1. How AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning Differ
 Muhammad Fahad Bashir
Muhammad Fahad Bashir
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a transformative technology that is reshaping the world as we know it. From automating routine tasks to making complex decisions, AI is a powerful technology that is revolutionizing industries and changing the way we live. In this article, we will explore what AI is, its types, applications, and the relationship between AI, Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL).
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Technical Definition:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science focused on developing methods that enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. This involves learning from data, recognizing patterns, and making decisions without explicit programming.
Non-Technical Definition:
AI can be thought of as a digital brain that allows computers to perform tasks like understanding language, recognizing images, and making decisions, just like a human would.
The Value of Artificial Intelligence
AI is not just a technological advancement; it's adding values and leaving the impact various domains. Its value can be summarized in several key points:
Transforming Industries: AI is revolutionizing sectors like healthcare, finance, education, and entertainment by introducing smarter, more efficient processes.
Creating Opportunities: AI is generating new opportunities in fields such as data science, robotics, and AI ethics, leading to new job roles and industries.
Economic Growth: AI is significantly boosting the global economy by increasing productivity and enabling innovation.
Improving Life Quality: AI enhances our daily lives by making technology more intuitive and responsive, leading to faster, more personalized experiences.
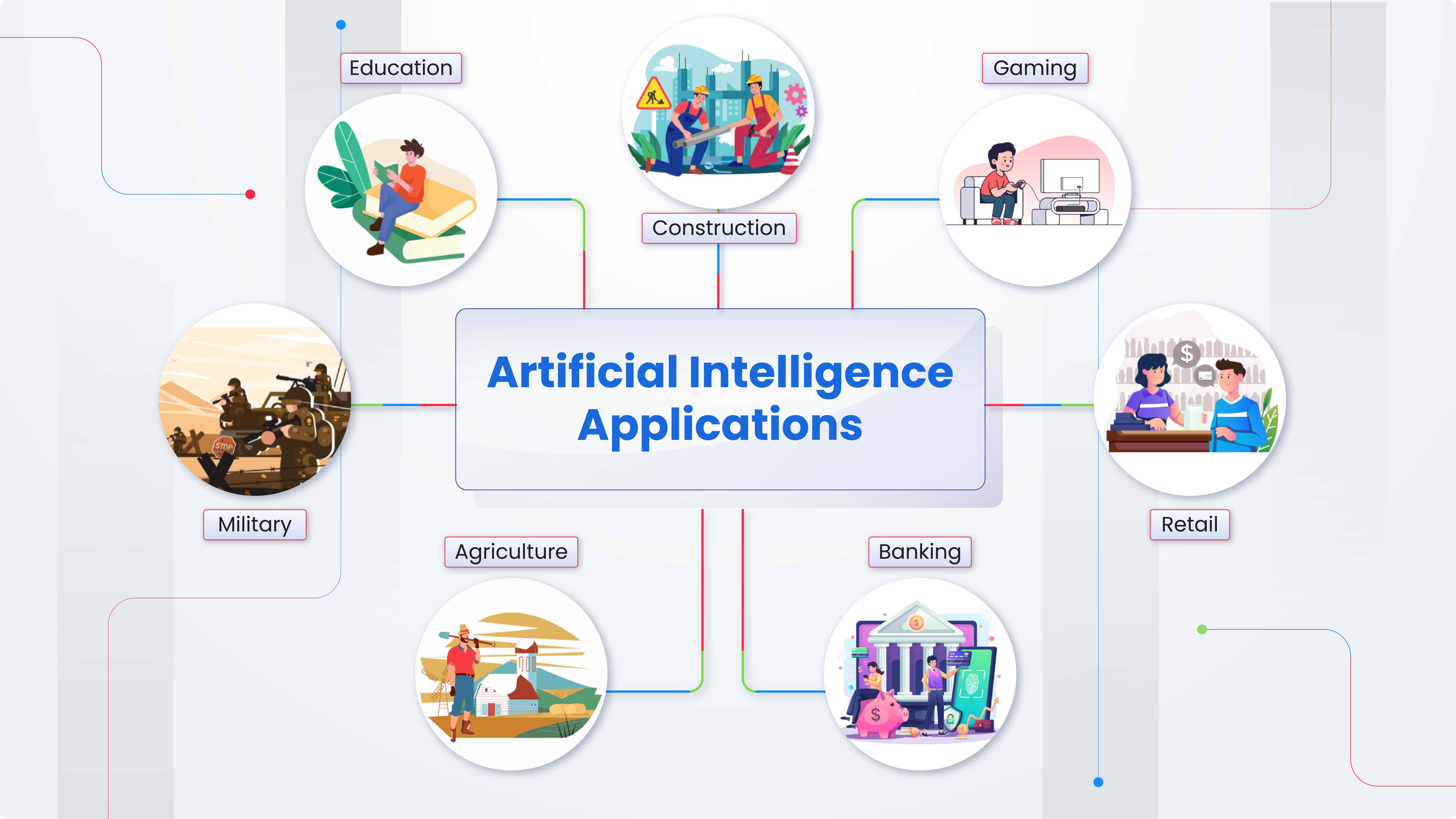
Applications of AI
AI has a wide range of applications across different industries, including:
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enabling machines to understand and respond to human language, such as chatbots and voice assistants.
