Web3 Explained: A Simple Guide to Understanding the Decentralized Internet
 Navya Srivastava
Navya Srivastava
Introduction
The internet has come a long way since its inception, evolving from a static collection of pages (Web1) in the 1990s, like Yahoo! Directory and Geocities, where users mainly consumed content, to the interactive, user-driven platforms of today (Web2). Web2 introduced social media, content sharing, and centralized data control on sites like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter. However, as technology progresses, the demand for a more decentralized, transparent, and secure internet grows, leading us to Web3—the next evolution, set to revolutionize our digital interactions.
A Brief History of Web3
The concept of Web3 was first introduced by Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum, in 2014. Wood envisioned a new kind of internet where users have more control over their data and online interactions, free from centralized entities like large tech companies. Web3 aims to decentralize the web by leveraging blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer interactions and removing the need for intermediaries.
The Need for Web3
While Web2 has brought us immense convenience and innovation, it also comes with significant drawbacks:
Centralization: A few tech giants control vast amounts of data, creating single points of failure and opportunities for censorship.
Privacy Concerns: User data is often collected, stored, and sold without explicit consent, leading to widespread privacy issues.
Security Risks: Centralized databases are attractive targets for hackers, leading to frequent and large-scale data breaches.
Web3 addresses these concerns by using decentralized networks and cryptographic principles to ensure that no single entity has control over the data and that users maintain ownership of their digital identities.
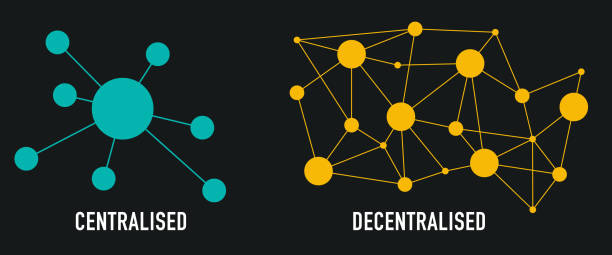
What is Decentralization?
Decentralization is the principle that no single entity or group has control over a network, system, or process. In the context of Web3, decentralization means distributing control across a network of nodes rather than relying on a central authority. This shift in control enhances transparency, reduces the risk of censorship, and increases security by eliminating single points of failure.
Transparency: In a decentralized system, all participants can view and verify transactions, reducing the possibility of fraud or manipulation.
Security: Decentralization spreads out the risk, making it harder for bad actors to compromise the system.
User Empowerment: By decentralizing control, users have greater autonomy and ownership over their data and interactions.
Key Components of Web3
Blockchain Technology: At the core of Web3 is blockchain technology, a decentralized ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. It ensures transparency and security, making it difficult for any single party to alter data without consensus.
Cryptocurrencies: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum play a crucial role in Web3. They facilitate peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries, providing financial sovereignty to users.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written into code. They automate transactions and processes, reducing the need for third parties and increasing efficiency.
Decentralized Applications (dApps): dApps run on blockchain networks, allowing for decentralized, transparent, and user-controlled applications. Unlike traditional apps, dApps operate without central servers, reducing the risk of downtime and censorship.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): DAOs are organizations governed by smart contracts, where decision-making power is distributed among token holders rather than centralized leadership. They represent a new model of collective governance in the digital age.
Conclusion
Web3 represents a significant leap forward in how we interact with the internet. By embracing decentralization, Web3 has the potential to empower users, enhance security, and foster innovation in ways that were previously unimaginable. As we continue to explore and build on this new paradigm, understanding its history, necessity, and components will be crucial for anyone looking to participate in the future of the internet.
What's Next?
In the next part of this series, we will delve deeper into the building blocks of Web3, including how blockchain, smart contracts, and cryptocurrencies work together to create a decentralized web.
Read more: Blockchain Basics Part 1: Hashes, Blocks, Nonces, and Mining Explained
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Navya Srivastava directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Navya Srivastava
Navya Srivastava
Hi! I am Navya, a dedicated coding enthusiast, deeply interested in Web3 technologies and exploring the future of decentralized applications and blockchain innovation.