Day 88 - Deploying a Django Todo App on AWS EC2 Using Kubeadm Kubernetes Cluster 🚀
 Nilkanth Mistry
Nilkanth Mistry
Welcome to Day 88 of the #90DaysOfDevOps Challenge! 🚀
Today, we have an exciting project ahead where we will be deploying a Django Todo app on AWS EC2 using a Kubeadm Kubernetes cluster. Let’s dive in step by step! 📋
Project Description
In this project, our goal is to deploy a Django Todo app on AWS EC2 using a Kubernetes cluster created with Kubeadm. Kubernetes provides us with a scalable and fault-tolerant environment for running our applications, ensuring that they can handle varying loads and recover from failures automatically. 💡
Hands-on Project: Deploying Django Todo App on AWS EC2 with Kubernetes Cluster
Pre-requisites
Before we start, let’s ensure we have the necessary pre-requisites set up:
Create AWS EC2 Instances:
Create two AWS EC2 servers with t2.medium configuration. One will act as the master server, and the other as the node server.
Install Docker on Both Servers:
SSH into each EC2 instance and install Docker:
sudo apt update sudo apt install apt-transport-https curl sudo snap install kubectl --classic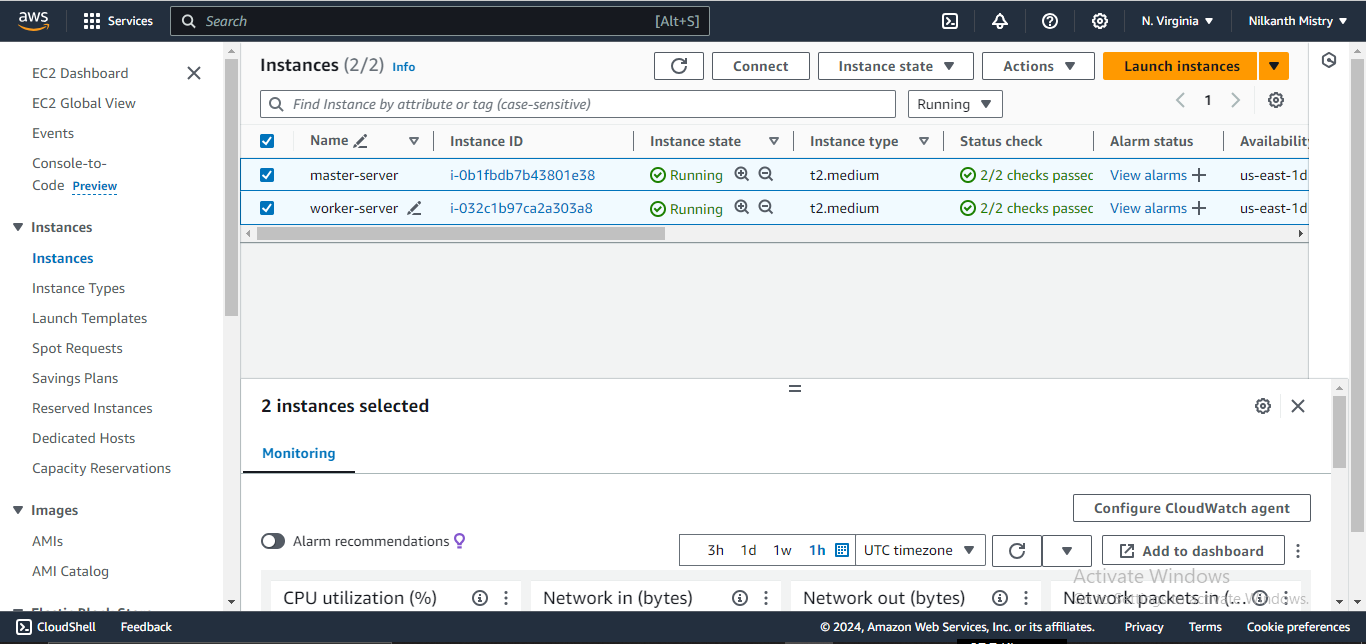
Project Steps
Step 1: Clone the GitHub Repository
Begin by obtaining the Django Todo app from the GitHub repository provided. Clone it to your local environment or directly onto the AWS EC2 instance where we will set up the Kubernetes cluster. 🛠️
git clone https://github.com/LondheShubham153/django-todo-cicd.git
Step 2: Setup the Kubernetes Cluster
Now, let’s set up the Kubernetes cluster using Kubeadm on both the master and worker nodes. 🌐
Master Node Setup:
# Run these commands on the master node as root or using sudo
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install docker.io -y
# Install Kubernetes components
sudo curl -fsSL "https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg" | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg
echo 'deb https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt kubernetes-xenial main' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install kubeadm=1.20.0-00 kubectl=1.20.0-00 kubelet=1.20.0-00 -y
# Initialize Kubernetes cluster
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
# Set up kubeconfig for the current user
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
# Apply a networking addon (Weave Net)
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/weaveworks/weave/releases/download/v2.8.1/weave-daemonset-k8s.yaml
Worker Node Setup:
# Run these commands on the worker node as root or using sudo
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install docker.io -y
# Install Kubernetes components
sudo curl -fsSL "https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg" | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg
echo 'deb https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt kubernetes-xenial main' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install kubeadm=1.20.0-00 kubectl=1.20.0-00 kubelet=1.20.0-00 -y
# Join the worker node to the cluster (use the join command obtained from master)
sudo kubeadm join <master_node_ip>:6443 --token <token> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash <hash> --v=5
Replace <master_node_ip>, <token>, and <hash> with appropriate values obtained from the master node.
Step 3: Setup Deployment and Service for Kubernetes
Now, let’s deploy our Django Todo app using Kubernetes Deployment and Service YAML files. 🚢
Deployment.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: django-todo-app-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: django-todo-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: django-todo-app
spec:
containers:
- name: django-todo-app
image: trainwithshubham/django-todo:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Apply the Deployment YAML:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
Service.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: django-todo-app-service
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: django-todo-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 30080
Apply the Service YAML:
kubectl apply -f service.yaml
Step 4: Access Your Django Todo App
Your Django Todo app should now be accessible through the specified port on the master server. You can access it using the public IP or DNS name of the master server. 🌐
Conclusion:
Congratulations on completing Day 88 of the #90DaysOfDevOps challenge! 🎉 You have successfully deployed a Django Todo app on AWS EC2 using a Kubeadm Kubernetes cluster. Kubernetes provides a robust platform for managing containerized applications, ensuring scalability and resilience. Stay tuned for tomorrow’s challenge, where we will explore another exciting DevOps project!
I hope you found this guide helpful. Don’t forget to follow and give a thumbs up 👍 if you enjoyed it! Subscribe for more updates.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment below. Thanks for reading and have an amazing day ahead! 😄
Connect with me on LinkedIn and GitHub for more updates and discussions.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Nilkanth Mistry directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Nilkanth Mistry
Nilkanth Mistry
Embark on a 90-day DevOps journey with me as we tackle challenges, unravel complexities, and conquer the world of seamless software delivery. Join my Hashnode blog series where we'll explore hands-on DevOps scenarios, troubleshooting real-world issues, and mastering the art of efficient deployment. Let's embrace the challenges and elevate our DevOps expertise together! #DevOpsChallenges #HandsOnLearning #ContinuousImprovement