Power Up Your Circuits: The Essential Guide to Choosing the Perfect Capacitor
 aeliyamarine tech
aeliyamarine tech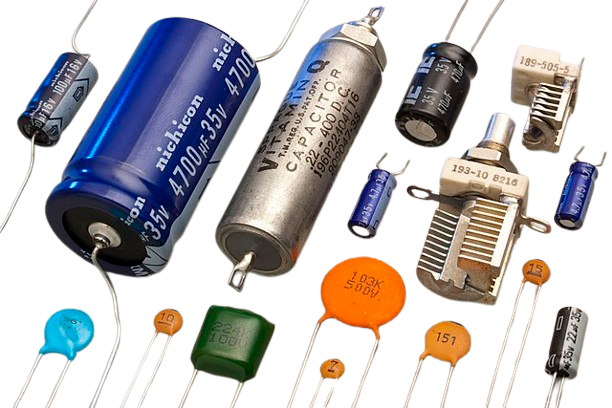
Capacitors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, playing a crucial role in storing and releasing electrical energy. Whether you're working on simple DIY projects or complex industrial applications, understanding capacitors and choosing the right one for your needs can significantly enhance your circuit's performance and reliability. In this guide, we'll explore the basics of capacitors, their types, features, and practical applications to help you make an informed decision.
What is a Capacitor?
A capacitor is an electronic device that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. When voltage is applied across the plates, an electric field is created, and energy is stored. Capacitors can quickly release this stored energy when needed, making them essential for various applications.
Types of Capacitors
Ceramic Capacitors:
Features: Small size, low cost, high stability.
Applications: Used in filtering, coupling, and decoupling in high-frequency circuits.
Electrolytic Capacitors:
Features: High capacitance values, polarized, relatively large size.
Applications: Commonly used in power supply filters, audio amplifiers, and other applications requiring large capacitance.
Tantalum Capacitors:
Features: High capacitance per volume, stable performance, polarized.
Applications: Ideal for space-constrained applications, such as mobile phones and portable electronics.
Film Capacitors:
Features: Non-polarized, excellent stability, low ESR.
Applications: Used in audio equipment, power supplies, and motor run applications.
Supercapacitors:
Features: Extremely high capacitance values, fast charge and discharge rates.
Applications: Energy storage, backup power, and load balancing.
Key Features to Consider
Capacitance Value: The primary parameter of a capacitor, measured in Farads (F). Choose a capacitance value that matches your circuit's requirements.
Voltage Rating: Ensure the capacitor can handle the maximum voltage in your circuit to prevent failure.
Tolerance: Indicates the accuracy of the capacitance value. Choose capacitors with tight tolerances for precise applications.
Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR): Lower ESR values are preferable for high-frequency applications as they minimize energy losses.
Temperature Coefficient: Affects the capacitance stability over temperature variations. Choose capacitors with low-temperature coefficients for applications requiring high stability.
Practical Applications of Capacitors
Power Supply Smoothing: Capacitors are used to filter out voltage spikes and smooth the output of power supplies, ensuring a stable voltage for electronic circuits.
Coupling and Decoupling: Capacitors allow AC signals to pass while blocking DC, making them essential for coupling and decoupling stages in amplifiers and other signal-processing circuits.
Timing and Oscillators: Capacitors, in combination with resistors, can create timing circuits and oscillators used in clocks, timers, and signal generators.
Energy Storage: Supercapacitors provide rapid energy storage and release, useful in applications requiring quick bursts of energy, such as regenerative braking in electric vehicles.
Motor Starters: Capacitors provide the necessary phase shift for starting single-phase induction motors, ensuring smooth operation.
Choosing the Right Capacitor
When selecting a capacitor, consider the following steps:
Identify the Application: Determine the specific role of the capacitor in your circuit (e.g., filtering, coupling, energy storage).
Calculate Requirements: Determine the required capacitance, voltage rating, and other parameters based on your circuit's design.
Select the Type: Choose the appropriate type of capacitor based on the application's requirements and the capacitor's characteristics.
Verify Specifications: Ensure the selected capacitor meets the necessary specifications, including capacitance tolerance, ESR, and temperature coefficient.
Consider Size and Cost: Balance the physical size and cost of the capacitor with the performance requirements of your application.
Conclusion
Capacitors are versatile and essential components in electronic circuits, offering a wide range of functionalities from energy storage to signal filtering. By understanding the different types of capacitors and their key features, you can make informed decisions and optimize your circuit's performance. At Aeliya Marine Tech, we provide a comprehensive selection of high-quality capacitors to meet the diverse needs of our customers. Contact us today to find the perfect capacitor for your application and experience the difference in quality and reliability.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from aeliyamarine tech directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
