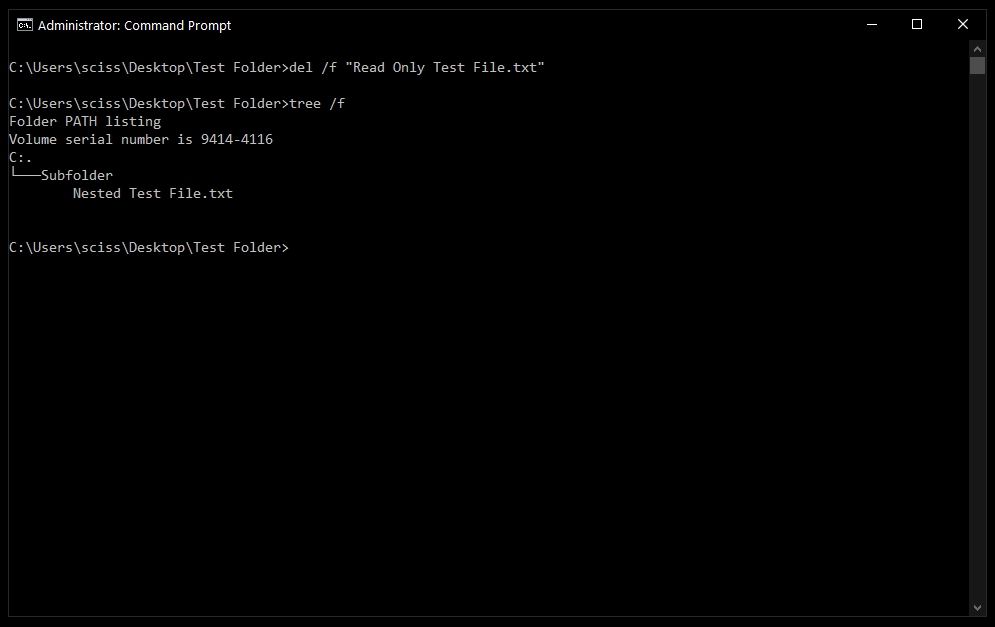
How to delete folders with the rmdir command
To delete directories/folders, you'll need to use the rmdir or rd command. Both commands work the same way, but let's stick with rmdir since it's a bit more expressive.
Also, I'll use the terms directory and folder interchangeably for the rest of the tutorial. "Folder" is a newer term that became popular with early desktop GUIs, but folder and directory basically mean the same thing.
To remove a directory, just use the command rmdir <directory name>.
Note: Any directories deleted with the rmdir command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
In this case I want to remove a directory named Subfolder, so I'll use the command rmdir Subfolder:
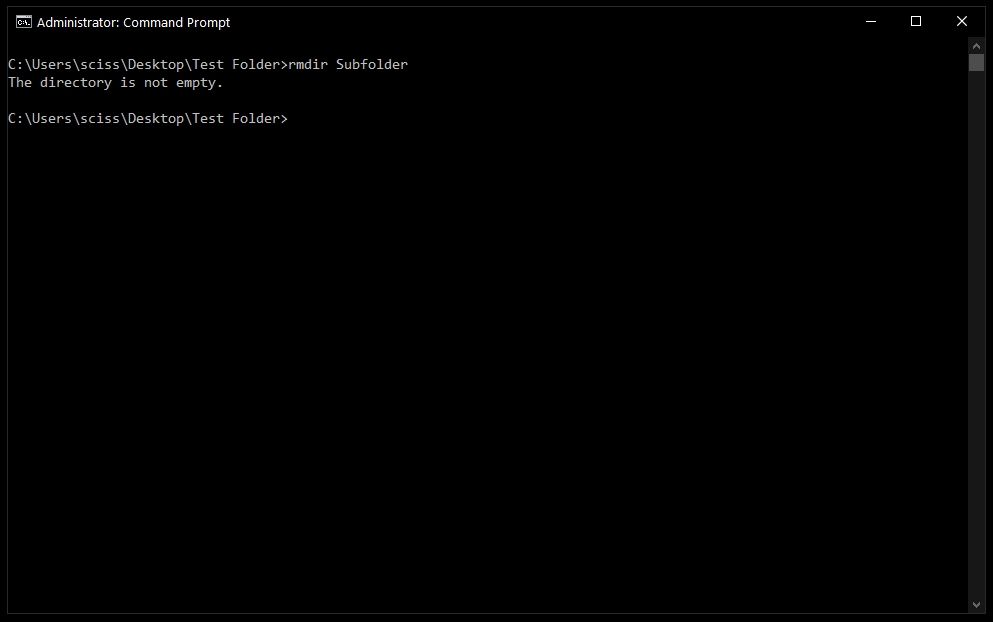
But, if you remember earlier, Subfolder has a file in it named Nested Test File.
