From Web 2.0 to Web 3.0: A Journey into the Decentralized Future
 Aniket Dhaygude
Aniket Dhaygude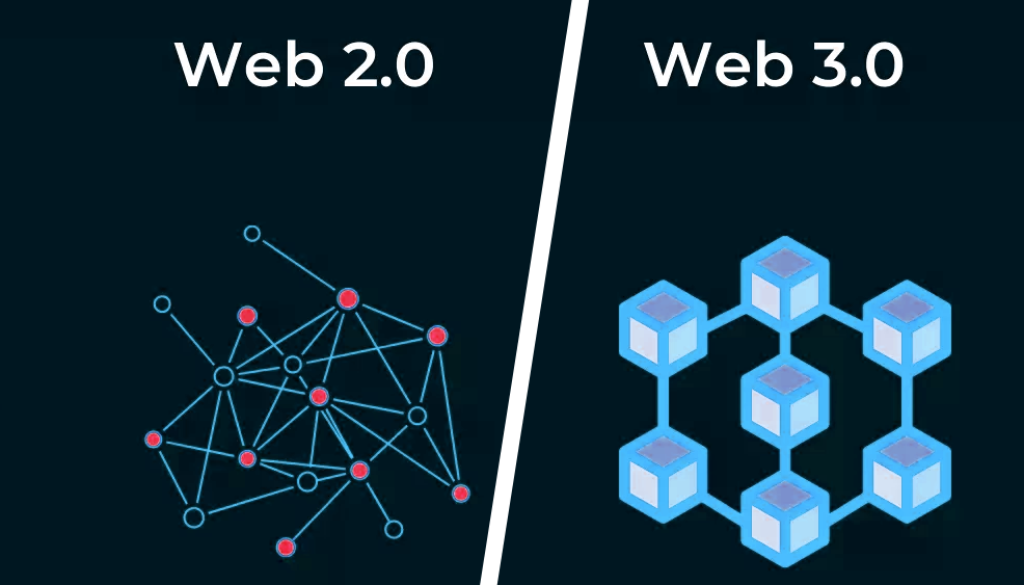
The internet has evolved dramatically over the past few decades. We've seen the rise of Web 1.0, the static web, to Web 2.0, the interactive and social web. Now, we are on the brink of a new era: Web 3.0, or Web3. This evolution promises to revolutionize the way we interact with the internet, bringing more control to users and creating a more decentralized and secure digital environment. But what exactly are Web 2.0 and Web 3.0, and why is this transition important?
Understanding Web 2.0
Web 2.0 is the version of the internet most of us are familiar with today. It transformed the static, read-only Web 1.0 into an interactive and collaborative platform. Here are some key features of Web 2.0:
User-Generated Content: Platforms like YouTube, Twitter, and Instagram allow users to create and share content easily.
Social Networking: Sites like Facebook and LinkedIn connect people globally, fostering communication and community building.
Dynamic Content: Websites can update content in real-time without needing a page refresh, thanks to technologies like AJAX.
Web Applications: Services like Google Docs and Dropbox provide powerful online tools that can replace traditional desktop applications.
While Web 2.0 has brought significant advancements, it also has its limitations. Most notably, it is highly centralized. Major companies like Google, Facebook, and Amazon control large portions of the internet, raising concerns about data privacy, security, and censorship.
Enter Web 3.0
Web 3.0, or Web3, aims to address the issues of centralization by leveraging blockchain technology and decentralized networks. Here are some core principles and features of Web 3.0:
Decentralization: Unlike Web 2.0, Web 3.0 operates on decentralized networks, reducing the control of a few centralized entities.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain underpins Web 3.0, providing a secure and transparent method for recording transactions and data.
Cryptocurrencies and Tokens: Digital assets enable new economic models and incentivize user participation.
Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code can automate complex processes.
Interoperability: Web 3.0 aims to create a more connected and seamless internet, where applications can interact with each other effortlessly.
Why Transition to Web 3.0?
The shift from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 is not just a technological upgrade; it's a fundamental change in how we interact with the internet. Here are some reasons why this transition is important:
User Empowerment: Web 3.0 gives users more control over their data and online identities. Instead of relying on centralized platforms that monetize user data, individuals can own and manage their information.
Enhanced Security: Decentralized networks are inherently more secure. Blockchain technology ensures that data is tamper-proof and transparent, reducing the risk of hacks and data breaches.
Privacy: Web 3.0 enhances privacy by enabling users to interact online without needing to disclose personal information. Cryptographic techniques ensure that transactions and communications are secure and private.
Censorship Resistance: Decentralization makes it harder for any single entity to control or censor information. This leads to a freer and more open internet.
New Economic Models: Cryptocurrencies and tokens enable new ways of incentivizing and rewarding users. This can lead to more equitable economic systems and innovative business models.
The Scope of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is still in its early stages, but its potential is vast. Here are some areas where Web 3.0 can make a significant impact:
Finance: Decentralized finance (DeFi) is already disrupting traditional banking by offering services like lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries.
Supply Chain: Blockchain can provide transparency and traceability, improving efficiency and trust in supply chains.
Healthcare: Secure and interoperable medical records can improve patient care and data privacy.
Voting: Blockchain-based voting systems can enhance the security and transparency of elections.
Content Creation: Artists and creators can directly monetize their work using NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), bypassing traditional intermediaries.
Conclusion
The transition from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 marks a significant shift in the internet's evolution. While Web 2.0 has brought tremendous advancements in connectivity and interactivity, it has also led to centralization and privacy concerns. Web 3.0 promises to address these issues by creating a more decentralized, secure, and user-centric internet. As we continue to explore the possibilities of Web 3.0, we are entering an exciting new era that has the potential to transform not just the internet, but society as a whole.
By embracing Web 3.0, we are taking a step towards a more equitable, secure, and innovative digital future. Whether it's through decentralized finance, improved data privacy, or new economic models, the impact of Web 3.0 will be profound and far-reaching.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aniket Dhaygude directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aniket Dhaygude
Aniket Dhaygude
👨💻 Freelance Developer | UI/UX Enthusiast | Tech Blogger Transforming ideas into engaging digital experiences. I specialize in front-end development, UI/UX design, and creating dynamic web apps. Let's build something amazing together! 🚀