Computer Vision: Allowing machines to interpret and make decisions based on visual data, such as facial recognition and autonomous vehicles.
Robotics: Enhancing the capabilities of robots to perform complex tasks in manufacturing, healthcare, and service industries.
Expert Systems: AI systems that simulate the decision-making abilities of a human expert, used in areas like medical diagnosis and financial forecasting.
Recommendation Systems: Powering personalized recommendations in e-commerce, streaming services, and social media platforms.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
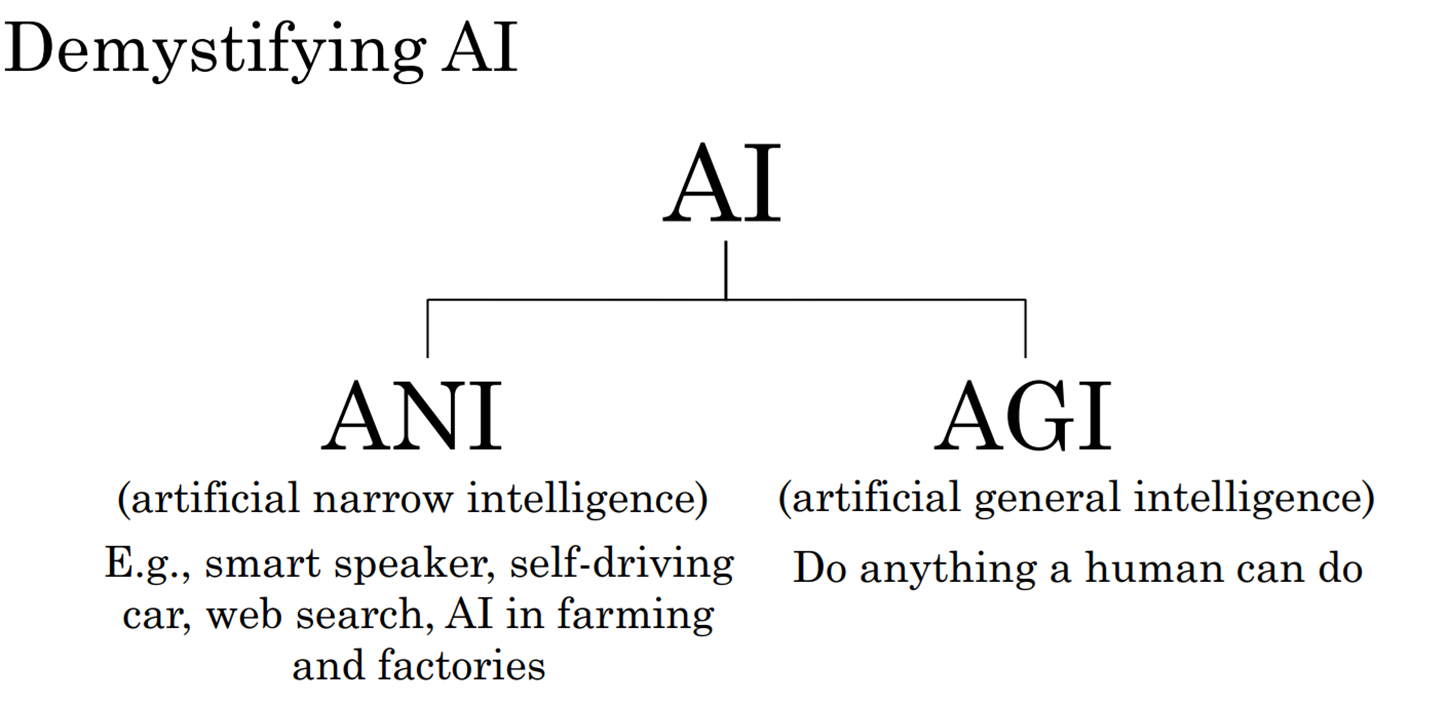
AI can be categorized into two main types:
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI):
Definition: Also known as weak AI, ANI is designed to perform a specific task, such as language translation or playing chess. It operates under a limited set of pre-defined rules and is the type of AI most prevalent today.
Example: A virtual assistant like Siri or Alexa that can perform tasks like setting reminders or playing music.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI):
Definition: Also known as strong AI, AGI refers to a future state of AI where machines will be capable of performing any intellectual task that a human can do. It will have the ability to learn, understand, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks.
Example: A hypothetical AI that can seamlessly transition between tasks like solving mathematical problems, writing poetry, and providing emotional support, just like a human.
