The first step in the journey of Java Full Stack by deep diving into SQL :
 Prafull Tripathi
Prafull TripathiData :
Data are the raw facts that describe the attributes/properties of an entity/object.

Database :
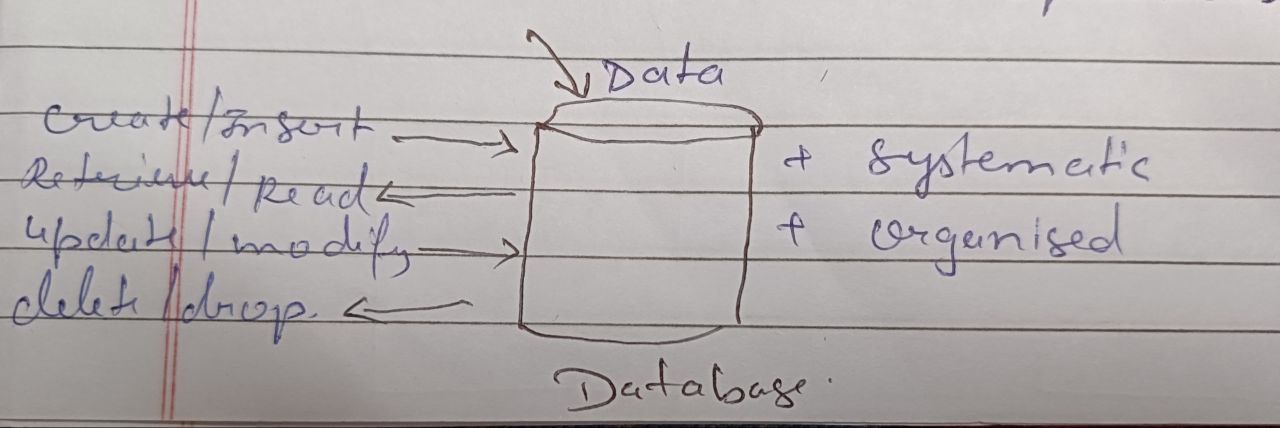
A database is a place or medium in which data stored in a systematic and organized manner.
On the Database, we can perform several operations such as:
i).Create/Insertii).Retrieve/Readiii).Update/Modifyiv).Delete/DropAll these operations are universally known as CRUD operations.
Data Base Management System(DBMS) :
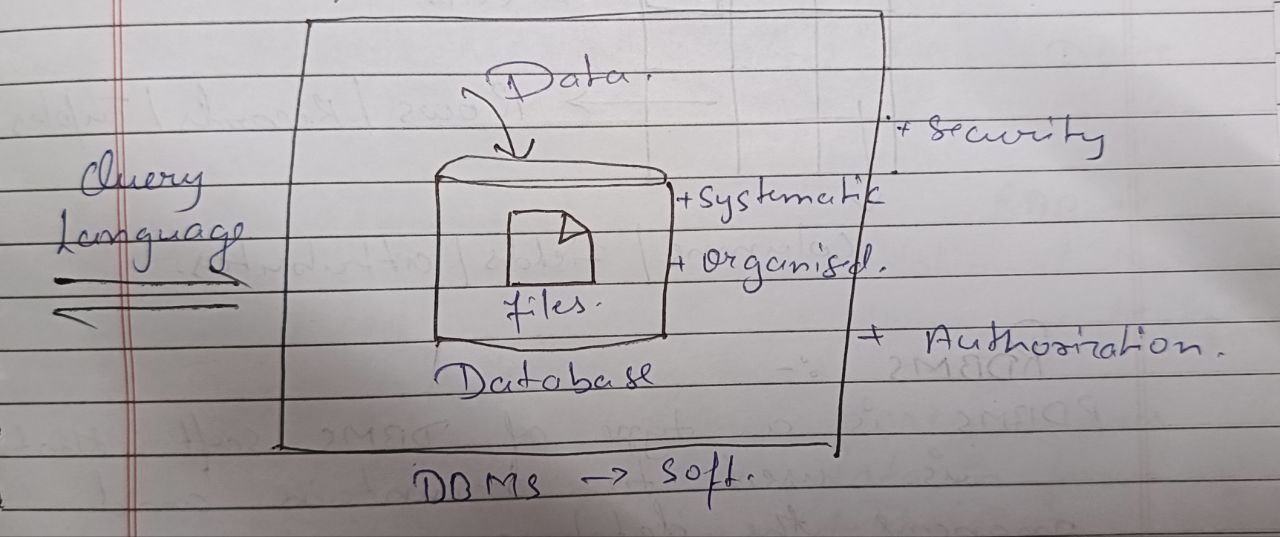
DBMS is soft. that is used to maintain and manage the database.
DBMS provides us with two important features :
i).Securityii).AuthorizationTo communicate with DBMS we require Query Language.
In DBMS we store the data in the form of files.
Classification of DBMS :
NDBMS: Networking Database Management System
HDBMS: Hierarchial Database Management System
OODBMS: Object-Oriented Database Management System
RDBMS: Relational Database Management System
( Stable, Flexible, Scalable, Highly demanding)
Relational Model :
The relational Model was introduced by a computer scientist named E.F.Codd ( Edger Frank Codd).
The relational model stores the data in the form of tables.
RDBMS :
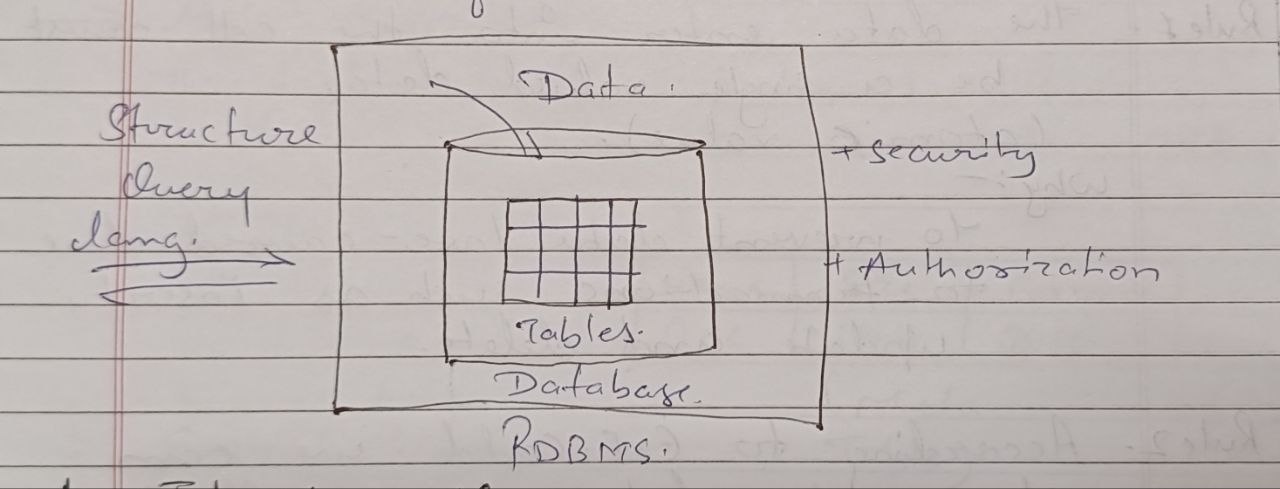
RDBMS is a type of DBMS software that is used to maintain and manage the database.
RDBMS provides two important features:
i).Securityii).AuthorizationTo communicate with RDBMS we require Structured Query Language(SQL).
In RDBMS we store the data in table form.
Interview Question :
What is the difference between DBMS and RDBMS?

