Positioning (CSS)
 Akansha Dangi
Akansha Dangi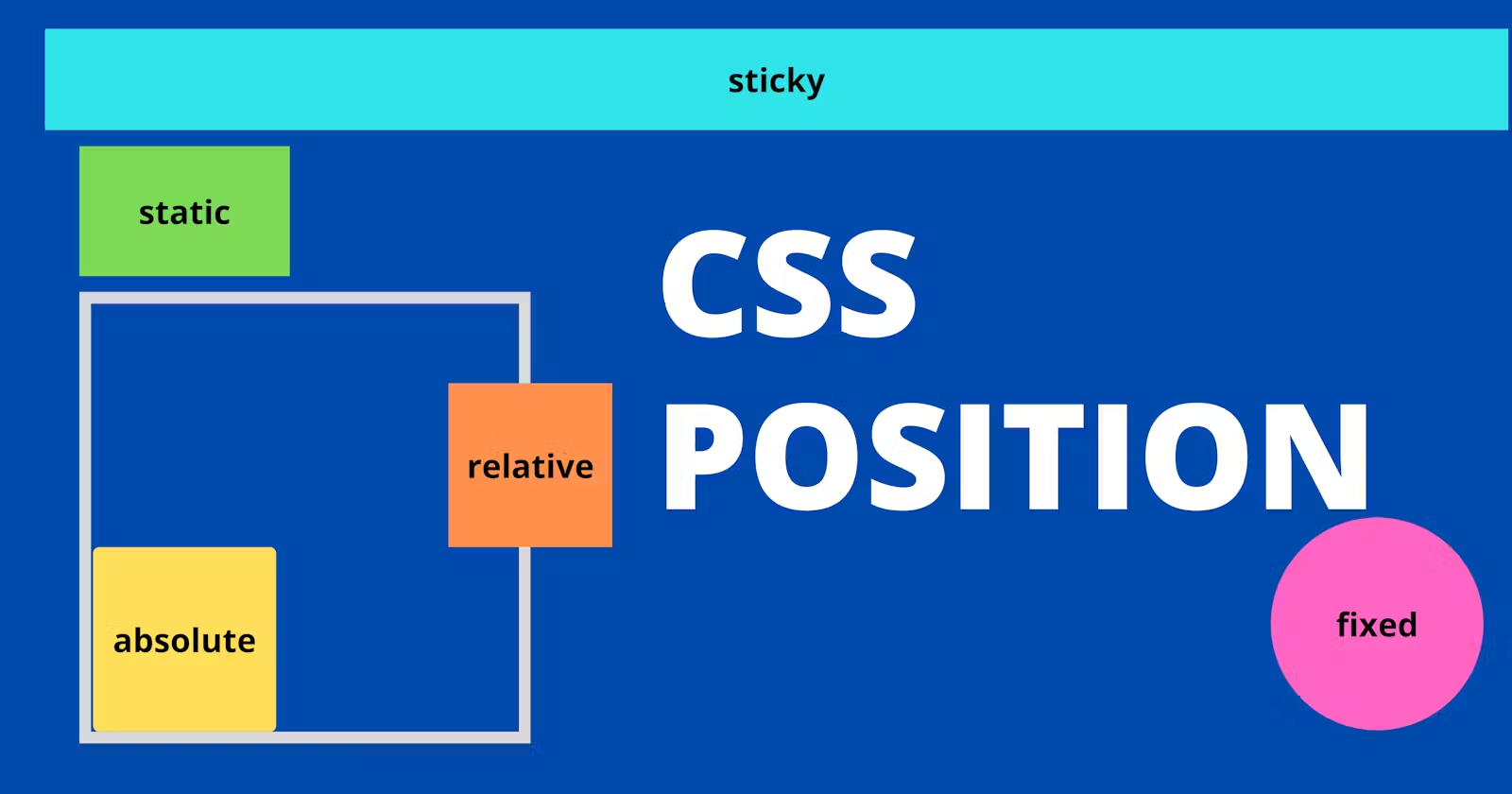
What is the CSS Position Property ?
The CSS position property is used to modify how elements are placed on a webpage. With the CSS position property, you can adjust the position of an element on your webpage. The CSS position property allows us to move our elements around the webpage using the top, left, right, and bottom properties.
Types of CSS Positions
The following are the five different types of CSS positions:
static
relative
absolute
fixed
sticky
Static Position
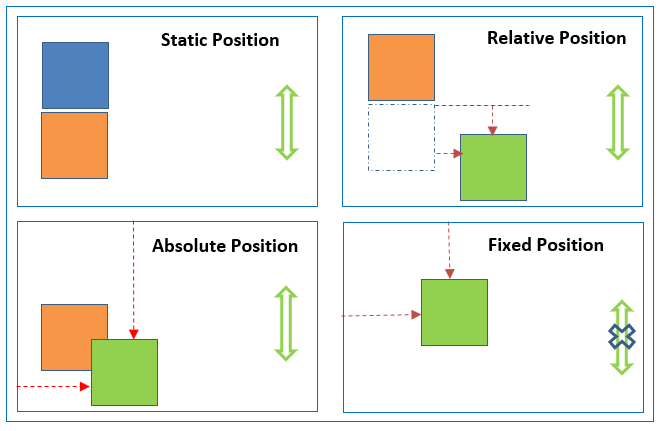
This is the default CSS position applicable to all HTML elements. This position place the HTML elements based on normal document flow. Using this position, top/right/bottom/left properties can not be applicable to elements (ie., static position elements don’t obey top/right/bottom/left properties).