You could cd into the Subfolder directory and remove the file, then come back with cd .. and run the rmdir Subfolder command again, but that would get tedious. And just imagine if there were a bunch of other nested files and directories!
Like with the del command, there's a helpful flag we can use to make things much faster and easier.
How to use the /s flag with rmdir
To remove a directory, including all nested files and subdirectories, just use the /s flag:
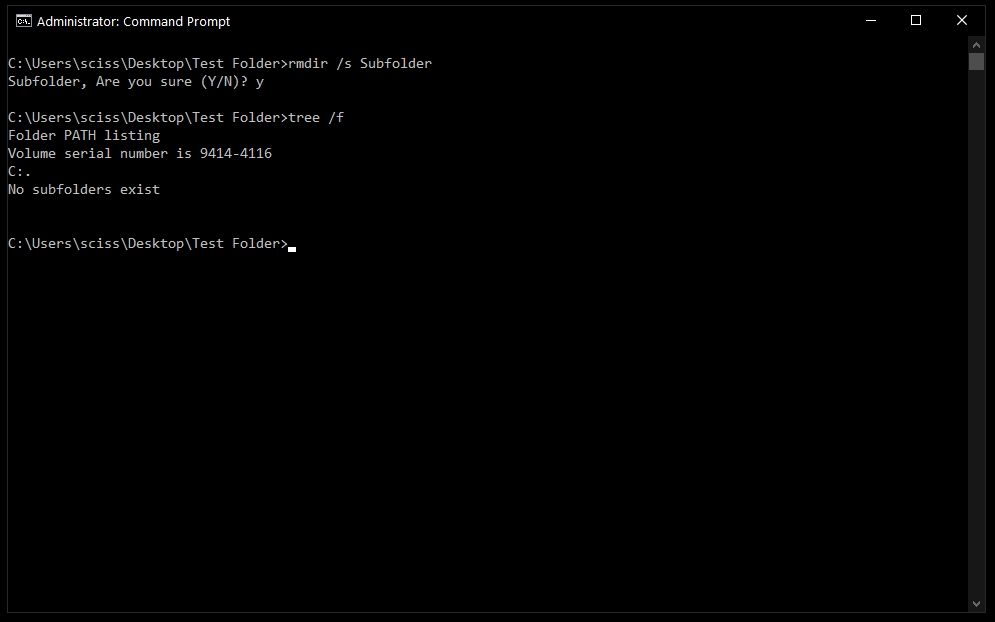
There will probably be a prompt asking if you want to remove that directory. If so, just type "y" and hit enter.
And that's it! That should be everything you need to know to remove files and folders in the Windows Command Prompt.
All of these commands should work in PowerShell, which is basically Command Prompt version 2.0. Also, PowerShell has a bunch of cool aliases like ls and clear that should feel right at home if you're familiar with the Mac/Linux command line.
Did these commands help you? Are there any other commands that you find useful? Either way, let me know over on Twitter.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Kristofer Koishigawa directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