Relationship Between AI, ML, and DL
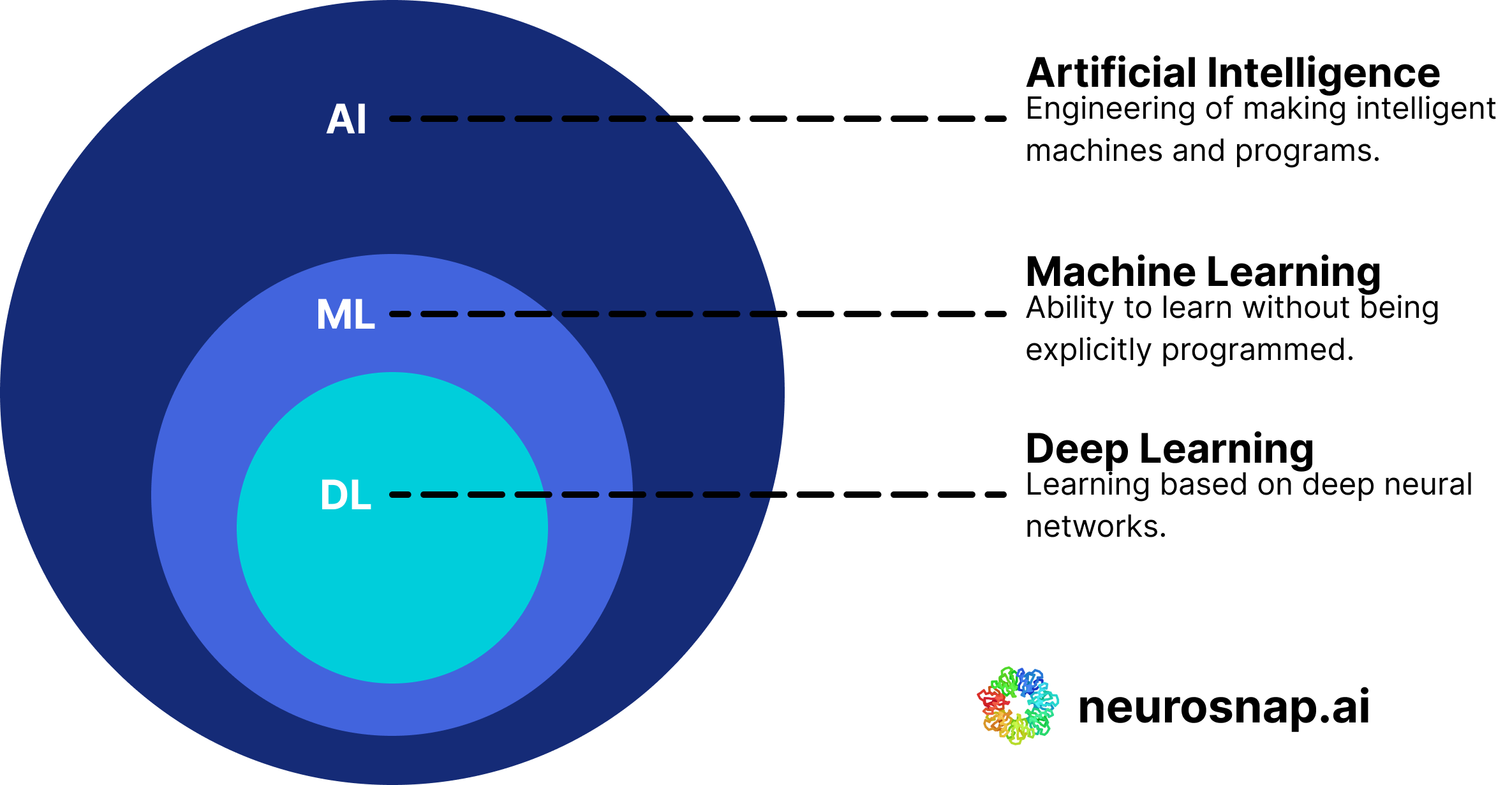
Understanding the relationship between AI, Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) is crucial for grasping how these technologies interconnect:
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI is the broadest concept, encompassing all efforts to make machines perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. It includes rule-based systems that automate tasks, such as sorting emails or controlling smart home devices.
Machine Learning (ML):
Subset of AI: ML is a subfield of AI where machines learn from data rather than being explicitly programmed. It involves feeding data to algorithms that then identify patterns and make decisions based on this learning.
- Example: A spam filter that learns to identify unwanted emails based on the content of previous spam messages.
Deep Learning (DL):
Subset of ML: DL is a specialized area of Machine Learning that uses neural networks, inspired by the human brain, to process data. It is particularly effective for tasks like image and speech recognition.
The left side figure is human brain neurons while on the right there are artificial neural networks which is reshaping the world.

- Example: A self-driving car that uses deep learning to process visual input and navigate roads safely.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is a dynamic and evolving field that is transforming the world. By understanding its types, applications, and the relationship between AI, ML, and DL, we can better appreciate its potential and harness its power to drive innovation and improve our lives. Whether through technical advancements or enhancing daily experiences, AI is poised to be a cornerstone of future technological progress.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Muhammad Fahad Bashir directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