.p1 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:cornflowerblue;
position:static;
}
.p2 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:sandybrown;
}
<body>
<div class="p1">
</div>
<div class="p2">
</div>
</body>
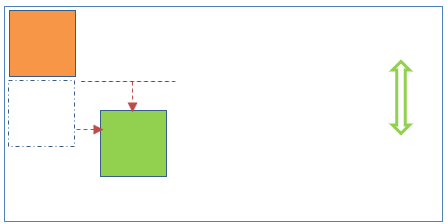
Relative Position
This position places the element relative to its normal position. This position is relative to normal document flow. Here top/right/bottom/left properties can be applied to elements.
.p1 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:sandybrown;
}
.p2 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:lightgreen;
position:relative;
left:60px;
top:20px;
}
<body>
<div class="p1">
</div>
<div class="p2">
</div>
</body>
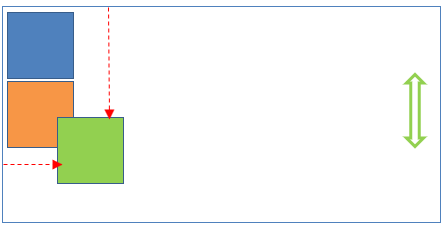
Absolute Position
This position places the element at the exact position specified.
This position is relative to
its parent element position when parent element position is relative/absolute.
document body (browser viewport) when parent element position is static.
document body (browser viewport) when there is no parent element.
.p1 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:cornflowerblue;
}
.p2 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:sandybrown;
}
.p3 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:lightgreen;
position:absolute;
left:60px;
top:20px;
}
<body>
<div class="p1">
</div>
<div class="p2">
</div>
<div class="p3">
</div>
</body>
Fixed Position
This position places the element at a fixed place relative to the viewport. Page scrolling does not affect this position.

.p1 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:lightgreen;
position:fixed;
left:40px;
top:40px;
}
<body>
<div class="p1">
</div>
</body>
Sticky Position
Sticky position is a combination of relative and fixed. It is relative until it crosses a specified threshold, at which point it is treated as static position.
.stick{
background: #000;
height: 20vh;
width: 100%;
position: sticky;
top: 0;
color: #fff;
padding-left: 60px;
}
z-index
The ‘z-index’ property specifies the stack order of an element.
An element with greater stack order is always in front of an element with a lower stack order.
Z-index only works on positioned elements (position: absolute/relative/ fixed/sticky) and flex items.
Syntax-
z-index: value;
like-
z-index: auto;
z-index: inherit;
z-index: 0;
z-index: -1; /*negative value to lower the priority*/

Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Akansha Dangi directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Akansha Dangi
Akansha Dangi
"Full Stack Web Dev | Passionate about building meaningful digital experiences. Let's create the future together!"