Rules of E.F.Codd :
Rule 1. The data entered into the cell must be single-valued (atomic value).
why? : To prevent data loss due to transactions such as insert, update, and delete.
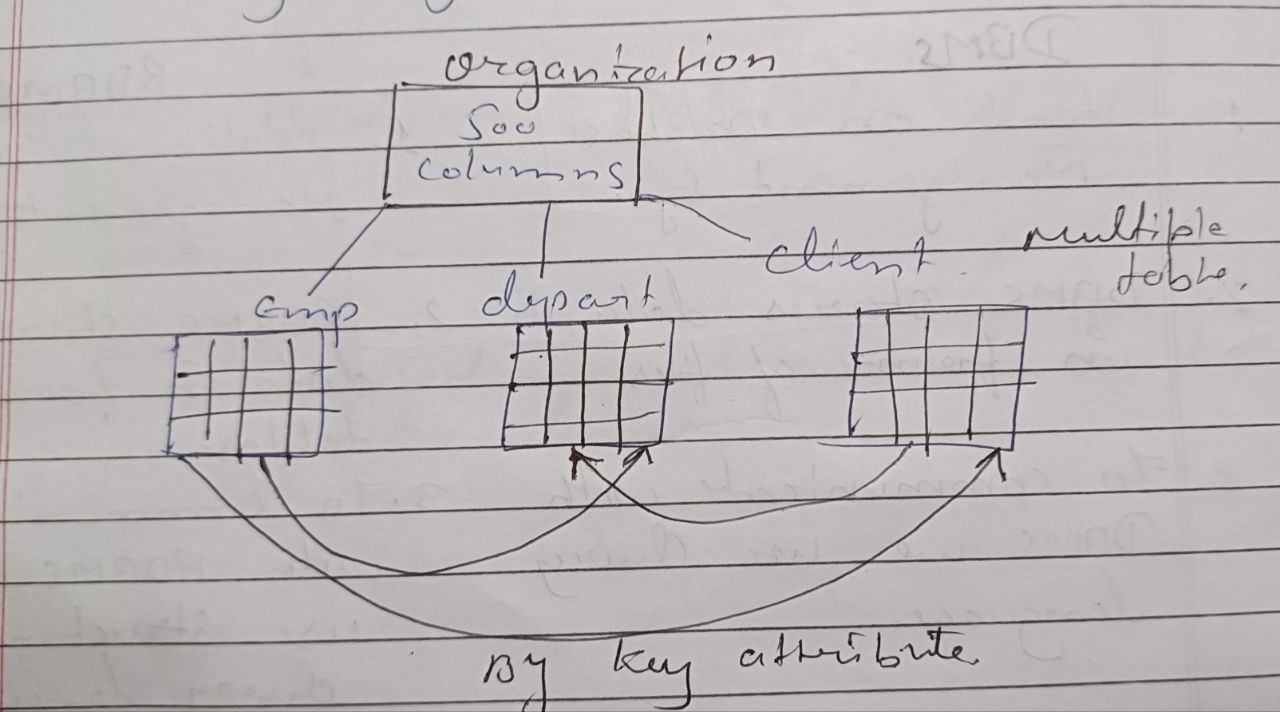
Rule 2. According to E.F.Codd, we can store the data in multiple tables if needed we can establish a relationship between the tables by using KEY ATTRIBUTES.
Rule 3. In RDBMS we store everything in the form of a table including #metadata.
Meta Data :
The details about the data are known as metadata.
Meta Tables :
The table store in which metadata is stored is known as metatables.

Rule 4. The data entered into the table can be validated in two steps :
i). By assigning Data Types ( #Mandatory).
ii). By assigning Constraints ( #Optional).
"As we wrap up, I want to express my gratitude for your attention. I hope this post has illuminated key takeaways about SQL. Thank you for being a part of this journey. Until next time, keep exploring and innovating!"
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Prafull Tripathi directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
