SQL Commands
 Swatipb
Swatipb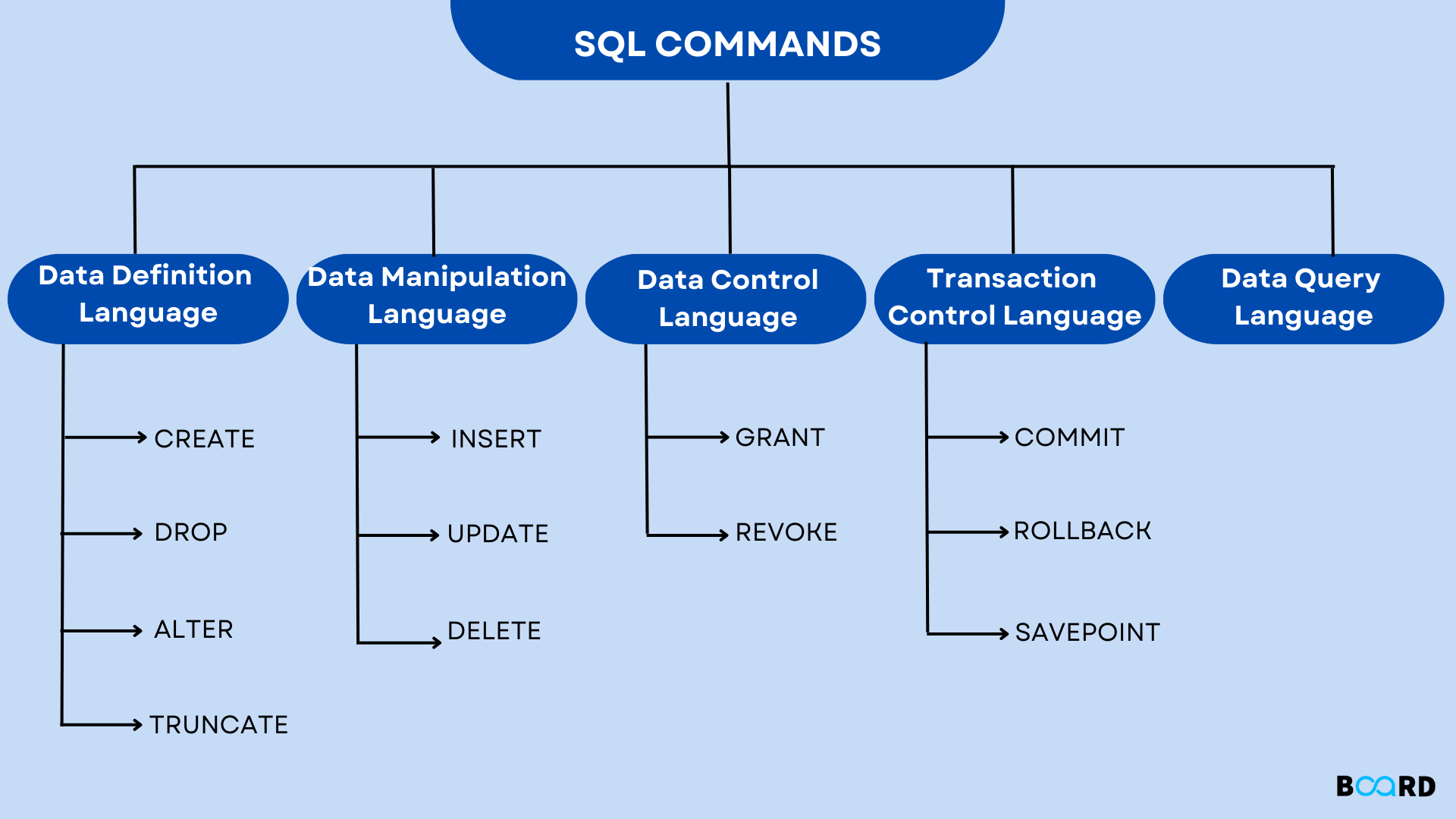
- Data Definition Language (DDL): It changes the structure of the table by creating, deleting, or altering the table. DDL commands are auto-committed, meaning they save all changes in the database.
Create: This command is used to create a new table in the database.
Create table Student;
Drop: This command is used to delete both the records and the structure of the table.
Drop table Student;
Alter: This command is used to change the structure of the table. It can modify an existing attribute or add a new one.
alter table Student
rename column name to stud_name; //renaming the column name
alter table Student
add gender char(1); //adding new attribute
alter table Student
modify gender varchar(6); //changing the size
Truncate: Deletes all rows in the table.
Truncate table Student;
Data Manipulation Language (DML): These commands are used to modify the database. They are not auto-committed, meaning changes are not permanently saved.
Insert: This command is used to add data into a row of the table.
Insert into Student values(1, "A", 21, "XYZ"),(2, "B", 22,"PQR")(3, "C", 21, "PQR"):;Update: This command is used to update or modify the values of a column in a table.
Update Student set age=null where id=2;Delete: This command is used to remove one or more rows from a table.
Delete from Student where id=3;Data Query Language (DQL): This command fetches data from the table.
Select: This command is used to display the contents of the table.
Select * from Student;
I have referred to various resources to understand and simplify it. Other commands will be covered in the next blog.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Swatipb directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Swatipb
Swatipb
The feeling of learning something new:-).